Sandbox Reserved 1779
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
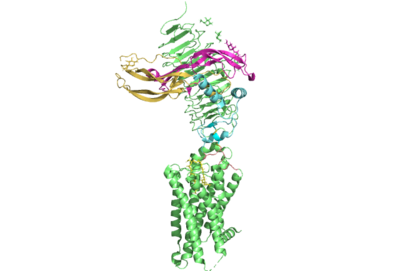
[[Image:All_TSHR.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. TSHR with TSH bound. The extracellular and transmembrane domains of the GPCR are shown in green, the hinge region in cyan, the P10 peptide in pink, and thyrotropin bound in pink and yellow.]] | [[Image:All_TSHR.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. TSHR with TSH bound. The extracellular and transmembrane domains of the GPCR are shown in green, the hinge region in cyan, the P10 peptide in pink, and thyrotropin bound in pink and yellow.]] | ||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_hormones Thyroid hormones] exercise essential functions related to thymocyte activity as well as metabolic processes and oxygen consumption. Misregulation of thyroid hormones is the cause of many disorders related to [https://www.endocrineweb.com/conditions/thyroid/hyperthyroidism-vs-hypothyroidism hypo- or hyperthyroidism]. Thus, understanding the signaling of synthesis and release of these hormones is essential to the development therapeutic drugs to combat [https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/disorders-of-the-thyroid specific thyroid hormone disorders]<ref name="Yen">Yen PM. Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev. 2001 Jul;81(3):1097-142. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.3.1097. PMID: 11427693.</ref>. The initiation of the synthesis and release of these hormones is caused by the glycoprotein, thyroid stimulating hormone, commonly referred to as TSH or thyrotropin. The thyrotropin receptor <scene name='95/952709/Initial_scene_with_edited_7utz/2'>(TSHR)</scene> is a [https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/gpcr-14047471/ G-protein coupled receptor] that binds TSH and transduces signal to initiate synthesis and release of thyroid hormones. It is important to note that autoantibodies may also bind to this receptor causing inhibition or activation of its desired function. (Figure 1)<ref name="Duan et al.">PMID:35940204</ref><ref name="Kohn et al.">Kohn LD, Shimura H, Shimura Y, Hidaka A, Giuliani C, Napolitano G, Ohmori M, Laglia G, Saji M. The thyrotropin receptor. Vitam Horm. 1995;50:287-384. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60658-5. PMID: 7709602.</ref> | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_hormones Thyroid hormones] exercise essential functions related to thymocyte activity as well as metabolic processes and oxygen consumption. Misregulation of thyroid hormones is the cause of many disorders related to [https://www.endocrineweb.com/conditions/thyroid/hyperthyroidism-vs-hypothyroidism hypo- or hyperthyroidism]. Thus, understanding the signaling of synthesis and release of these hormones is essential to the development therapeutic drugs to combat [https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/disorders-of-the-thyroid specific thyroid hormone disorders]<ref name="Yen">Yen PM. Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev. 2001 Jul;81(3):1097-142. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.3.1097. PMID: 11427693.</ref>. The initiation of the synthesis and release of these hormones is caused by the glycoprotein, thyroid stimulating hormone, commonly referred to as TSH or thyrotropin. The thyrotropin receptor <scene name='95/952709/Initial_scene_with_edited_7utz/2'>(TSHR)</scene> is a [https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/gpcr-14047471/ G-protein coupled receptor] that binds TSH and transduces signal to initiate synthesis and release of thyroid hormones. It is important to note that autoantibodies may also bind to this receptor causing inhibition or activation of its desired function. (Figure 1)<ref name="Duan et al.">PMID:35940204</ref><ref name="Kohn et al.">Kohn LD, Shimura H, Shimura Y, Hidaka A, Giuliani C, Napolitano G, Ohmori M, Laglia G, Saji M. The thyrotropin receptor. Vitam Horm. 1995;50:287-384. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60658-5. PMID: 7709602.</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | == Structure == | ||
| - | ===Overview=== | ||
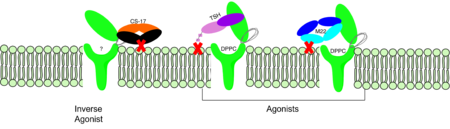
| - | The thyrotropin receptor has an extracellular domain (ECD) that is composed of a <scene name='95/952709/Lrrd_real/2'>leucine rich repeat domain (LRRD)</scene> as well as a hinge region. This <scene name='95/952709/Hinge_region_real/2'>hinge region</scene> links the ECD to the seven transmembrane helices <scene name='95/952709/7tm_helices/4'>(7TM domain)</scene>, which span from the extracellular domain to the intracellular domain <ref name= "Keinau et al.">Kleinau, G., Worth, C. L., Kreuchwig, A., Biebermann, H., Marcinkowski, P., Scheerer, P., & Krause, G. (2017). Structural–functional features of the thyrotropin receptor: A class A G-protein-coupled receptor at work. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00086</ref>. When thyrotropin or an autoantibody binds, it causes a conformational change in the receptor through the transmembrane helices. This causes the thyrotropin receptor to interact differently with its respective <scene name='95/952709/G_protein/2'>G-protein</scene> when in the active and inactive states. | ||
=== Grave's Disease === | === Grave's Disease === | ||
| Line 18: | Line 14: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
===Overview=== | ===Overview=== | ||
