This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1785
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
===Fab Region=== | ===Fab Region=== | ||
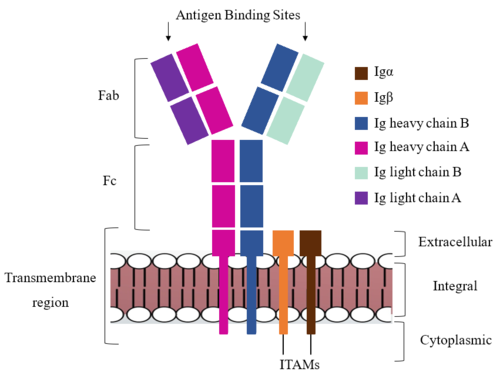
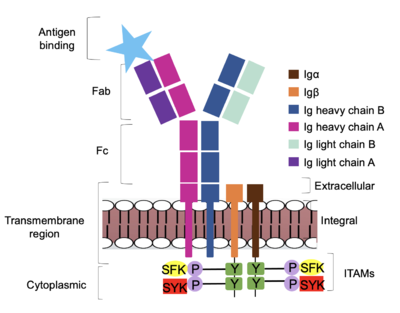
| - | The Fab region of the antibody is where antigen recognition occurs upon binding. On each arm is one heavy and one light chain, both containing domains identical to their respective counterparts. Repeats of β-sandwiches form the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antibody constant and variable domains] within the Fab region as antigen recognition occurs at the variable domain while the constant domain connects it to the rest of the IgM complex. Because the Fab region of IgM is poorly resolved, a structural analysis of an HIV neutralizing antibody called VCR01 was performed to approximate where an antigen would bind to at the | + | The Fab region of the antibody is where antigen recognition occurs upon binding. On each arm is one heavy and one light chain, both containing domains identical to their respective counterparts. Repeats of β-sandwiches form the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antibody constant and variable domains] within the Fab region as antigen recognition occurs at the variable domain while the constant domain connects it to the rest of the IgM complex. Because the Fab region of IgM is poorly resolved, a structural analysis of an HIV neutralizing antibody called VCR01 was performed to approximate where an antigen would bind to at the <scene name='95/952713/Variable_region/1'>variable region</scene> (cite). |
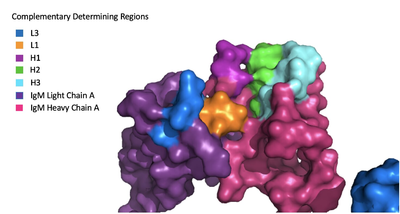
The IgM-BCR contains areas referred to as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Complementarity-determining_region complementary-determining regions](CDRs), which are where the antigen makes contact with the antibody on the Fab domain. Figure 2 depicts this as a surface representation on one of the IgM arms given that the specific residues within the antigen-binding motif are unknown. | The IgM-BCR contains areas referred to as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Complementarity-determining_region complementary-determining regions](CDRs), which are where the antigen makes contact with the antibody on the Fab domain. Figure 2 depicts this as a surface representation on one of the IgM arms given that the specific residues within the antigen-binding motif are unknown. | ||
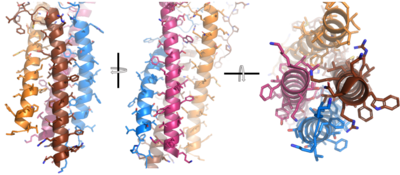
| - | Due to the poor resolution of the Fab region, specific side chain interactions between the heavy and light chains have not been determined. It is estimated that each β-sandwich contains one disulfide bridge with additional hydrogen bonds. The <scene name='95/952713/Heavy-light_chain_interface/ | + | Due to the poor resolution of the Fab region, specific side chain interactions between the heavy and light chains have not been determined. It is estimated that each β-sandwich contains one disulfide bridge with additional hydrogen bonds. The <scene name='95/952713/Heavy-light_chain_interface/2'>heavy-light chain interface</scene> shows how the four heavy and light chain β-sandwiches fit together. The Fab region heavy chains attach to the Fc region heavy chains, before continuing down into the intracellular domain to interact with the Igα/Igβ subunits. The light chains however are only connected to the heavy chains within the Fab region, thus have no contact with the subsequent domains. |
[[Image:Igm_surface.png|400 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 3. Surface Representation of IgM Antibody Binding Pocket.''' On one arm of the IgM antibody, the antigen makes contact with light chain A at the L1 and L3 complementary-determining regions. Furthermore, it makes contact with heavy chain A at the H1, H2, and H3 complementary-determining regions. The location of the complementary-determining regions were approximated using the structure of the VCR01 variable region and were visualized using Pymol.]] | [[Image:Igm_surface.png|400 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 3. Surface Representation of IgM Antibody Binding Pocket.''' On one arm of the IgM antibody, the antigen makes contact with light chain A at the L1 and L3 complementary-determining regions. Furthermore, it makes contact with heavy chain A at the H1, H2, and H3 complementary-determining regions. The location of the complementary-determining regions were approximated using the structure of the VCR01 variable region and were visualized using Pymol.]] | ||
Revision as of 17:28, 7 April 2023
Human B-cell Antigen Receptor: IgM BCR
| |||||||||||
References
Student Contributors
Detonyeá Dickson, Allison Goss, Jackson Payton