SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS
Introduction
(SMP) is a ternary holophosphotase complex formed by the individual proteins: SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. Formation of this complex begins with a signal binding to a receptor tyrosine kinase receptor(RTK). This causes membrane-bound MRAS to exchange GDP for GTP. From here the complex comes together in the plasma membrane. Its role in MAPK signaling is the dephosphorylation of the N-terminal phosphoserine (NTpS) on the RAF complex leading to further downstream signaling effects [1].
Overall Structure
SHOC2
is a scaffold protein that is composed of 20 repeat domains that form a solenoid structure. The leucine rich region forms a concave hydrophobic core which is necessary for binding with PP1C and MRAS. SHOC2 is the crucial mediator for SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS complex formation [1].
PP1C
is a catalytic protein. After forming a ternary complex, the hydrophobic active site on the protein interacts with Raf to act as a phosphatase and dephosphorylate Ser 259. PP1C's active site is adjacent to a hydrophobic patch. It's theorized that the hydrophobic patch binds to the C-terminal of N-terminal phosphoserine of RAF, the target for dephosphorylation. PP1C can act as a phosphatase in the absence of SHOC2 but PP1C lasks intrinsic substrate selectively. So SMP complex formation is necessary for PP1C specificity to RAF [1].
SHOC2 and PP1C interactions
on its leucine rich region(LRR). Between LRR2 and LRR5 and between LRR7 and LRR11. Mutations between SHOC2 and PP1C to the LRR were shown to completely inhibit the binding of PP1C. Five main are made between PP1C and SHOC2 respectively: E56-R182, E167-R203, E54-K180, R187-H178, R188-E155 [2]. Reflecting this ionic character, the binding regions are contained within extensive acidic and basic patches on and . The negative acidic patches of PP1C interact with the positive basic patches of SHOC2 and vice versa to form a . These interactions do not result in significant conformational changes to PP1C in comparison to other protein interactions that can be made with PP1C [2].
MRAS
is a monomeric GTPase. MRAS is membrane-bound due to post-translational lipidation which allows the protein to interact with the inner membrane leaflet. [3] MRAS localizes the SMP complex near RAF and other components of downstream signaling. The region of MRAS not directly bound to the membrane binds SHOC2 and PP1C to orient the complex such that PP1C’s active site faces the serine that will get dephosphorylated on RAF. MRAS also controls SMP complex formation in connection with extracellular signaling based on its dualistic switching between its inactive and active state. In its inactive state, MRAS is bound to GDP. When signaled by growth factors, the GDP is exchanged for GTP when a ligand binds to the RTK [1]. The now undergoes a conformational change of the . These regions are the major binding sites with SHOC2. This conformational change activates MRAS allowing it to bind with the SHOC2-PP1C complex. In its inactive GDP-bound state, MRAS is sterically occluded from binding SHOC2. For example, R83 of GDP-bound MRAS directly clashes with SHOC2 as shown in figure 2. In comparison to other RAS proteins such as H/K/NRAS, MRAS has a greater affinity for the SHOC2-PP1C complex[4]. This indicates that the specific structure of MRAS is necessary for SMP function. While MRAS engages the SHOC2-PP1C complex to bring the complex to the membrane, an additional membrane-bound RAS binds RAF nearby. This binding is also stimulated by ligand binding to the RTK. This indicates that for full RAF activation and continuous signaling of Raf, two separate active RAS proteins are needed. Having two MRASs also help with the co-localization of PP1C to the NTpS region on RAF. To inactivate Raf signaling, MRAS uses its intrinsic GTPase to remove the activating gamma-phosphate on GTP. In the GDP-bound state, switch I and II move to the position shown in green in Figure 2. This inactivates SHOC2 binding due to steric clashing which causes the SMP structure to dissociate.
SHOC2 and MRAS interactions
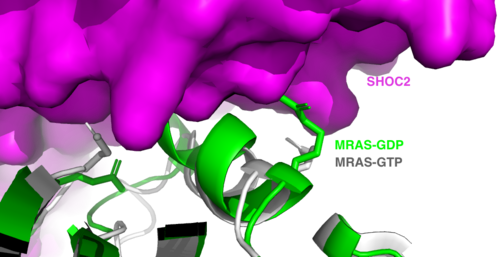
Figure 2:Steric clashing of Switch I and II of GDP bound MRAS, in green, with the surface of SHOC2, in magenta. GTP-bound MRAS, in white, shows no steric clashing with SHOC2s surface.</div></font>
MRAS is initially bound to GDP causing it to be in its inactive state. Inactive GDP-MRAS cannot bind to the SHOC2-PP1C complex due to steric clashing of the switch I and II regions of MRAS and its binding zone on SHOC2. Once GDP is exchanged for GTP when signaled by growth factors, MRAS is activated and conformational changes occur within the switch I and switch II regions to allow . These between SHOC2 and the switch I and II regions of MRAS include hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, and π stacking. There is a hydrogen bond at R288-Q71 and ionic interaction at R177-E47. π staking occurs at R104-R83. These interactions occur between SHOC2 and MRAS respectively [5].
PP1C and MRAS
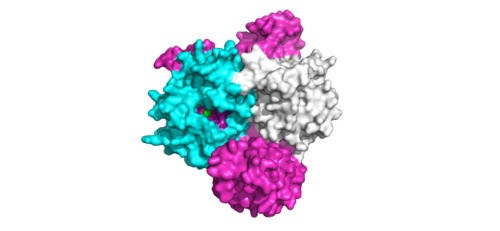
Figure 1:Active site of PP1C on SMP.</div></font>
The interactions between are respectively mediated by four main : ionic interactions are between D48-R188 and H53-D197, hydrogen bonds are between K36-Q198 and Q35-M190. As the complex forms, the active site for the dephosphorylation of RAF's S259 is oriented such that it remains accessible for RAF [1]. The relative order of complex ordering is still an area of debate. Some experiments indicate that PP1C must bind to SHOC2 before MRAS binds[5] but others indicated that PP1C and MRAS can bind to SHOC2 at the same time [1].
