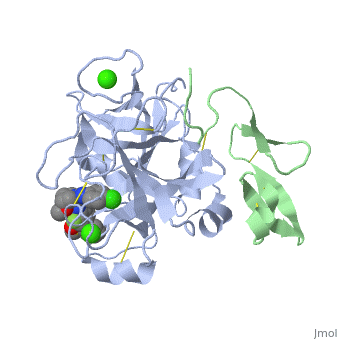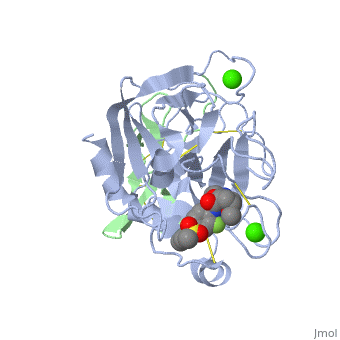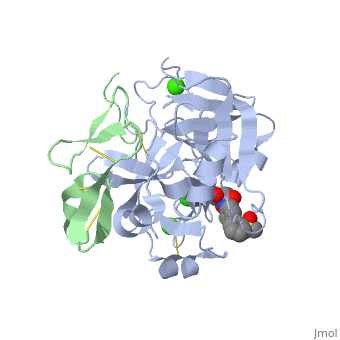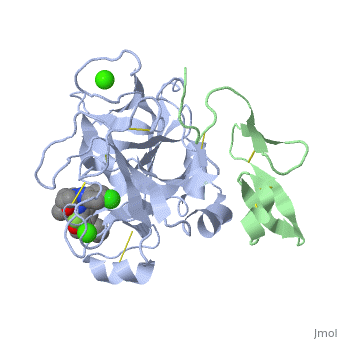
Factor Xa
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<scene name='Factor_Xa/Transparent_-_no_inhib_s4/2'>S4 pocket</scene> is formed between the 90s and 170s loops and binds an Ile 12. This region contains 3 ligand binding domains. The <scene name='Factor_Xa/Transparent_-_no_inhib_phob_bo/4'>hydrophobic box</scene> is located at the entrance to S4 and contains Phe174, Tyr99 and Trp215, which form a deep aryl-binding pocket. The <scene name='Factor_Xa/Transparent_-_no_inhib_oxianio/3'>cationic hole</scene> is formed by the backbone carbonyl and side chain of Glu97 and the backbone carbonyl of Lys96. The <scene name='Factor_Xa/Transparent_-_no_inhib-_h2o_si/3'>water site</scene> is composed of the hydrophillic side chains of Thr98, Ile175 and Thr177 and traps a water molecule. <ref name="Inhib" /> | <scene name='Factor_Xa/Transparent_-_no_inhib_s4/2'>S4 pocket</scene> is formed between the 90s and 170s loops and binds an Ile 12. This region contains 3 ligand binding domains. The <scene name='Factor_Xa/Transparent_-_no_inhib_phob_bo/4'>hydrophobic box</scene> is located at the entrance to S4 and contains Phe174, Tyr99 and Trp215, which form a deep aryl-binding pocket. The <scene name='Factor_Xa/Transparent_-_no_inhib_oxianio/3'>cationic hole</scene> is formed by the backbone carbonyl and side chain of Glu97 and the backbone carbonyl of Lys96. The <scene name='Factor_Xa/Transparent_-_no_inhib-_h2o_si/3'>water site</scene> is composed of the hydrophillic side chains of Thr98, Ile175 and Thr177 and traps a water molecule. <ref name="Inhib" /> | ||
| - | The cation-pi interaction is a strong, non-covalent bond formed by electrostatic interactions between the side chains of aromatic residues and various cations. These bonds are characterized by the fact that sp2 carbons are more electronegative then hydrogen, and 6 local Cδ- - Hδ+ bond dipoles are created around the benzene ring. Collectively, these dipoles create an accumulation of negative charge in the center of the ring and a belt of positive charge around the edge. This charge distribution allows for cation binding to the center of the ring, however, if the ring is not properly positioned, the cation will be repulsed by the positive charge of the outer ring. The S4 binding pocket of Factor Xa is formed from three aromatic residues, tyrosine 99, phenylalanine 174, tryptophan 215, sufficiently rich in properly positioned pi-electrons that it is not only a hydrophobic pocket, but also forms a cation recognition site. Many factor Xa inhibitors have a basic residue binding in this pocket, when protonated, cation-pi interactions are formed. | + | The cation-pi interaction is a strong, non-covalent bond formed by electrostatic interactions between the side chains of aromatic residues and various cations. These bonds are characterized by the fact that sp2 carbons are more electronegative then hydrogen, and 6 local Cδ- - Hδ+ bond dipoles are created around the benzene ring. Collectively, these dipoles create an accumulation of negative charge in the center of the ring and a belt of positive charge around the edge. This charge distribution allows for cation binding to the center of the ring, however, if the ring is not properly positioned, the cation will be repulsed by the positive charge of the outer ring. The S4 binding pocket of Factor Xa is formed from three aromatic residues, tyrosine 99, phenylalanine 174, tryptophan 215, sufficiently rich in properly positioned pi-electrons that it is not only a hydrophobic pocket, but also forms a cation recognition site. Many factor Xa inhibitors have a basic residue binding in this pocket, when protonated, cation-pi interactions are formed. |
