|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | | | |
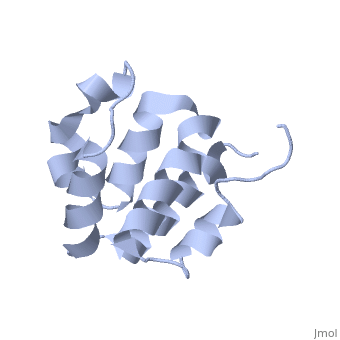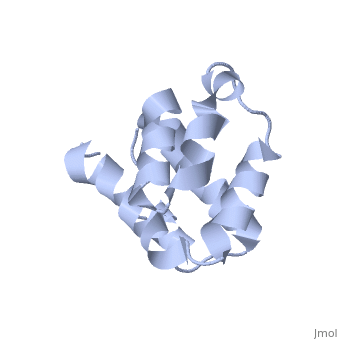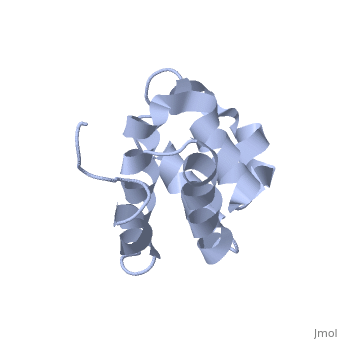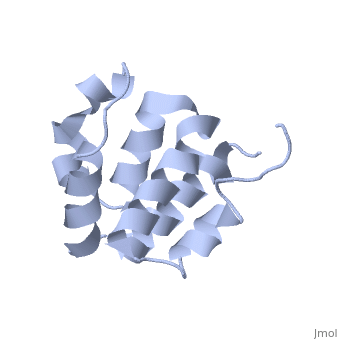
| | ==NMR structure of the NLRP7 Pyrin domain== | | ==NMR structure of the NLRP7 Pyrin domain== |
| - | <StructureSection load='2km6' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2km6]], [[NMR_Ensembles_of_Models | 20 NMR models]]' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='2km6' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2km6]]' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2km6]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2KM6 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2KM6 FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2km6]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2KM6 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2KM6 FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">NLRP7, NALP7, NOD12, PYPAF3 ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN])</td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2km6 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2km6 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2km6 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2km6 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2km6 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2km6 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2km6 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2km6 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2km6 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2km6 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2km6 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2km6 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Disease == | | == Disease == |
| - | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NALP7_HUMAN NALP7_HUMAN]] Partial hydatidiform mole;Complete hydatidiform mole. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.<ref>PMID:16462743</ref> <ref>PMID:19246479</ref>
| + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NALP7_HUMAN NALP7_HUMAN] Partial hydatidiform mole;Complete hydatidiform mole. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.<ref>PMID:16462743</ref> <ref>PMID:19246479</ref> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NALP7_HUMAN NALP7_HUMAN]] Inhibits CASP1/caspase-1-dependent IL1B secretion.<ref>PMID:15817483</ref>
| + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NALP7_HUMAN NALP7_HUMAN] Inhibits CASP1/caspase-1-dependent IL1B secretion.<ref>PMID:15817483</ref> |
| | == Evolutionary Conservation == | | == Evolutionary Conservation == |
| | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] |
| Line 37: |
Line 36: |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Human]] | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| | [[Category: Large Structures]] | | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Peti, W]] | + | [[Category: Peti W]] |
| - | [[Category: Pinheiro, A]] | + | [[Category: Pinheiro A]] |
| - | [[Category: Proell, M]] | + | [[Category: Proell M]] |
| - | [[Category: Schwarzenbacher, R]] | + | [[Category: Schwarzenbacher R]] |
| - | [[Category: Atp-binding]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Disease mutation]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Immune system]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Innate immune system]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Leucine-rich repeat]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Nalp]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Nlrp7]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Nucleotide-binding]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Protein binding]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Pyrin domain]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Signaling protein]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Disease
NALP7_HUMAN Partial hydatidiform mole;Complete hydatidiform mole. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.[1] [2]
Function
NALP7_HUMAN Inhibits CASP1/caspase-1-dependent IL1B secretion.[3]
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
The innate immune system provides an initial line of defense against infection. Nucleotide-binding domain- and leucine-rich repeat-containing protein (NLR or (NOD-like)) receptors play a critical role in the innate immune response by surveying the cytoplasm for traces of intracellular invaders and endogenous stress signals. NLRs themselves are multi-domain proteins. Their N-terminal effector domains (typically a pyrin or caspase activation and recruitment domain) are responsible for driving downstream signaling and initiating the formation of inflammasomes, multi-component complexes necessary for cytokine activation. However, the currently available structures of NLR effector domains have not yet revealed the mechanism of their differential modes of interaction. Here, we report the structure and dynamics of the N-terminal pyrin domain of NLRP7 (NLRP7 PYD) obtained by NMR spectroscopy. The NLRP7 PYD adopts a six-alpha-helix bundle death domain fold. A comparison of conformational and dynamics features of the NLRP7 PYD with other PYDs showed distinct differences for helix alpha3 and loop alpha2-alpha3, which, in NLRP7, is stabilized by a strong hydrophobic cluster. Moreover, the NLRP7 and NLRP1 PYDs have different electrostatic surfaces. This is significant, because death domain signaling is driven by electrostatic contacts and stabilized by hydrophobic interactions. Thus, these results provide new insights into NLRP signaling and provide a first molecular understanding of inflammasome formation.
Three-dimensional structure of the NLRP7 pyrin domain: insight into pyrin-pyrin-mediated effector domain signaling in innate immunity.,Pinheiro AS, Proell M, Eibl C, Page R, Schwarzenbacher R, Peti W J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 27;285(35):27402-10. Epub 2010 Jun 11. PMID:20547486[4]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Murdoch S, Djuric U, Mazhar B, Seoud M, Khan R, Kuick R, Bagga R, Kircheisen R, Ao A, Ratti B, Hanash S, Rouleau GA, Slim R. Mutations in NALP7 cause recurrent hydatidiform moles and reproductive wastage in humans. Nat Genet. 2006 Mar;38(3):300-2. Epub 2006 Feb 5. PMID:16462743 doi:http://dx.doi.org/ng1740
- ↑ Wang CM, Dixon PH, Decordova S, Hodges MD, Sebire NJ, Ozalp S, Fallahian M, Sensi A, Ashrafi F, Repiska V, Zhao J, Xiang Y, Savage PM, Seckl MJ, Fisher RA. Identification of 13 novel NLRP7 mutations in 20 families with recurrent hydatidiform mole; missense mutations cluster in the leucine-rich region. J Med Genet. 2009 Aug;46(8):569-75. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2008.064196. Epub 2009 Feb, 25. PMID:19246479 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/jmg.2008.064196
- ↑ Kinoshita T, Wang Y, Hasegawa M, Imamura R, Suda T. PYPAF3, a PYRIN-containing APAF-1-like protein, is a feedback regulator of caspase-1-dependent interleukin-1beta secretion. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 10;280(23):21720-5. Epub 2005 Apr 6. PMID:15817483 doi:http://dx.doi.org/M410057200
- ↑ Pinheiro AS, Proell M, Eibl C, Page R, Schwarzenbacher R, Peti W. Three-dimensional structure of the NLRP7 pyrin domain: insight into pyrin-pyrin-mediated effector domain signaling in innate immunity. J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 27;285(35):27402-10. Epub 2010 Jun 11. PMID:20547486 doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.113191
|