We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Vytorin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | < | + | <StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='Ezetimibe and Simvastatin come together to make up the medication known as Vytorin'> |
==Vytorin (ezetimibe & simvastatin)== | ==Vytorin (ezetimibe & simvastatin)== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
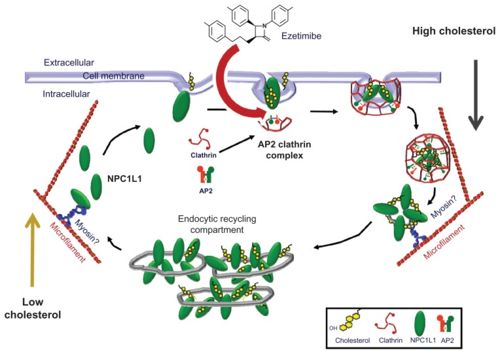
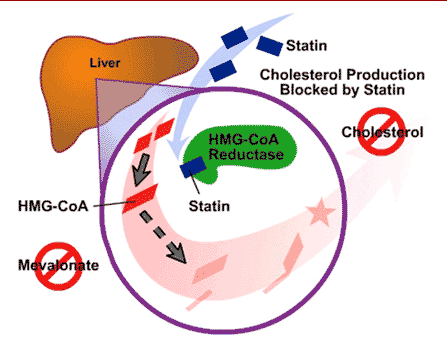
When the drug is administered, it is initially inactive. It must be hydrolyzed in order to become active. Once hydrolyzed, simvastatin reduces the amount of mevalonic acid in the blood by competing for HMG-CoA reductase with HMG-CoA. To produce cholesterol, Acetyl CoA is converted into HMG-CoA, which is then converted into mevalonate. Mevalonate is then converted into isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP), IPP is converted into squalene, and then finally squalene is converted into cholesterol. Simvastatin reduces the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, therefore lowering cholesterol levels. Simvastatin targets <scene name='75/758993/Simvastatin_bound/1'>HMG-CoA reductase</scene> which is the enzyme responsible for said conversion. With the synthesis of cholesterol being divided into five major steps, this inability to convert targets only the second step in cholesterol synthesis.<ref>http://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/v/vytorin/vytorin_pi.pdf</ref> | When the drug is administered, it is initially inactive. It must be hydrolyzed in order to become active. Once hydrolyzed, simvastatin reduces the amount of mevalonic acid in the blood by competing for HMG-CoA reductase with HMG-CoA. To produce cholesterol, Acetyl CoA is converted into HMG-CoA, which is then converted into mevalonate. Mevalonate is then converted into isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP), IPP is converted into squalene, and then finally squalene is converted into cholesterol. Simvastatin reduces the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, therefore lowering cholesterol levels. Simvastatin targets <scene name='75/758993/Simvastatin_bound/1'>HMG-CoA reductase</scene> which is the enzyme responsible for said conversion. With the synthesis of cholesterol being divided into five major steps, this inability to convert targets only the second step in cholesterol synthesis.<ref>http://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/v/vytorin/vytorin_pi.pdf</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 12:12, 23 April 2023
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00973
- ↑ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ezetimibe#section=Experimental-Properties
- ↑ http://e-lactancia.org/media/papers/StatinasFK-FundClinPhar2004.pdf
- ↑ https://www.rpi.edu/dept/bcbp/molbiochem/MBWeb/mb2/part1/cholesterol.htm==Mechanism of Action
- ↑ https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/021445s019lbl.pdf
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18522832
- ↑ http://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/v/vytorin/vytorin_pi.pdf