| - | Hydrogen bonds form between the carbonyl oxygen of Ser214 and the NH of the P1 (Arg 14) residue, the NH of | + | *<scene name='95/953982/Cv/2'>Apixaban binding site</scene>. |
| - | Trp215 and the carbonyl of P3 (Asp 113) and the carbonyl of Gly216 and the NH of P3 (Asp 113). These interactions are a general feature of chymotrypsin-like proteases and are critical for efficient substrate hydrolysis. | + | *<scene name='95/954035/Cv/5'>Rivaroxaban binding site</scene>. |
| + | |||
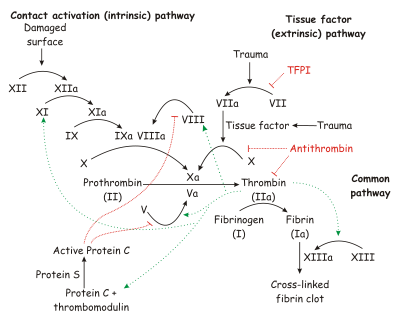
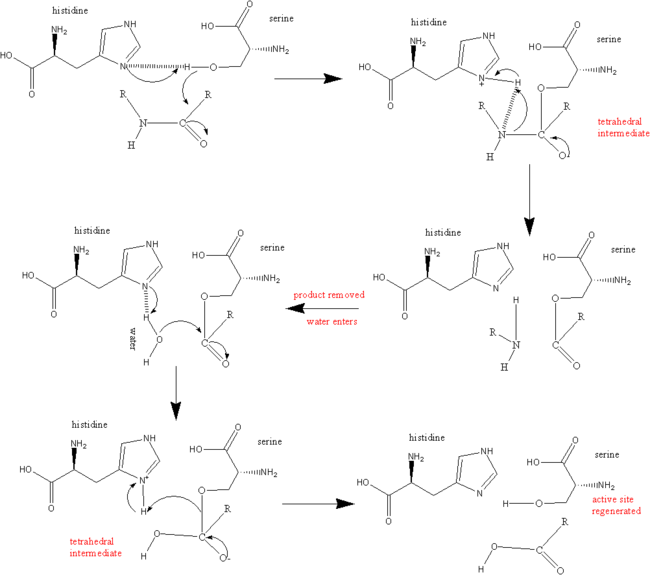
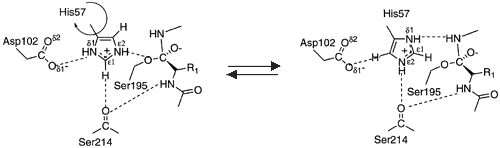
| + | Hydrogen bonds form between the carbonyl oxygen of Ser214 and the NH of the P1 (Arg 14) residue, the NH of Trp215 and the carbonyl of P3 (Asp 113) and the carbonyl of Gly216 and the NH of P3 (Asp 113). These interactions are a general feature of chymotrypsin-like proteases and are critical for efficient substrate hydrolysis. | ||
The precise interactions of the P' side chains have not been defined. The P1' and P3' residues point in the same direction as a consequence of the beta sheet alignment of the substrate, so that the S1' and S3' sites overlap. The S1'/S3' sites are bounded by His57, the 60’s loop and the 40’s loop. The P2' residue points in the opposite direction and may interact with the 150’s loop. | The precise interactions of the P' side chains have not been defined. The P1' and P3' residues point in the same direction as a consequence of the beta sheet alignment of the substrate, so that the S1' and S3' sites overlap. The S1'/S3' sites are bounded by His57, the 60’s loop and the 40’s loop. The P2' residue points in the opposite direction and may interact with the 150’s loop. | ||
Revision as of 16:12, 28 February 2023
| |||||||||||
3D structures of factor Xa
Updated on 28-February-2023
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Hemophilia
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Greer, John (2008). Wintrobe's Clinical Hematology, p. 545-546. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0781765072.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Department of Chemistry, University of Maine, Orono, ME. http://chemistry.umeche.maine.edu/CHY252/Peptidase3.html
- ↑ Padmanabhan K, Padmanabhan KP, Tulinsky A, Park CH, Bode W, Huber R, Blankenship DT, Cardin AD, Kisiel W. Structure of human des(1-45) factor Xa at 2.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1993 Aug 5;232(3):947-66. PMID:8355279 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1993.1441
- ↑ Friedman PA, Przysiecki CT. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. Int J Biochem. 1987;19(1):1-7. PMID:3106112
- ↑ Vermeer C. Gamma-carboxyglutamate-containing proteins and the vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):625-36. PMID:2183788
- ↑ Price PA, Fraser JD, Metz-Virca G. Molecular cloning of matrix Gla protein: implications for substrate recognition by the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8335-9. PMID:3317405
- ↑ Freedman SJ, Furie BC, Furie B, Baleja JD. Structure of the metal-free gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-rich membrane binding region of factor IX by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 7;270(14):7980-7. PMID:7713897
- ↑ Freedman SJ, Blostein MD, Baleja JD, Jacobs M, Furie BC, Furie B. Identification of the phospholipid binding site in the vitamin K-dependent blood coagulation protein factor IX. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 5;271(27):16227-36. PMID:8663165
- ↑ Morita T, Jackson CM. Preparation and properties of derivatives of bovine factor X and factor Xa from which the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid containing domain has been removed. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4015-23. PMID:3512564