Signaling Pathway
The SMP signaling pathway begins with the formation of the SMP complex. Initially, a ligand must bind to a receptor tyrosine kinase. This signals SHOC2 to bind to PP1C forming a binary complex that then binds to the membrane bound MRAS. Some literature indicates that the three proteins bind at the same time but the order is largely unknown. Figure 2 shows the proteins binding one at a time. Once the SMP complex forms, its target is the NTpS also known as S259. The serine is directly dephosphorylated by PP1C by SHOC2 and MRAS increase its specificity for S259.
Mutations affecting SMP complex formation and stability have been shown to increase or decrease MAPK signaling. Increased stability of the complex increases MAPK signaling while decreased stability decreases signaling[6].
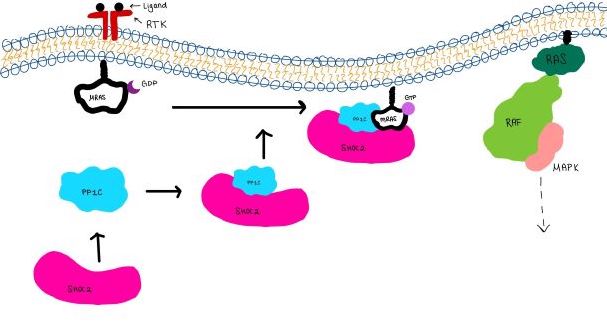
Figure 3:Signaling cascade is shown with SHOC2 in pink, PP1C in blue, and MRAS in white.
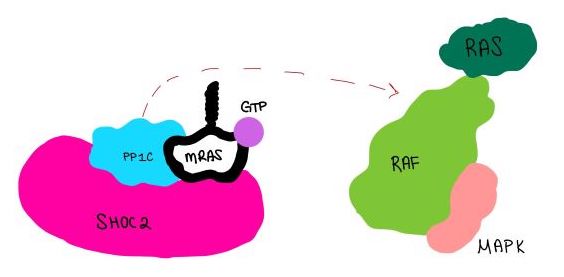
Figure 4:PP1C dephosphorylates RAF protein at serine 259
Disease Relevance
RASopathies
RASopathy is a broad term used to describe developmental syndromes that stem from germline mutations of proteins along the RAS/MAPK pathway such as SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. These mutations can be either gain or loss of function. Rasopathies can also lead to cancer [7].
Cancer
Because the RAS/MAPK pathway activated by SMP regulates cell proliferation and survival, overactivity can cause tumor formation and cancer. For example, the complex has been found to play a role in the perpetuation of melanoma, leukemia, and lung cancer [2].
Future Studies
Further study of the SMP complex includes clarification of the steps of the pathway. Firstly, the order of binding to form the SMP complex is unclear. Furthermore, the interaction between SMP and the Raf complex is largely unknown. Study into this step is especially important to understand how SMP activates downstream signaling.
The current knowledge of SMP can be used to study possible treatments for rasopathies and cancer. For example, the development of inhibitors that target SMP binding could prevent the effects caused by mutations that overactivate SMP. Another possible point of inhibition is the growth factor that signals SHOC2-PP1C and Raf to the cell membrane. [6] .
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Hauseman ZJ, Fodor M, Dhembi A, Viscomi J, Egli D, Bleu M, Katz S, Park E, Jang DM, Porter KA, Meili F, Guo H, Kerr G, Molle S, Velez-Vega C, Beyer KS, Galli GG, Maira SM, Stams T, Clark K, Eck MJ, Tordella L, Thoma CR, King DA. Structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Jul 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. PMID:35830882 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Kwon JJ, Hajian B, Bian Y, Young LC, Amor AJ, Fuller JR, Fraley CV, Sykes AM, So J, Pan J, Baker L, Lee SJ, Wheeler DB, Mayhew DL, Persky NS, Yang X, Root DE, Barsotti AM, Stamford AW, Perry CK, Burgin A, McCormick F, Lemke CT, Hahn WC, Aguirre AJ. Structure-function analysis of the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Jul 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. PMID:35831509 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2
- ↑ Seabra MC. Membrane association and targeting of prenylated Ras-like GTPases. Cell Signal. 1998 Mar;10(3):167-72. PMID:9607139 doi:10.1016/s0898-6568(97)00120-4
- ↑ Kubicek M, Pacher M, Abraham D, Podar K, Eulitz M, Baccarini M. Dephosphorylation of Ser-259 regulates Raf-1 membrane association. J Biol Chem. 2002 Mar 8;277(10):7913-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108733200.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Lavoie H, Therrien M. Structural keys unlock RAS-MAPK cellular signaling pathway. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):248-249. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7. PMID: 35970881.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Liau NPD, Johnson MC, Izadi S, Gerosa L, Hammel M, Bruning JM, Wendorff TJ, Phung W, Hymowitz SG, Sudhamsu J. Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Nature. 2022 Jun 29. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. PMID:35768504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3
- ↑ Rauen KA. The RASopathies. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2013;14:355-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153523.
Student Contributors
Madeline Gilbert
Inaya Patel
Rushda Hussein




