This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1785
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
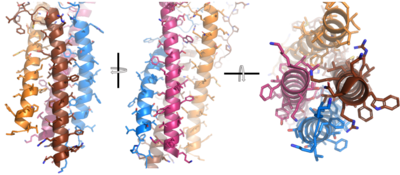
| - | Within the transmembrane region, '''{{Font color|violet|heavy chain A}}''' and <b><span class="text-blue">heavy chain B</span></b> associate (Figure 1) asymmetrically to facilitate intracellular signaling cascades. The transmembrane heavy chain interface allows them to pack together via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Van_der_Waals_force Van der Waals] contacts, but there are also prominent <scene name='95/952713/Trans_heavy/ | + | Within the transmembrane region, '''{{Font color|violet|heavy chain A}}''' and <b><span class="text-blue">heavy chain B</span></b> associate (Figure 1) asymmetrically to facilitate intracellular signaling cascades. The transmembrane heavy chain interface allows them to pack together via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Van_der_Waals_force Van der Waals] contacts, but there are also prominent <scene name='95/952713/Trans_heavy/11'>hydrogen bonds</scene> between each chain. More specifically, the hydroxyl group from Ser584 on '''{{Font color|violet|heavy chain A}}''' donates a hydrogen bond to Ser584 and to Ser588 on <b><span class="text-blue">heavy chain B</span></b>. This creates a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_bond bifurcated hydrogen bond], essentially forming a “fork” between the two chains to help stabilize them and maintain the transmission of the signal once the cell is activated. Because transmembrane Ig molecules cannot efficiently initiate the signal cascade, they must associate with the <b><span class="text-brown">Igα</span></b> and <b><span class="text-orange">Igβ</span></b> chains within the BCR. <ref name="Su">PMID:35981043</ref> |
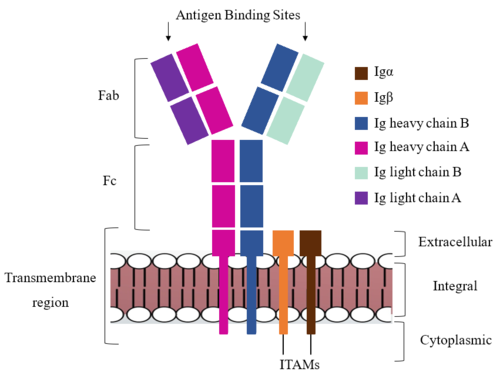
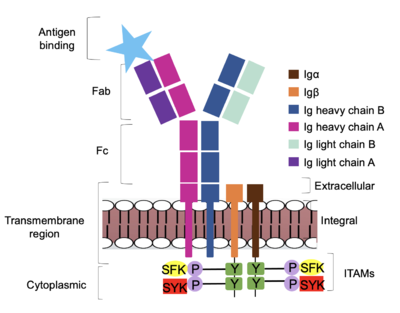
Furthermore, both the <b><span class="text-brown">Igα</span></b> and <b><span class="text-orange">Igβ</span></b> chains have cytoplasmic tails that extend into the B cell (Figure 1). Each of these tails contain an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunoreceptor_tyrosine-based_activation_motif ITAM region] to facilitate signal transduction (Figure 4). <ref name="Ma">PMID:35981028</ref> | Furthermore, both the <b><span class="text-brown">Igα</span></b> and <b><span class="text-orange">Igβ</span></b> chains have cytoplasmic tails that extend into the B cell (Figure 1). Each of these tails contain an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunoreceptor_tyrosine-based_activation_motif ITAM region] to facilitate signal transduction (Figure 4). <ref name="Ma">PMID:35981028</ref> | ||
Revision as of 18:52, 20 April 2023
Human B-cell Antigen Receptor: IgM BCR
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Sathe A, Cusick JK. Biochemistry, Immunoglobulin M. 2022 Dec 19. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–. PMID: 32310455. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32310455/
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Su Q, Chen M, Shi Y, Zhang X, Huang G, Huang B, Liu D, Liu Z, Shi Y. Cryo-EM structure of the human IgM B cell receptor. Science. 2022 Aug 19;377(6608):875-880. doi: 10.1126/science.abo3923. Epub 2022, Aug 18. PMID:35981043 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abo3923
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Ma X, Zhu Y, Dong, Chen Y, Wang S, Yang D, Ma Z, Zhang A, Zhang F, Guo C, Huang Z. Cryo-EM structures of two human B cell receptor isotypes. Science. 2022 Aug 19;377(6608):880-885. doi: 10.1126/science.abo3828. Epub 2022, Aug 18. PMID:35981028 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abo3828
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Tolar P, Pierce SK. Unveiling the B cell receptor structure. Science. 2022 Aug 19;377(6608):819-820. doi: 10.1126/science.add8065. Epub 2022 Aug 18.[http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.add8065 DOI:10.1126/science.add8065
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Dylke J, Lopes J, Dang-Lawson M, Machtaler S, Matsuuchi L. Role of the extracellular and transmembrane domain of Ig-alpha/beta in assembly of the B cell antigen receptor (BCR). Immunol Lett. 2007 Sep 15;112(1):47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.06.005. Epub 2007 Jul 23. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2007.06.005 DOI:10.1016/j.imlet.2007.06.005
- ↑ Zhou T, Georgiev I, Wu X, Yang ZY, Dai K, Finzi A, Do Kwon Y, Scheid JF, Shi W, Xu L, Yang Y, Zhu J, Nussenzweig MC, Sodroski J, Shapiro L, Nabel GJ, Mascola JR, Kwong PD. Structural basis for broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by antibody VRC01. Science. 2010 Aug 13;329(5993):811-7. Epub 2010 Jul 8. PMID:20616231 doi:10.1126/science.1192819
Student Contributors
DeTonyeá Dickson, Allison Goss, Jackson Payton