BASIL2023GVP76586
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
The InterPro figure really help us narrow down that it could be either of those to substrates because again it shown a sugar kinase and a ATPase which would mean that there is potentially a nucloeside or something to with ATP. | The InterPro figure really help us narrow down that it could be either of those to substrates because again it shown a sugar kinase and a ATPase which would mean that there is potentially a nucloeside or something to with ATP. | ||
== Molecular Docking == | == Molecular Docking == | ||
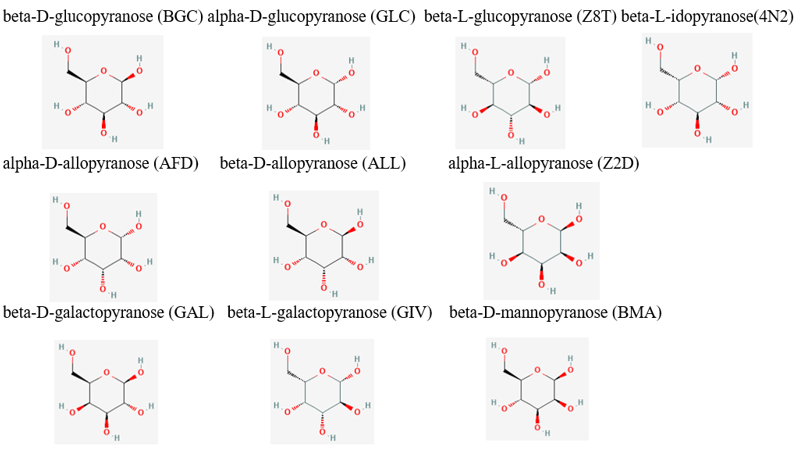
| - | From the initial search throughout all of the computational tools, we decided that our putative kinase was potentially a glucokinase. We docked other sugars along with glucose in figure 1. [[Image:Sugar_substrates.png]] Taking in consideration of the DNA binding domain found in the InterPro results we docked DNA nitrogenous bases and nucleosides, the structures of the nitrogenous bases are shown in figure 2. [[Image:Nitrogenous_Bases_Structures.png] | + | From the initial search throughout all of the computational tools, we decided that our putative kinase was potentially a glucokinase. We docked other sugars along with glucose in figure 1. |
| - | + | [[Image:Sugar_substrates.png]] | |
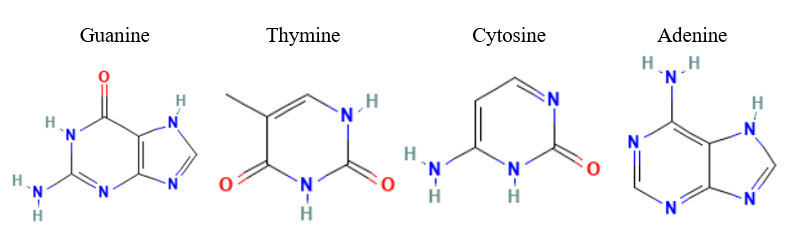
| - | + | Taking in consideration of the DNA binding domain found in the InterPro results we docked DNA nitrogenous bases and nucleosides, the structures of the nitrogenous bases are shown in figure 2. | |
| - | + | [[Image:Nitrogenous_Bases_Structures.png]] | |
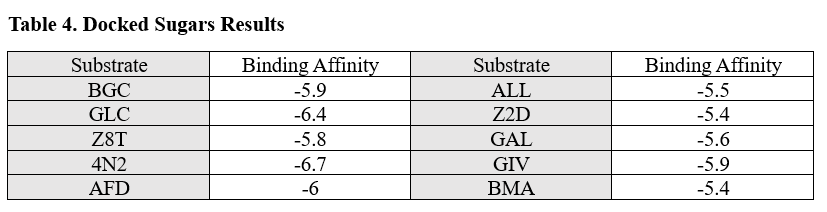
| - | + | From the results of the docked sugars, shown in table 4, nitrogenous bases, and nucleosides, we determined that guanosine was a strong potential substrate but still wanted to test glucose due to the computational tools results since glucokinase was a common output in all of our searches. | |
| - | From the results of the docked sugars, nitrogenous bases, and nucleosides, we determined that guanosine was a strong potential substrate but still wanted to test glucose due to the computational tools results since glucokinase was a common output in all of our searches. | + | [[Image:Sugar_affinities.png]] |
We used Pymol to visualize the intermolecular interactions in the active site with guanosine (figure 3) and glucose (figure 4). | We used Pymol to visualize the intermolecular interactions in the active site with guanosine (figure 3) and glucose (figure 4). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Guanosine experienced possible hydrogen bonding with residues Arg183, Gln393, and Tyr23. Glucose experienced possible hydrogen bonds with Tyr23, Asp81, Arg183, and a possible pi stacking interaction with Tyr389. | ||
==Structural Highlights== | ==Structural Highlights== | ||
Revision as of 17:45, 24 April 2023
Investigating the Function of Protein P76586
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644