We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1790
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[Image:ActiveSiteProto.png|500 px|thumb|'''Figure 2:'''Active site of PP1C on SMP.</div></font>]] | [[Image:ActiveSiteProto.png|500 px|thumb|'''Figure 2:'''Active site of PP1C on SMP.</div></font>]] | ||
==MRAS== | ==MRAS== | ||
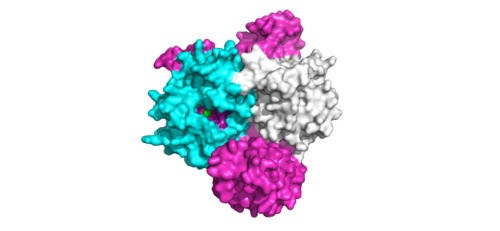
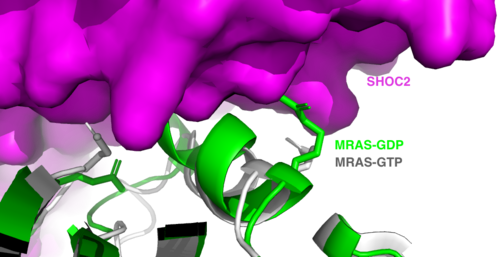
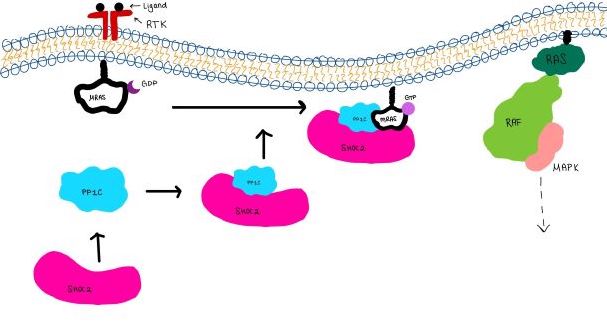
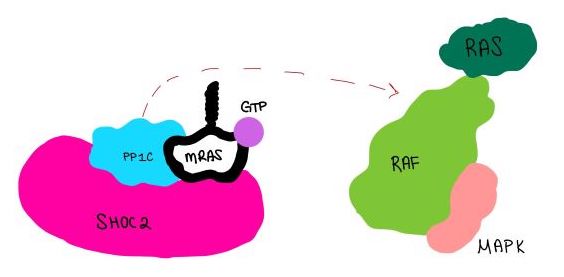
| - | <scene name='95/952717/Mras/2'>MRAS</scene> is a membrane-bound structure that aids the complex in localizing near other structures such as the RAS-RAF-MAPK complex in order to initiate downstream signaling. In its inactive state, MRAS is bound to GDP. When signaled by growth factors, the GDP is exchanged for GTP. The now <scene name='95/952718/Zoom_in_gtp/1'>GTP bound MRAS</scene> undergoes a conformational change of the <scene name='95/952716/Ras-switch-zoomed/1'>switch I and switch II regions</scene>. This conformational change activates the protein allowing it to bind with the SHOC2-PP1C complex. Without the conformational change when GDP is exchanged to GTP, the GDP-MRAS wouldn't be able to bind to SHOC2 because of steric clashing. In comparison to other RAS proteins, MRAS has a greater affinity for the SHOC2-PP1C complex<ref name=”Kubicek”> | + | <scene name='95/952717/Mras/2'>MRAS</scene> is a membrane-bound structure that aids the complex in localizing near other structures such as the RAS-RAF-MAPK complex in order to initiate downstream signaling. In its inactive state, MRAS is bound to GDP. When signaled by growth factors, the GDP is exchanged for GTP. The now <scene name='95/952718/Zoom_in_gtp/1'>GTP bound MRAS</scene> undergoes a conformational change of the <scene name='95/952716/Ras-switch-zoomed/1'>switch I and switch II regions</scene>. This conformational change activates the protein allowing it to bind with the SHOC2-PP1C complex. Without the conformational change when GDP is exchanged to GTP, the GDP-MRAS wouldn't be able to bind to SHOC2 because of steric clashing. In comparison to other RAS proteins, MRAS has a greater affinity for the SHOC2-PP1C complex<ref name=”Kubicek”>Kubicek M, Pacher M, Abraham D, Podar K, Eulitz M, Baccarini M. Dephosphorylation of Ser-259 regulates Raf-1 membrane association. J Biol Chem. 2002 Mar 8;277(10):7913-9. [http://10.1074/jbc.M108733200 doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108733200.]</ref>. MRAS engages the SHOC2-PP1C complex and RAF on the same surface indicating that for RAF signaling two separate active MRASs are needed. Having two MRASs also help with the co-localization of PP1C to the NTpS region on RAF. |
[[Image:Switches.png|500 px|thumb|'''Figure 2:'''Steric clashing of Switch I and II of GDP bound MRAS, in green, with the surface of SHOC2, in magenta. GTP-bound MRAS, in white, shows no steric clashing with SHOC2s surface.</div></font>]] | [[Image:Switches.png|500 px|thumb|'''Figure 2:'''Steric clashing of Switch I and II of GDP bound MRAS, in green, with the surface of SHOC2, in magenta. GTP-bound MRAS, in white, shows no steric clashing with SHOC2s surface.</div></font>]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
==SHOC2 and MRAS== | ==SHOC2 and MRAS== | ||
| - | MRAS is initially bound to GDP causing it to be in its inactive state. This form cannot bind to the SHOC2-PP1C complex due to steric clashing. Once GDP is exchanged for GTP to activate the protein, <scene name='95/952716/conformational changes/1'>SHOC2-MRAS (residues)</scene> occur within the switch I and switch II regions to allow <scene name='95/952716/MRAS to interact with SHOC2/2'>SHOC2-MRAS(full-image)</scene>. These <scene name='95/952716/Scho2-mras-interactions/1'>interactions</scene> include hydrogen bonds and pi stacking. The primary hydrogen bonds are R288-Q71 and R177-E47. Pi staking occurs at R104-R83 <ref name=”Lavoie”>PMID:35970881</ref>. | + | MRAS is initially bound to GDP causing it to be in its inactive state. This form cannot bind to the SHOC2-PP1C complex due to steric clashing. Once GDP is exchanged for GTP to activate the protein, <scene name='95/952716/conformational changes/1'>SHOC2-MRAS (residues)</scene> occur within the switch I and switch II regions to allow <scene name='95/952716/MRAS to interact with SHOC2/2'>SHOC2-MRAS(full-image)</scene>. These <scene name='95/952716/Scho2-mras-interactions/1'>interactions</scene> include hydrogen bonds and pi stacking. The primary hydrogen bonds are R288-Q71 and R177-E47. Pi staking occurs at R104-R83 <ref name=”Lavoie”>Lavoie H, Therrien M. Structural keys unlock RAS-MAPK cellular signalling pathway. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):248-249. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7 doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7. PMID: 35970881.]</ref>. |
==PP1C and MRAS== | ==PP1C and MRAS== | ||
Revision as of 16:44, 7 April 2023
| |||||||||||