We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Corticosteroid-binding globulin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
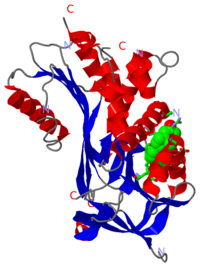
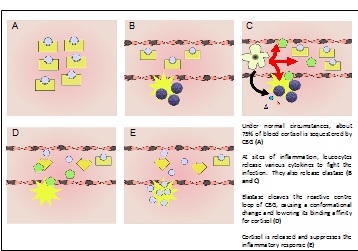
'''Corticosteroid-binding globulin''' (CBG) is a blood plasma protein 50 to 60 kDa in size <ref>PMID:13395526 </ref>,<ref>PMID:7074030 </ref>. Although it is a member of the serine protease inhibitor (SERPIN) structural family, it does not have any known intrinsic serine protease inhibitor activity <ref>PMID:3143075 </ref>. Its physiological function is conventionally thought to be the transport of the weakly water-soluble hormone, cortisol, throughout the circulation <ref>PMID:13395526 </ref>,<ref>PMID:7074030 </ref>. Structural studies of native rat CBG <ref>PMID:17644521 </ref> and a cleaved human CBG-antitrypsin chimera <ref>PMID:18513745 </ref> have corroborated earlier biochemical studies showing that cortisol binds to CBG with a one-to-one stoichiometry. Additionally, CBG is believed to buffer the concentration of free cortisol in the blood, keeping the level constant despite its pulsatile secretion pattern <ref>PMID:9751481 </ref>. CBG is also thought to participate in the stress response by releasing cortisol specifically at inflammatory sites upon cleavage by human neutrophil elastase between residues 344 and 345<ref>PMID:3143075 </ref>. | '''Corticosteroid-binding globulin''' (CBG) is a blood plasma protein 50 to 60 kDa in size <ref>PMID:13395526 </ref>,<ref>PMID:7074030 </ref>. Although it is a member of the serine protease inhibitor (SERPIN) structural family, it does not have any known intrinsic serine protease inhibitor activity <ref>PMID:3143075 </ref>. Its physiological function is conventionally thought to be the transport of the weakly water-soluble hormone, cortisol, throughout the circulation <ref>PMID:13395526 </ref>,<ref>PMID:7074030 </ref>. Structural studies of native rat CBG <ref>PMID:17644521 </ref> and a cleaved human CBG-antitrypsin chimera <ref>PMID:18513745 </ref> have corroborated earlier biochemical studies showing that cortisol binds to CBG with a one-to-one stoichiometry. Additionally, CBG is believed to buffer the concentration of free cortisol in the blood, keeping the level constant despite its pulsatile secretion pattern <ref>PMID:9751481 </ref>. CBG is also thought to participate in the stress response by releasing cortisol specifically at inflammatory sites upon cleavage by human neutrophil elastase between residues 344 and 345<ref>PMID:3143075 </ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: [[Corticosteroids]]. | ||
==Gene== | ==Gene== | ||
Revision as of 09:08, 9 January 2023
| |||||||||||
3D structures of corticosteroid-binding globulin
Updated on 09-January-2023
2v95 – rSer-A6 – rat
2vdx, 4c41 – hSer-A6 (mutant) - human
2vdy, 4c49 – hSer-A6 (mutant) + cortisol
4bb2 – hSer-A6 (mutant) + progesterone
Resources
Nucleotide and amino acid sequence [1]
PDB structure of S-state rat CBG [2]
PDB structure of R-state human CBG-antitrypsin chimera [3]
PDB structure of R-state human CBG-antitrypsin chimera [4]
References
- ↑ WESTPHAL U. Steroid-protein interactions. III. Spectrophotometric demonstration of interaction between proteins and progesterone, deoxycorticosterone and cortisol. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Jan;66(1):71-90. PMID:13395526
- ↑ Mickelson KE, Harding GB, Forsthoefel M, Westphal U. Steroid-protein interactions. Human corticosteroid-binding globulin: characterization of dimer and electrophoretic variants. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 16;21(4):654-60. PMID:7074030
- ↑ Pemberton PA, Stein PE, Pepys MB, Potter JM, Carrell RW. Hormone binding globulins undergo serpin conformational change in inflammation. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):257-8. PMID:3143075 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/336257a0
- ↑ WESTPHAL U. Steroid-protein interactions. III. Spectrophotometric demonstration of interaction between proteins and progesterone, deoxycorticosterone and cortisol. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Jan;66(1):71-90. PMID:13395526
- ↑ Mickelson KE, Harding GB, Forsthoefel M, Westphal U. Steroid-protein interactions. Human corticosteroid-binding globulin: characterization of dimer and electrophoretic variants. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 16;21(4):654-60. PMID:7074030
- ↑ Klieber MA, Underhill C, Hammond GL, Muller YA. Corticosteroid-binding globulin, a structural basis for steroid transport and proteinase-triggered release. J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 5;282(40):29594-603. Epub 2007 Jul 19. PMID:17644521 doi:10.1074/jbc.M705014200
- ↑ Zhou A, Wei Z, Stanley PL, Read RJ, Stein PE, Carrell RW. The S-to-R transition of corticosteroid-binding globulin and the mechanism of hormone release. J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 27;380(1):244-51. Epub 2008 May 14. PMID:18513745 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.05.012
- ↑ Windle RJ, Wood SA, Lightman SL, Ingram CD. The pulsatile characteristics of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal activity in female Lewis and Fischer 344 rats and its relationship to differential stress responses. Endocrinology. 1998 Oct;139(10):4044-52. PMID:9751481
- ↑ Pemberton PA, Stein PE, Pepys MB, Potter JM, Carrell RW. Hormone binding globulins undergo serpin conformational change in inflammation. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):257-8. PMID:3143075 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/336257a0
- ↑ Torpy DJ, Ho JT. Corticosteroid-binding globulin gene polymorphisms: clinical implications and links to idiopathic chronic fatigue disorders. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007 Aug;67(2):161-7. Epub 2007 Jun 4. PMID:17547679 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02890.x
- ↑ Lin HY, Muller YA, Hammond GL. Molecular and structural basis of steroid hormone binding and release from corticosteroid-binding globulin. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Mar 5;316(1):3-12. Epub 2009 Jul 28. PMID:19643161 doi:10.1016/j.mce.2009.06.015
- ↑ Klieber MA, Underhill C, Hammond GL, Muller YA. Corticosteroid-binding globulin, a structural basis for steroid transport and proteinase-triggered release. J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 5;282(40):29594-603. Epub 2007 Jul 19. PMID:17644521 doi:10.1074/jbc.M705014200
- ↑ Zhou A, Wei Z, Stanley PL, Read RJ, Stein PE, Carrell RW. The S-to-R transition of corticosteroid-binding globulin and the mechanism of hormone release. J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 27;380(1):244-51. Epub 2008 May 14. PMID:18513745 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.05.012
- ↑ Klieber MA, Underhill C, Hammond GL, Muller YA. Corticosteroid-binding globulin, a structural basis for steroid transport and proteinase-triggered release. J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 5;282(40):29594-603. Epub 2007 Jul 19. PMID:17644521 doi:10.1074/jbc.M705014200
- ↑ Zhou A, Wei Z, Stanley PL, Read RJ, Stein PE, Carrell RW. The S-to-R transition of corticosteroid-binding globulin and the mechanism of hormone release. J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 27;380(1):244-51. Epub 2008 May 14. PMID:18513745 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.05.012
- ↑ Pemberton PA, Stein PE, Pepys MB, Potter JM, Carrell RW. Hormone binding globulins undergo serpin conformational change in inflammation. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):257-8. PMID:3143075 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/336257a0
- ↑ Fernandez-Real JM, Grasa M, Casamitjana R, Pugeat M, Barret C, Ricart W. Plasma total and glycosylated corticosteroid-binding globulin levels are associated with insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999 Sep;84(9):3192-6. PMID:10487686
- ↑ Teves ME, Guidobaldi HA, Unates DR, Sanchez R, Miska W, Giojalas LC. Progesterone sperm chemoattraction may be modulated by its corticosteroid-binding globulin carrier protein. Fertil Steril. 2010 May 1;93(7):2450-2. Epub 2009 Nov 6. PMID:19896663 doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.09.012
- ↑ Torpy DJ, Ho JT. Corticosteroid-binding globulin gene polymorphisms: clinical implications and links to idiopathic chronic fatigue disorders. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007 Aug;67(2):161-7. Epub 2007 Jun 4. PMID:17547679 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02890.x
- ↑ Lin HY, Muller YA, Hammond GL. Molecular and structural basis of steroid hormone binding and release from corticosteroid-binding globulin. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Mar 5;316(1):3-12. Epub 2009 Jul 28. PMID:19643161 doi:10.1016/j.mce.2009.06.015