We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
SARS Coronavirus Main Proteinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
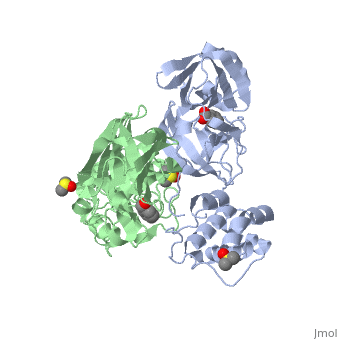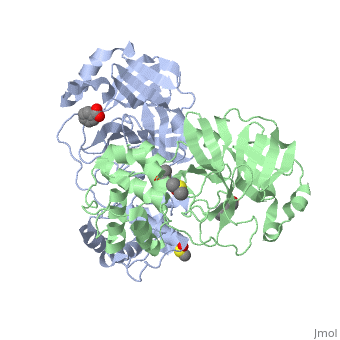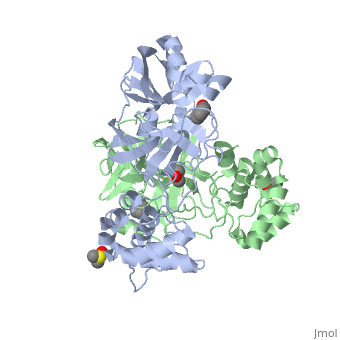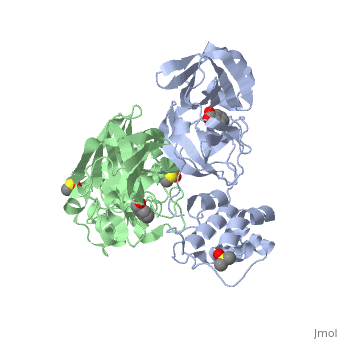
Each monomer of the SARS M<sup>pro</sup> consists of three domains. The two monomers are arranged perpendicular to each other and the active site is located at the connection between the first <scene name='SARS_Coronavirus_Main_Proteinase/Domains_1-3/1'>domain</scene> (residues 1-101) and second domain (residues 102-184). The catalytic dyad is composed of Histidine 41 and Cysteine 145. From the pH dependency of enzymatic activity, the pKa's have been determined as 6.4 for the histidine and 8.3 for the cysteine. The cysteine acts as the nucleophile in the proteolytic cleavage reaction. <ref>Anad, K., Ziebhr, J., Wadhani, P., Mesters, J.R., and Hilgenfeld, R. (2003). Coronavirus main protease (3CLPro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science300, 1763-1767.</ref> | Each monomer of the SARS M<sup>pro</sup> consists of three domains. The two monomers are arranged perpendicular to each other and the active site is located at the connection between the first <scene name='SARS_Coronavirus_Main_Proteinase/Domains_1-3/1'>domain</scene> (residues 1-101) and second domain (residues 102-184). The catalytic dyad is composed of Histidine 41 and Cysteine 145. From the pH dependency of enzymatic activity, the pKa's have been determined as 6.4 for the histidine and 8.3 for the cysteine. The cysteine acts as the nucleophile in the proteolytic cleavage reaction. <ref>Anad, K., Ziebhr, J., Wadhani, P., Mesters, J.R., and Hilgenfeld, R. (2003). Coronavirus main protease (3CLPro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science300, 1763-1767.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Peptidic inhibitors== | ||
| + | A number of structures of MPro with candidate inhibitors have been determined, including <scene name='42/426139/6xa4/1'>6XA4</scene>, <scene name='42/426139/6xfn/1'>6XFN</scene>, <scene name='42/426139/6xbg/1'>6XBG</scene>, <scene name='42/426139/6xbh/1'>6XBH</scene>, <scene name='42/426139/6xbi/1'>6XBI</scene>, and 6WTT. | ||
==Mechanism of Inactivation by Benzotriazole Esters== | ==Mechanism of Inactivation by Benzotriazole Esters== | ||
Revision as of 19:33, 20 February 2023
| |||||||||||
3D structures of virus proteinase
See Virus protease 3D structures
References
- ↑ Takahashi D, Hiromasa Y, Kim Y, Anbanandam A, Yao X, Chang KO, Prakash O. Structural and dynamics characterization of norovirus protease. Protein Sci. 2013 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/pro.2215. PMID:23319456 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pro.2215
- ↑ Murray, Patrick R., Ken S. Rosenthal, and Michael A. Pfaller. "Coronaviruses and Noroviruses." Medical Microbiology. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby/Elsevier, 2009. 565-68. Print.
- ↑ Ziebuhr, J., Herold,J., and Siddell, S.G. (1995). Characterization of a human coronavirus (strain 229E) 3C-like proteinase activity. J. Virol. 69, 4331-4338.
- ↑ Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med 2003;348:1953-1966
- ↑ "Summary of probable SARS cases with onset of illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003". WHO. Retrieved 2008-10-31.
- ↑ Li W, Shi Z, Yu M, et al. (2005). "Bats are natural reservoirs of SARS-like coronaviruses". Science (journal) 310 (5748): 676–9. doi:10.1126/science.1118391. PMID 16195424.
- ↑ Sharma A, Ahmad Farouk I, Lal SK. COVID-19: A Review on the Novel Coronavirus Disease Evolution, Transmission, Detection, Control and Prevention. Viruses. 2021 Jan 29;13(2):202. PMID:33572857 doi:10.3390/v13020202
- ↑ Ziebuhr, J., Snijder, E.J., and Gorbaleya, A.E. (2000). Virus-encoded proteinases and proteolytic processing in Nidovirales. J. Gen. Virol. 81, 853-879.
- ↑ Anad, K., Ziebhr, J., Wadhani, P., Mesters, J.R., and Hilgenfeld, R. (2003). Coronavirus main protease (3CLPro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science300, 1763-1767.
- ↑ Anad, K., Ziebhr, J., Wadhani, P., Mesters, J.R., and Hilgenfeld, R. (2003). Coronavirus main protease (3CLPro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science300, 1763-1767.
- ↑ Verschueren, Koen H.G., Ksenia Pumpor, Stefan Anemüller, Shuai Chen, Jeroen R. Mesters, and Rolf Hilgenfeld. "A Structural View of the Inactivation of the SARS Coronavirus Main Proteinase by Benzotriazole Esters." Chemistry & Biology 15.6 (2008): 597-606. Web. Oct. 2010.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Sarra Borhanian, Michal Harel, David Canner, Ann Taylor, Alexander Berchansky