14-3-3 protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
Research on 14-3-3 proteins continues to uncover their intricate roles in cellular signaling and their involvement in various diseases. Understanding their interactions and regulatory mechanisms provides insights into fundamental cellular processes and offers potential avenues for therapeutic interventions. | Research on 14-3-3 proteins continues to uncover their intricate roles in cellular signaling and their involvement in various diseases. Understanding their interactions and regulatory mechanisms provides insights into fundamental cellular processes and offers potential avenues for therapeutic interventions. | ||
| - | == Structure == | ||
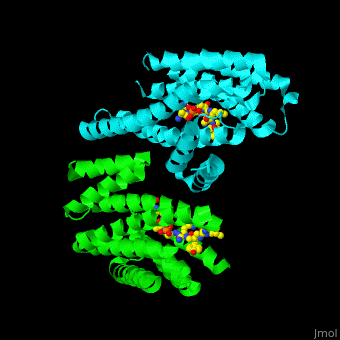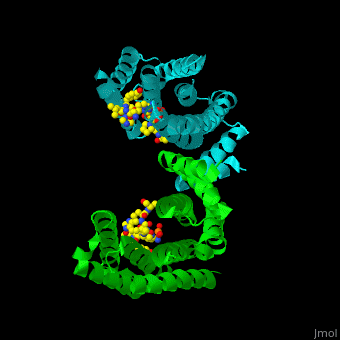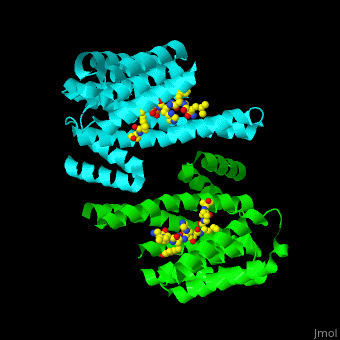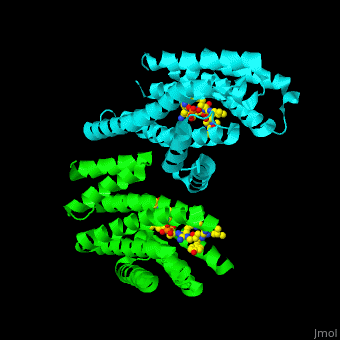
| - | The 14-3-3 proteins exist as dimers, with each dimer composed of two identical or closely related subunits. There are seven isoforms of 14-3-3 proteins identified in mammals, labeled as alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon, eta, and zeta. These isoforms share a high degree of sequence similarity but can have distinct functions and binding partners. | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 06:55, 11 June 2023
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Benzinger A, Popowicz GM, Joy JK, Majumdar S, Holak TA, Hermeking H. The crystal structure of the non-liganded 14-3-3sigma protein: insights into determinants of isoform specific ligand binding and dimerization. Cell Res. 2005 Apr;15(4):219-27. PMID:15857576 doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7290290