We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1786
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
===Transmembrane Region=== | ===Transmembrane Region=== | ||
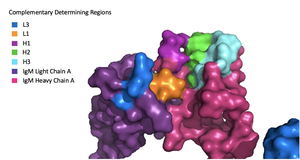
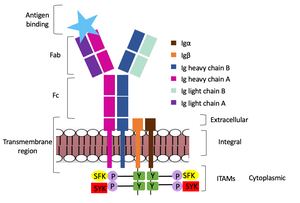
| - | The IgM BCR is anchored to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/B_cell B-cell] membranes through the <scene name='95/952714/Integral_region/11'>transmembrane region</scene> which is broken up into both extracellular and integral domains which sit on top of or span through the membrane, respectively. IgM BCR assembly requires dimerization of the <b><span class="text-brown">Ig alpha</span></b> and <b><span class="text-orange">Ig beta</span></b> subunits which embed within the B-cell membrane. The <scene name='95/952714/Ig_alpha_beta/5'>Ig alpha and beta heterodimer</scene> dimerizes within the extracellular region with a <scene name='95/952714/Extracellular_disulfide_bridge/6'>disulfide bridge</scene>. Additional dimerization is believed to occur within the integral region via a hydrogen bond; the involved residues and interaction have not been confirmed. Although the mechanism of disulfide bridge formation is still unknown, it is believed that <scene name='95/952714/Extracellular_glycosylation/2'>extracellular glycosylation</scene> via <b><span class="text-lightgreen">N-linked glycosylation</span></b> (NAGs) on various asparagine residues in the extracellular region of both the <b><span class="text-brown">alpha</span></b> and <b><span class="text-orange">beta</span></b> chains help facilitate this process. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chaperone_(protein) Chaperone proteins] remain bound to the alpha and beta subunits until both dimerizations occur; at this point the rest of the BCR complex can be recruited. | + | The IgM BCR is anchored to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/B_cell B-cell] membranes through the <scene name='95/952714/Integral_region/11'>transmembrane region</scene> which is broken up into both extracellular and integral domains which sit on top of or span through the membrane, respectively. IgM BCR assembly requires dimerization of the <b><span class="text-brown">Ig alpha</span></b> and <b><span class="text-orange">Ig beta</span></b> subunits which embed within the B-cell membrane. The <scene name='95/952714/Ig_alpha_beta/5'>Ig alpha and beta heterodimer</scene> dimerizes within the extracellular region with a <scene name='95/952714/Extracellular_disulfide_bridge/6'>disulfide bridge</scene>. Additional dimerization is believed to occur within the integral region via a hydrogen bond; the involved residues and interaction have not been confirmed. Although the mechanism of disulfide bridge formation is still unknown, it is believed that <scene name='95/952714/Extracellular_glycosylation/2'>extracellular glycosylation</scene> via <b><span class="text-lightgreen">N-linked glycosylation</span></b> (NAGs) on various asparagine residues in the extracellular region of both the <b><span class="text-brown">alpha</span></b> and <b><span class="text-orange">beta</span></b> chains help facilitate this process. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chaperone_(protein) Chaperone proteins] remain bound to the alpha and beta subunits until both dimerizations occur; at this point the rest of the BCR complex can be recruited. |
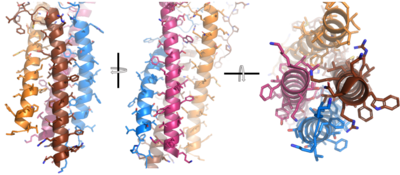
[[Image:Integral_helix_figure.png|400 px|left|thumb|'''Figure__. 4-pass integral helix.''' Pymol image of the integral helices in IgM BCR (PDB:7xq8) rotated on the x and y axes. Side chains are shown as sticks. Brown=Ig alpha, orange=Ig beta, pink=heavy chain A, blue=heavy chain B.]] | [[Image:Integral_helix_figure.png|400 px|left|thumb|'''Figure__. 4-pass integral helix.''' Pymol image of the integral helices in IgM BCR (PDB:7xq8) rotated on the x and y axes. Side chains are shown as sticks. Brown=Ig alpha, orange=Ig beta, pink=heavy chain A, blue=heavy chain B.]] | ||
| - | After <b><span class="text-brown">Ig alpha</span></b>/<b><span class="text-orange">Ig beta</span></b> dimerization, the transmembrane helices of the heavy chains can embed within the B-cell membrane. The side chains of this <scene name='95/952714/Integral_helices_2/2'>4-pass integral helix structure</scene> are primarily hydrophobic side chains that allow for interactions with the hydrophobic tails in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipid_bilayer phospholipid bilayer]. The 4 helices (Figure ___) are primarily held together through hydrophobic interactions; however, a a few polar residues are included on the interior of the helix structure which interact with a few polar residues on the <b><span class="text-brown">Ig alpha</span></b> and <b><span class="text-orange">Ig beta</span></b> chains. | + | After <b><span class="text-brown">Ig alpha</span></b>/<b><span class="text-orange">Ig beta</span></b> dimerization, the transmembrane helices of the heavy chains can embed within the B-cell membrane. The side chains of this <scene name='95/952714/Integral_helices_2/2'>4-pass integral helix structure</scene> are primarily hydrophobic side chains that allow for interactions with the hydrophobic tails in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipid_bilayer phospholipid bilayer]. The 4 helices (Figure ___) are primarily held together through hydrophobic interactions; however, a a few polar residues are included on the interior of the helix structure which interact with a few polar residues on the <b><span class="text-brown">Ig alpha</span></b> and <b><span class="text-orange">Ig beta</span></b> chains. |
===Fc Region=== | ===Fc Region=== | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| - | <ref name="Su">PMID:35981043</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <ref name="Tolar">PMID:35981020</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <ref name="Ma">PMID:35981028</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <ref name="Dylke">PMID:17675166</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <ref name="Zhou">PMID:20616231</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <ref name="Bannish">PMID:11733573</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <ref name="Sathe">PMID:32310455</ref> | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 17:36, 6 April 2023
Human B-cell Antigen Receptor: IgM BCR
| |||||||||||
References
Student Contributors
Detonyeá Dickson, Allison Goss, Jackson Payton