Introduction
Significance and Background
Immunoglobulin M, or IgM, is one of multiple types of immunoglobulins that exist in humans. IgM presents itself on the surface of a B cell to act as a B Cell Receptor (BCR). Upon the binding of an antigen to the BCR, the B cell will activate, proliferate, and produce other Ig compounds. These include IgG, IgD, IgA, and IgE antibodies, which all have specific roles in the various forms of immune response. Because of this, activation of the IgM BCR is a critical step in the beginning of an immune response.
The structure of IgM was determined using Cryo-EM to visualize the atoms within the protein. However, due to poor resolution within specific regions of the IgM BCR, not every atom has been able to be visualized.
History and Discovery
Structure
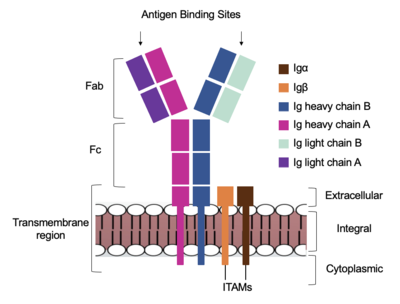
Figure 1. Cartoon Representation of IgM Antibody Receptor.
Transmembrane Region
The IgM BCR is tethered to B-cell membranes through the which is broken up into both extracellular and integral domains. IgM BCR assembly requires dimerization of the Ig alpha and Ig beta subunits which embed within the B-cell membrane. The is dimerized in both the integral region, with a hydrogen bond, and within the extracellular region with a . Although the mechanism of disulfide bridge formation is still unknown, it is believed that via N-linked glycosylation (NAGs, shown in green) of various asparagine residues in the extracellular region of both the alpha and Ig beta chains help to facilitate this process. Chaperon proteins remain bound to the alpha and beta subunits until both dimerizations occur at which point the rest of the BCR complex can be recruited.
After Ig alpha/Ig beta dimerization the transmembrane helices of the heavy chains can embed within the B-cell membrane as well. The side chains of this are primarily hydrophobic side chains that allow for interactions with the hydrophobic tails in the phospholipid bilayer. A total of 9 polar residues (picture that zooms in here??) between each of the heavy chains are included on the interior of the helix structure which interact with a few polar residues on the Ig alpha and Ig beta chains to hold the complex together. Additional interactions between the Ig alpha/Ig beta dimer and the heavy chains occur in the constant region.
Fc Region
The constant region of IgM is made up of the 2 . These heavy chains form a bridge to connect the Fab fragment, or variable region, to the transmembrane region. They also act as a wire to allow the variable region to send a cellular signal through to the intermembrane region once an antigen has been bound.
help to stabilize and hold the heavy chains and Ig Alpha/Beta chains together in the extracellular portion of the intermembrane region.
Fab Region
Because the Fab region of IgM is so poorly resolved, a structural comparison to another antibody was performed to approximate where an antigen would bind to the . Figure 1 on the left shows the antigen binding motif (located on the Fab region) of an Ig-BCR complex that was engineered to contain the variable region of a neutralizing antibody called VCR01, an antibody that targets the epitope of HIV molecules. It contains areas referred to as complementary-determining regions, or CDRs, which are where the antigen makes contact with the antibody on the Fab domain. Showing them as surface representation allows us to make structural comparisons to the IgM antibody, and to highlight their similarities. The CDRs are similarly placed within the heavy and light chain variable regions between both antibodies. It is speculated that they are structurally similar because the VCR01 antibody can effectively target multiple HIV strains while IgM is the preliminary antibody produced and released during early stages of the immune response, thus it is able to respond in larger concentrations while antibodies that are more specific to the antigen are being produced.
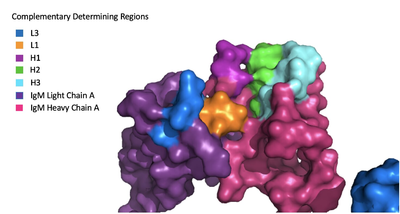
Figure 1. Surface Representation of IgM Antibody Binding Pocket. Due to the Fab region of the IgM antibody being poorly resolved, the specific side chain interactions between the heavy and light chains have not been determined. This depiction of the shows how the 4 β-sandwiches fit together; heavy chain A and B of the Fab region form a complex with the rest of the molecule via interactions with the heavy A and B of the Fc region, before continuing down into the intracellular domain to interact with the transmembrane region. The light chains however are only connected to the complex by forming interactions with the heavy chains within the Fab region. Although the specific residues within the Fab region have yet to be identified, it is estimated that each β-sandwich contains one disulfide bridge with additional hydrogen bonds.
Relevance
Signal Transduction
The diagram in figure 2 depicts the initial process of B cell activation by the antigen binding to the antibody at the Fab region. The underlying mechanism for signal transduction is unknown but it is speculated to operate under what is known as the conserved assembly mechanism. This means that upon antigen binding, BCRs on the surface of the cell begin to cluster to cause the phosphorylation of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs located in Igα and Igβ. In its “off” state, the constant region 4 of heavy chain B overlaps the extracellular components of Igα and Igβ. As the antigen binds, it induces a conformational change to release the overlap and allow for clustering about the BCR. Now, in its “on” state the phosphorylation of the ITAM region (observed here as the conserved tyrosine residues are phosphorylated) within the intracellular tails of Igα and Igβ drives downstream kinase activity to continue to process of signal cascading.
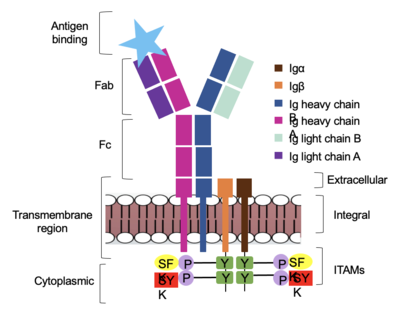
Figure 2. IgM Antibody Signal Transduction following Antigen Binding.



