Sandbox Reserved 1773
From Proteopedia
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
===Medical Relevancy=== | ===Medical Relevancy=== | ||
Janeway CA Jr, Travers P, Walport M, et al. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2001. | Janeway CA Jr, Travers P, Walport M, et al. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2001. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Disease=== | ||
| + | B-cells and their respective receptors play an important role in the immune response. Therefore, if the receptors were to not function properly, there would be damaging consequences. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autoimmune_disease Autoimmune disease] is suggested to occur when somatic cells are recognized as foreign antigens and the body tries to eliminate them. It is thought that B-cell receptors are an essential part of these diseases due to their function and role in the immune systems. B-cell receptors are improperly recognizing somatic cells from different tissues depending on the disease and eliciting a response against them. Examples of these diseases include [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rheumatoid_arthritis rheumatoid arthritis] where the lining of joints is targeted and degraded, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiple_sclerosis multiple sclerosis] which targets the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve cells, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_1_diabetes type 1 diabetes mellitus] where the insulin producing cells are targeted for destruction, and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lupus systematic lupus erythematosus] where multiple organ systems are targeted (skin, brain, lungs, and kidneys are common targets). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Therapeutics=== | ||
Revision as of 06:30, 1 April 2023
Contents |
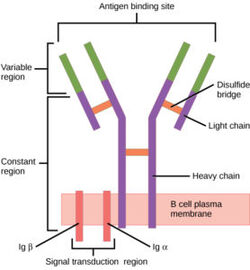
H. sapiens mIgM B Cell Receptor
| |||||||||||
Medical Relevancy
Janeway CA Jr, Travers P, Walport M, et al. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2001.
Disease
B-cells and their respective receptors play an important role in the immune response. Therefore, if the receptors were to not function properly, there would be damaging consequences. Autoimmune disease is suggested to occur when somatic cells are recognized as foreign antigens and the body tries to eliminate them. It is thought that B-cell receptors are an essential part of these diseases due to their function and role in the immune systems. B-cell receptors are improperly recognizing somatic cells from different tissues depending on the disease and eliciting a response against them. Examples of these diseases include rheumatoid arthritis where the lining of joints is targeted and degraded, multiple sclerosis which targets the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve cells, type 1 diabetes mellitus where the insulin producing cells are targeted for destruction, and systematic lupus erythematosus where multiple organ systems are targeted (skin, brain, lungs, and kidneys are common targets).