We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Malate synthase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
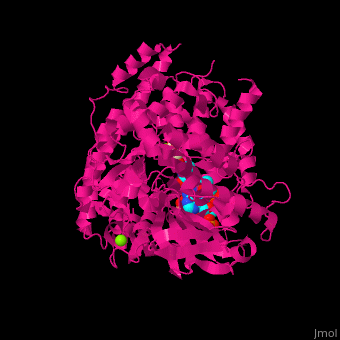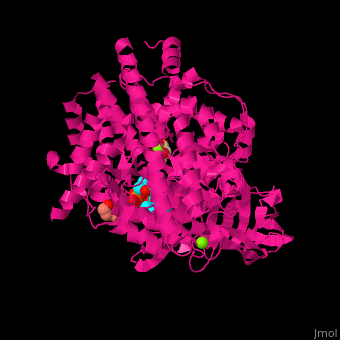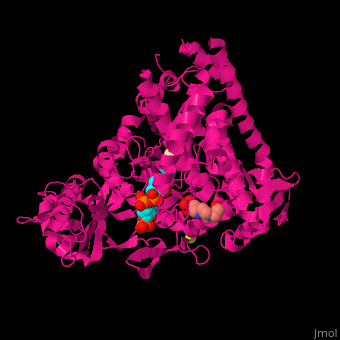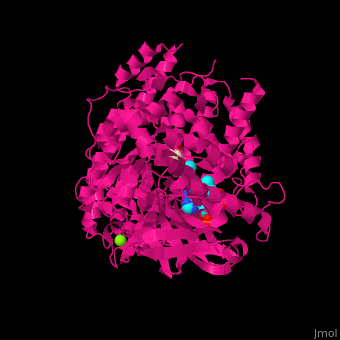
'''Malate synthase''' (MS) catalyzes the reversible conversion of acetyl-CoA, glyoxylate and water to [[R/S nomenclature|(S)]]-malate and CoA. MS participates in pyruvate, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism. There are 2 isozymes of MS. '''MS G''' is formed during growth on glycolate<ref>PMID:12930982</ref> and '''MS A''' which metabolizes glyoxylate formed in the dissimilation of acetate. | '''Malate synthase''' (MS) catalyzes the reversible conversion of acetyl-CoA, glyoxylate and water to [[R/S nomenclature|(S)]]-malate and CoA. MS participates in pyruvate, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism. There are 2 isozymes of MS. '''MS G''' is formed during growth on glycolate<ref>PMID:12930982</ref> and '''MS A''' which metabolizes glyoxylate formed in the dissimilation of acetate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: [[Glyoxylate cycle]] | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Anstrom DM, Kallio K, Remington SJ. Structure of the Escherichia coli malate synthase G:pyruvate:acetyl-coenzyme A abortive ternary complex at 1.95 A resolution. Protein Sci. 2003 Sep;12(9):1822-32. PMID:12930982
- ↑ Anstrom DM, Remington SJ. The product complex of M. tuberculosis malate synthase revisited. Protein Sci. 2006 Aug;15(8):2002-7. PMID:16877713 doi:15/8/2002
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Karsten Theis, Joel L. Sussman