Sandbox Reserved 1777
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
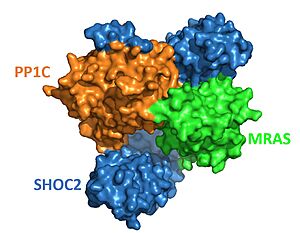
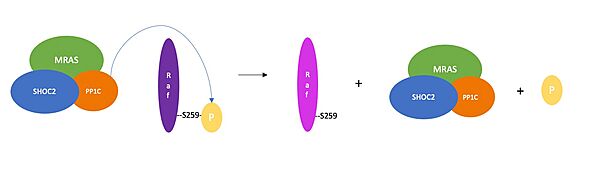
The SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C complex's key role in the regulation of the MAPK-RAF pathway means that minor changes in its structure or function can have drastic biological consequences. Unregulated activation of the MAPK pathway is the cause of several human cancers due to unchecked cell division and proliferation<ref name="Kwan" />. Mutations that stabilize the interactions of the SMP complex enhance PP1C phosphatase activity <Ref name="Jajian" />, leading to increased RAF signaling and accelerated cell division. Most SHOC2 or PP1C mutations alter residues that are the direct contact points, stabilizing the interaction between the two proteins. Mutations to MRAS result in persistent binding of GTP, leading to consistent activation of the cell signaling pathway<ref name="Kwan" />. | The SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C complex's key role in the regulation of the MAPK-RAF pathway means that minor changes in its structure or function can have drastic biological consequences. Unregulated activation of the MAPK pathway is the cause of several human cancers due to unchecked cell division and proliferation<ref name="Kwan" />. Mutations that stabilize the interactions of the SMP complex enhance PP1C phosphatase activity <Ref name="Jajian" />, leading to increased RAF signaling and accelerated cell division. Most SHOC2 or PP1C mutations alter residues that are the direct contact points, stabilizing the interaction between the two proteins. Mutations to MRAS result in persistent binding of GTP, leading to consistent activation of the cell signaling pathway<ref name="Kwan" />. | ||
| - | The unregulated MAPK pathway is also responsible for a multitude of developmental disorders commonly known as [https://dceg.cancer.gov/research/what-we-study/rasopathies#:~:text=RASopathies%20are%20a%20group%20of,to%20grow%20and%20work%20properly. RASopathies] <Ref name="Lavoie" />. One RASopathy caused by the mutation of a RAF kinase is known as [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/noonan-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20354422 Noonan Syndrome] (NS), which enhances complex formation by | + | The unregulated MAPK pathway is also responsible for a multitude of developmental disorders commonly known as [https://dceg.cancer.gov/research/what-we-study/rasopathies#:~:text=RASopathies%20are%20a%20group%20of,to%20grow%20and%20work%20properly. RASopathies] <Ref name="Lavoie" />. One RASopathy caused by the mutation of a RAF kinase is known as [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/noonan-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20354422 Noonan Syndrome] (NS), which enhances complex formation by stabilizing the interactions of each member <ref name="Kwan" />. NS is a genetic disorder that can prevent normal development during the neonatal period, leading to difficulties with feeding and a failure to thrive<Ref name= 'van der Burgt'> van der Burgt, I. Noonan syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2, 4 (2007). doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-2-4 [https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-2-4. DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-2-4]. </Ref>. The characteristic features of NS become more evident during infancy and childhood. NS patients often have atypical facial appearance, short stature, heart defects, and other physical problems<ref name="van der Burgt" />. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 16:23, 17 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bernal Astrain G, Nikolova M, Smith MJ. Functional diversity in the RAS subfamily of small GTPases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Apr 29;50(2):921-933. doi: 10.1042/BST20211166. DOI:10.1042/BST20211166
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Molina JR, Adjei AA. The Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway. J Thorac Oncol. 2006 Jan;1(1):7-9. DOI:10.1016/S1556-0864(15)31506-9.
- ↑ Li, L., Zhao, G. D., Shi, Z. et. al.The Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway (Figure 1) and its role in the occurrence and development of HCC. Oncology letters, 12(5), 3045–3050. DOI:10.3892/ol.2016.5110.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Hauseman, Z.J., Fodor, M., Dhembi, A. et al. Structure of the MRAS–SHOC2–PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature 609, 416–423 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Kwon, J. J., & Hahn, W. C. A Leucine-Rich Repeat Protein Provides a SHOC2 the RAS Circuit: a Structure-Function Perspective. Molecular and cellular biology, 41(4), e00627-20 (2021). doi:10.1128/MCB.00627-20. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00627-20.
- ↑ Zhou, Y., Prakash, P., Liang, H., et al. Lipid-Sorting Specificity Encoded in K-Ras Membrane Anchor Regulates Signal Output. Cell, 168(1-2), 239–251.e16 doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.059. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.059.
- ↑ Young, L., Rodriguez-Viciana, P. MRAS: A Close but Understudied Member of the RAS Family. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine (2018). doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033621. DOI: 0.1101/cshperspect.a033621.
- ↑ Daniel A. Bonsor, Patrick Alexander, Kelly Snead, Nicole Hartig, Matthew Drew, Simon Messing, Lorenzo I. Finci, Dwight V. Nissley, Frank McCormick, Dominic Esposito, Pablo Rodrigiguez-Viciana, Andrew G. Stephen, Dhirendra K. Simanshu. Structure of the SHOC2–MRAS–PP1C complex provides insights into RAF activation and Noonan syndrome. bioRxiv. 2022.05.10.491335. doi: 10.1101/2022.05.10.491335. DOI:10.1101/2022.05.10.491335.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Kwon, J.J., Hajian, B., Bian, Y. et al. Structure–function analysis of the SHOC2–MRAS–PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature 609, 408–415 (2022).doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Kwon, J., Jajian, B., Bian, Y. et al. Comprehensive structure-function evaluation of the SHOC2 holophosphatase reveals disease mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. In: Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2022. DOI: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2022-LB029.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Liau NPD, Johnson MC, Izadi S, Gerosa L, Hammel M, Bruning JM, Wendorff TJ, Phung W, Hymowitz SG, Sudhamsu J. Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Nature. 2022 Jun 29. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. PMID:35768504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Lavoie, H., Therrien, M. Structural keys unlock RAS–MAPK cellular signaling pathway. Nature 609, 248-249 (2022). doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7. DOI:10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 van der Burgt, I. Noonan syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2, 4 (2007). doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-2-4 DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-2-4.