| - | The thyrotropin receptor has an extracellular domain (ECD) that is composed of a <scene name='95/952709/Lrrd_real/2'>leucine rich repeat domain (LRRD)</scene> as well as a hinge region. This <scene name='95/952709/Hinge_region_real/2'>hinge region</scene> links the ECD to the seven transmembrane helices <scene name='95/952709/7tm_helices/4'>(7TM domain)</scene>, which span from the extracellular domain to the intracellular domain <ref name= "Keinau et al.">Kleinau, G., Worth, C. L., Kreuchwig, A., Biebermann, H., Marcinkowski, P., Scheerer, P., & Krause, G. (2017). Structural–functional features of the thyrotropin receptor: A class A G-protein-coupled receptor at work. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00086</ref>. When thyrotropin or an autoantibody binds, it causes a conformational change in the receptor through the transmembrane helices. This causes the thyrotropin receptor to interact differently with its respective <scene name='95/952709/G_protein/2'>G-protein</scene> when in active and inactive states. | + | The thyrotropin receptor has an extracellular domain (ECD) that is composed of a <scene name='95/952709/Lrrd_real/2'>leucine rich repeat domain (LRRD)</scene> as well as a hinge region. This <scene name='95/952709/Hinge_region_real/2'>hinge region</scene> links the ECD to the seven transmembrane helices <scene name='95/952709/7tm_helices/4'>(7TM domain)</scene>, which span from the extracellular domain to the intracellular domain <ref name= "Keinau et al.">Kleinau, G., Worth, C. L., Kreuchwig, A., Biebermann, H., Marcinkowski, P., Scheerer, P., & Krause, G. (2017). Structural–functional features of the thyrotropin receptor: A class A G-protein-coupled receptor at work. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00086</ref>. When thyrotropin or an autoantibody binds, it causes a conformational change in the receptor through the transmembrane helices. This causes the thyrotropin receptor to interact differently with its respective <scene name='95/952709/G_protein/2'>G-protein</scene> when in the active and inactive states. |
=== Leucine Rich Region === | === Leucine Rich Region === | ||
Revision as of 20:39, 3 April 2023
>
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Yen PM. Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev. 2001 Jul;81(3):1097-142. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.3.1097. PMID: 11427693.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Duan J, Xu P, Luan X, Ji Y, He X, Song N, Yuan Q, Jin Y, Cheng X, Jiang H, Zheng J, Zhang S, Jiang Y, Xu HE. Hormone- and antibody-mediated activation of the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. PMID:35940204 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3
- ↑ Kohn LD, Shimura H, Shimura Y, Hidaka A, Giuliani C, Napolitano G, Ohmori M, Laglia G, Saji M. The thyrotropin receptor. Vitam Horm. 1995;50:287-384. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60658-5. PMID: 7709602.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kleinau, G., Worth, C. L., Kreuchwig, A., Biebermann, H., Marcinkowski, P., Scheerer, P., & Krause, G. (2017). Structural–functional features of the thyrotropin receptor: A class A G-protein-coupled receptor at work. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00086
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Faust B, Billesbolle CB, Suomivuori CM, Singh I, Zhang K, Hoppe N, Pinto AFM, Diedrich JK, Muftuoglu Y, Szkudlinski MW, Saghatelian A, Dror RO, Cheng Y, Manglik A. Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. PMID:35940205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1
- ↑ Yumiko Mizutori, Chun-Rong Chen, Sandra M. McLachlan, Basil Rapoport, The Thyrotropin Receptor Hinge Region Is Not Simply a Scaffold for the Leucine-Rich Domain but Contributes to Ligand Binding and Signal Transduction, Molecular Endocrinology, Volume 22, Issue 5, 1 May 2008, Pages 1171–1182, https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2007-0407
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Faust, B., Billesbølle, C.B., Suomivuori, CM. et al. Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor. Nature 609, 846–853 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-
- ↑ Virginie Vlaeminck-Guillem, Su-Chin Ho, Patrice Rodien, Gilbert Vassart, Sabine Costagliola, Activation of the cAMP Pathway by the TSH Receptor Involves Switching of the Ectodomain from a Tethered Inverse Agonist to an Agonist, Molecular Endocrinology, Volume 16, Issue 4, 1 April 2002, Pages 736–746, https://doi.org/10.1210/mend.16.4.0816
- ↑ Goricanec, D., Stehle, R., Egloff, P., Grigoriu, S., Plückthun, A., Wagner, G., & Hagn, F. (2016). Conformational dynamics of a G-protein α subunit is tightly regulated by nucleotide binding. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(26). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1604125113
- ↑ Nunez Miguel R, Sanders J, Chirgadze DY, Furmaniak J, Rees Smith B. Thyroid stimulating autoantibody M22 mimics TSH binding to the TSH receptor leucine rich domain: a comparative structural study of protein-protein interactions. J Mol Endocrinol. 2009 May;42(5):381-95. Epub 2009 Feb 16. PMID:19221175 doi:10.1677/JME-08-0152
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Chen, C.-R., McLachlan, S. M., & Rapoport, B. (2007). Suppression of thyrotropin receptor constitutive activity by a monoclonal antibody with inverse agonist activity. Endocrinology, 148(5), 2375–2382. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2006-1754
- ↑ Duan J, Xu P, Luan X, Ji Y, He X, Song N, Yuan Q, Jin Y, Cheng X, Jiang H, Zheng J, Zhang S, Jiang Y, Xu HE. Hormone- and antibody-mediated activation of the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. PMID:35940204 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3