We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Daniel Key Takemoto/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Function and Structure== | ==Function and Structure== | ||
<StructureSection load='5DE5' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='5DE5' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
| - | Fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein (FMRP) is encoded by the fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1 (FMR1) gene, located in the X chromossome, associated with the fragile X syndrome (FXS), Fragile X Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) and Premature Ovarian Failure (POF1). | + | Fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein (FMRP) is encoded by the fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1 (FMR1) gene, located in the X chromossome, associated with the fragile X syndrome (FXS), Fragile X Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) and Premature Ovarian Failure (POF1). FMRP functions as a synaptic regulator by binding to mRNAs and inhibiting its translation, therefore regulating the synthesis of proteins in the synapse. It is also a RNA binding protein, which is reponsible for the transportation of mRNAs to cytoplam. The FMRP can also bind to its own FMR1 transcripts, possibly a self-regulatory mechanism. The RGG motif bind to G-quadruplexes, secondary structures formed in some RNAs. The structure being represented on the right represents the FMRP RGG motif and the G-quadruplex secondary structure in the RNA. The protein structure was obtained by X-ray diffraction with a 3 Å resolution <ref>doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1515737112 |
'''RGG motif''' | '''RGG motif''' | ||
| - | Different domains and motifs mediate the RNA binding mechanism and the exon 15-encoded RGG (arginine - glycine - glycine) motif is one of them. The RGG motif is well conserved in vertebrates.To easily represent the RGG motif binding to a RNA, this motif will be highlitghted in the scene <scene name='96/969643/Rgg_motif_binding_to_rna/16'>Crystal structure of the complex between human FMRP RGG motif and G-quadruplex RNA.</scene>. Therefore, the understanding of the interaction RGG-RNA is important for the comprehension of the FMRP and FXS. | + | Different domains and motifs mediate the RNA binding mechanism and the exon 15-encoded RGG (arginine - glycine - glycine) motif is one of them. The RGG motif is well conserved in vertebrates.To easily represent the RGG motif binding to a RNA, this motif will be highlitghted in the scene <scene name='96/969643/Rgg_motif_binding_to_rna/16'>Crystal structure of the complex between human FMRP RGG motif and G-quadruplex RNA.</scene>. Several tetrads can stack in a single G-quadruplex structure and be stabilized further by potassium cations, in the case of FMRP targets, whereas destabilized by lithium cations. FMRP RGG motifs seem to prefer binding to specific structures, not linear motifs. Therefore, the understanding of the interaction RGG-RNA is important for the comprehension of the FMRP and FXS. |
| - | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
[[Image:G-quadruplex.jpg]] | [[Image:G-quadruplex.jpg]] | ||
| - | + | A motif that is going to be explored is the RGG motif, that the protein uses to bind to guanine G-quadruplexes a structure that consists of nucleic acid folding in which four guanines arrange in a planar conformation stabilized by Hoogsteen-trype hydrogen bonds, named tetrad. | |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 20:00, 9 June 2023
Function and Structure
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1515737112
RGG motif
Different domains and motifs mediate the RNA binding mechanism and the exon 15-encoded RGG (arginine - glycine - glycine) motif is one of them. The RGG motif is well conserved in vertebrates.To easily represent the RGG motif binding to a RNA, this motif will be highlitghted in the scene . Several tetrads can stack in a single G-quadruplex structure and be stabilized further by potassium cations, in the case of FMRP targets, whereas destabilized by lithium cations. FMRP RGG motifs seem to prefer binding to specific structures, not linear motifs. Therefore, the understanding of the interaction RGG-RNA is important for the comprehension of the FMRP and FXS.
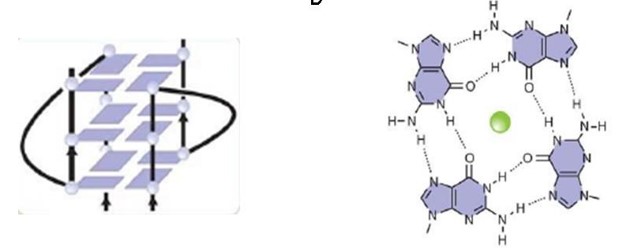 A motif that is going to be explored is the RGG motif, that the protein uses to bind to guanine G-quadruplexes a structure that consists of nucleic acid folding in which four guanines arrange in a planar conformation stabilized by Hoogsteen-trype hydrogen bonds, named tetrad.
A motif that is going to be explored is the RGG motif, that the protein uses to bind to guanine G-quadruplexes a structure that consists of nucleic acid folding in which four guanines arrange in a planar conformation stabilized by Hoogsteen-trype hydrogen bonds, named tetrad.
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
