3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1''' ( | + | '''3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1''' (PDK1) activates many other kinases. PDK1 main effector is protein kinase B (Akt). <scene name='54/542348/Cv/6'>Serine (Ser241 in human) is the PDK1 phosphorylated residue (PSer)</scene>. PDK1 is important in signaling pathways activated by growth factors and hormones. It interacts with membrane phospholipids. <ref>PMID:15209375</ref> |
PDK1 is an enzyme that plays a central role in signal transduction pathways involved in cell growth, metabolism, and survival. It belongs to the family of AGC (protein kinase A, G, and C) kinases and is a key regulator of various cellular processes. | PDK1 is an enzyme that plays a central role in signal transduction pathways involved in cell growth, metabolism, and survival. It belongs to the family of AGC (protein kinase A, G, and C) kinases and is a key regulator of various cellular processes. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | Inhibition of | + | Inhibition of PDK1 leads to increase in α-secretase activity at the neuronal surface causing cellular prion protein and amyloid precursor protein to be cleaved into their nonpathogenic forms. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
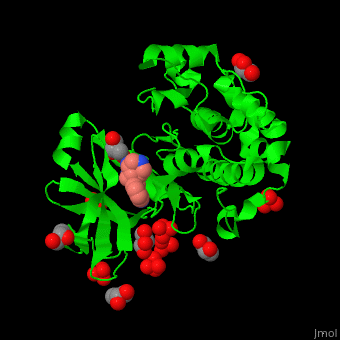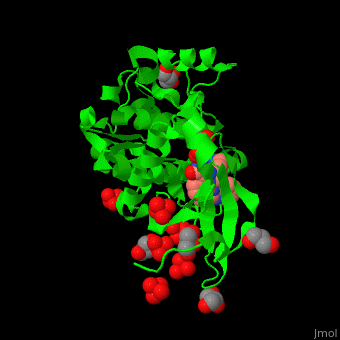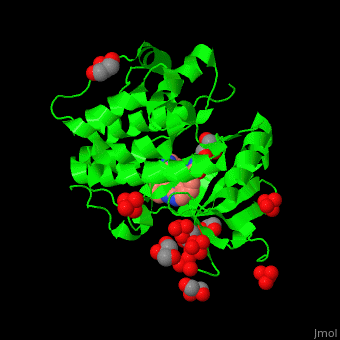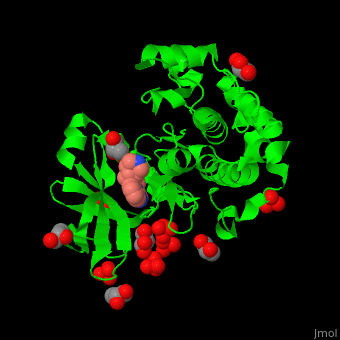
| - | + | PDK1 structure contains 2 domains: kinase (residues 71-359 in human) and PH (residues 459-550) in human). The PH (Plecksin Homology) domain interacts with phospholipids. The kinase domain (kd) contains 3 binding sites. These are for substrate-binding, ATP-binding and allosteric activator docking (PIF - [Pdk1-Interacting Fragment] -pocket). <scene name='54/542348/Cv/7'>Pyrazoloquinazoline inhibitor binding site</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. | |
| - | == 3D Structures of | + | == 3D Structures of PDK1== |
[[Pdk1 3D structures]] | [[Pdk1 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 08:29, 15 June 2023
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Mora A, Komander D, van Aalten DM, Alessi DR. PDK1, the master regulator of AGC kinase signal transduction. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Apr;15(2):161-70. PMID:15209375