- ↑ Muskavitch MA, Hoffmann FM. Homologs of vertebrate growth factors in Drosophila melanogaster and other invertebrates. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1990;24:289-328. PMID:2116263
- ↑ Ohlin AK, Linse S, Stenflo J. Calcium binding to the epidermal growth factor homology region of bovine protein C. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7411-7. PMID:3259233
- ↑ Selander-Sunnerhagen M, Ullner M, Persson E, Teleman O, Stenflo J, Drakenberg T. How an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain binds calcium. High resolution NMR structure of the calcium form of the NH2-terminal EGF-like domain in coagulation factor X. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19642-9. PMID:1527084
- ↑ Persson E, Hogg PJ, Stenflo J. Effects of Ca2+ binding on the protease module of factor Xa and its interaction with factor Va. Evidence for two Gla-independent Ca(2+)-binding sites in factor Xa. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22531-9. PMID:8226763
- ↑ Persson E, Selander M, Linse S, Drakenberg T, Ohlin AK, Stenflo J. Calcium binding to the isolated beta-hydroxyaspartic acid-containing epidermal growth factor-like domain of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16897-904. PMID:2789221
- ↑ Hopfner KP, Kopetzki E, Kresse GB, Bode W, Huber R, Engh RA. New enzyme lineages by subdomain shuffling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Aug 18;95(17):9813-8. PMID:9707558
- ↑ Factor X. Wikipedia
- ↑ Serine Protease. Wikipedia
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Hedstrom L. Serine protease mechanism and specificity. Chem Rev. 2002 Dec;102(12):4501-24. PMID:12475199
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Rai R, Sprengeler PA, Elrod KC, Young WB. Perspectives on factor Xa inhibition. Curr Med Chem. 2001 Feb;8(2):101-19. PMID:11172669
- ↑ www.bmolchem.wisc.edu/
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Bachovchin, W. Contributions of NMR spectroscopy to the study of hydrogen bonds in serine protease active sites. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry; (2001); 39(Spec. Issue); 199-213.
- ↑ Bachovchin WW. 15N NMR spectroscopy of hydrogen-bonding interactions in the active site of serine proteases: evidence for a moving histidine mechanism. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7751-9. PMID:3542033
- ↑ Brady K, Wei AZ, Ringe D, Abeles RH. Structure of chymotrypsin-trifluoromethyl ketone inhibitor complexes: comparison of slowly and rapidly equilibrating inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 21;29(33):7600-7. PMID:2271520
- ↑ Frey PA, Whitt SA, Tobin JB. A low-barrier hydrogen bond in the catalytic triad of serine proteases. Science. 1994 Jun 24;264(5167):1927-30. PMID:7661899
- ↑ Frey, Perry A. Strong hydrogen bonding in chymotrypsin and other serine proteases. Journal of Physical Organic Chemistry (2004), 17(6-7), 511-520.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Fuhrmann CN, Daugherty MD, Agard DA. Subangstrom crystallography reveals that short ionic hydrogen bonds, and not a His-Asp low-barrier hydrogen bond, stabilize the transition state in serine protease catalysis. J Am Chem Soc. 2006 Jul 19;128(28):9086-102. PMID:16834383 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja057721o
- ↑ Kuhn P, Knapp M, Soltis SM, Ganshaw G, Thoene M, Bott R. The 0.78 A structure of a serine protease: Bacillus lentus subtilisin. Biochemistry. 1998 Sep 29;37(39):13446-52. PMID:9753430 doi:10.1021/bi9813983
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Jacqueline Gertz, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky