Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
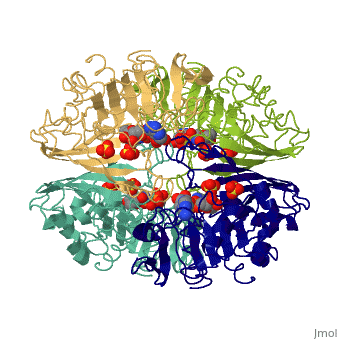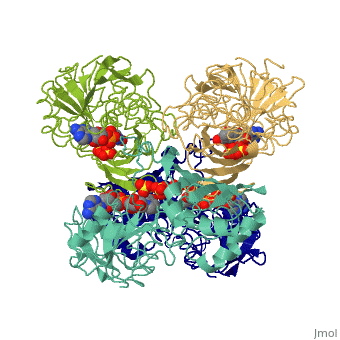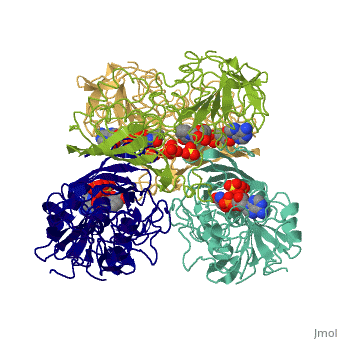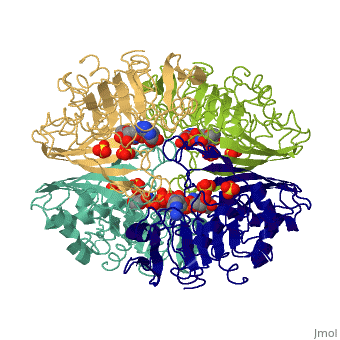
| - | '''Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase''' (GAPDH) is a very important enzyme in the production of energy and in photosynthesis. In the production of energy this enzyme catalyzes the sixth step in the process of breaking down glucose, also known as [[glycolysis]] which occurs in organisms of all phyla. The sixth step consists of of the oxidation of GAP by [[NAD]] and an inorganic phosphate to yield 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate. In photosynthesis, which is carried out by plants and algae, this enzyme uses '''NADPH''' in the reverse reaction in a step in the Calvin Cycle, which fixes gaseous CO<sub>2</sub> into carbohydrate. Though these are its main functions, GAPDH has been shown to perform other functions including transcription activation, initiation of apoptosis, and ER to Golgi apparatus vesicle transportation <ref>PMID: 22851451</ref>. However, this page will focus on GAPDH’s role in glycolysis. See [[2pkq]] for the plant Calvin Cycle enzyme. See [[Glycolysis Enzymes]] and [[Carbon Fixation]]. | + | '''Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase''' (GAPDH) is a very important enzyme in the production of energy and in photosynthesis. In the production of energy this enzyme catalyzes the sixth step in the process of breaking down glucose, also known as [[glycolysis]] which occurs in organisms of all phyla. The sixth step consists of of the oxidation of GAP by [[NAD]] and an inorganic phosphate to yield 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate. In photosynthesis, which is carried out by plants and algae, this enzyme uses '''NADPH''' in the reverse reaction in a step in the [[Calvin Cycle]], which fixes gaseous CO<sub>2</sub> into carbohydrate. Though these are its main functions, GAPDH has been shown to perform other functions including transcription activation, initiation of apoptosis, and ER to Golgi apparatus vesicle transportation <ref>PMID: 22851451</ref>. However, this page will focus on GAPDH’s role in glycolysis. See [[2pkq]] for the plant Calvin Cycle enzyme. See [[Glycolysis Enzymes]] and [[Carbon Fixation]]. |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 2 January 2023
| |||||||||||
References
1) Voet, D, Voet, J, & Pratt, C. (2008) 2)Family: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase-like, N-terminal domain. Retrieved from: http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/scop/data/scop.b.d.c.b.d.html
3)- Kundu S, Roy D. Computational study of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase of Entamoeba histolytica: implications for structure-based drug design. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2007 Aug;25(1):25-33. PMID:17676935
- Vospelnikova ND, Safronova MI, Shuvalova ER, Baratova LA, Kniazev SP, Nagradova NK. Identification of an arginine residue important for catalytic activity in the primary structure of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Studies with the rat skeletal-muscle enzyme. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):757-65. PMID:7340828
- Butterfield DA, Hardas SS, Lange ML. Oxidatively modified glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and Alzheimer's disease: many pathways to neurodegeneration. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20(2):369-93. PMID:20164570 doi:10.3233/JAD-2010-1375
- Seidler NW. Dynamic oligomeric properties. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;985:207-47. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4716-6_7. PMID:22851451 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4716-6_7
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Nathan Line, Andrew Swart, Alexander Berchansky, Alice Harmon, David Canner