User:Daniel Key Takemoto/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
The NTD was shown to adopt independent folding, and its tertiary structure was found to be compatible with two tandem <scene name='96/969643/Agenet_domains/3'>Agenet domains</scene>. Both of the Agenet domains resemble those of Argonaute, a protein involved in RNA interference, as they resemble structuraly Tudor domains, it is possible to assume functional similarities between them. | The NTD was shown to adopt independent folding, and its tertiary structure was found to be compatible with two tandem <scene name='96/969643/Agenet_domains/3'>Agenet domains</scene>. Both of the Agenet domains resemble those of Argonaute, a protein involved in RNA interference, as they resemble structuraly Tudor domains, it is possible to assume functional similarities between them. | ||
| - | The <scene name='96/969643/Beta_sheets_agenet/2'>Beta Sheets of the Agenet domains</scene>, characterize the Agenet domain and its structure, and there is a 13- | + | The <scene name='96/969643/Beta_sheets_agenet/2'>Beta Sheets of the Agenet domains</scene>, characterize the Agenet domain and its structure, and there is a <scene name='96/969643/13_residue/1'>13-residue loop</scene>, highlighted in magenta, between the beta sheets of the Agenet 1 and Agenet 2 connecting them. |
It's been shown that, when the FMRP is in the nucleus, the Agenet domain allow the FMRP to interact with the chromatin and regulate DNA damage response. | It's been shown that, when the FMRP is in the nucleus, the Agenet domain allow the FMRP to interact with the chromatin and regulate DNA damage response. | ||
| - | And has also been demonstrated that the Agenet domains bind to methylated lysine, in support to the histone binding function of the FMRP, due to its aromatic cage in the structure; specifically, the Agenet motif 2 binds to trimethylated lysine. The | + | And has also been demonstrated that the Agenet domains bind to methylated lysine, in support to the histone binding function of the FMRP, due to its aromatic cage in the structure; specifically, the Agenet motif 2 binds to trimethylated lysine. The <scene name='96/969643/Aminoacid_residues/1'>Aromatic aminoacid residues</scene> highlited in red are part of the Agenet 1 and the ones highlited in blue are part of the Agenet 2 domain related to the recognition of methylated lysine as they all have aromatic cages with the potential for this binding. |
<ref>MYRICK, L. K. et al. Human FMRP contains an integral tandem Agenet (Tudor) and KH motif in the amino terminal domain. Human Molecular Genetics, v. 24, n. 6, p. 1733–1740, 20 nov. 2014.[https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu586]</ref>. | <ref>MYRICK, L. K. et al. Human FMRP contains an integral tandem Agenet (Tudor) and KH motif in the amino terminal domain. Human Molecular Genetics, v. 24, n. 6, p. 1733–1740, 20 nov. 2014.[https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu586]</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 18:50, 21 June 2023
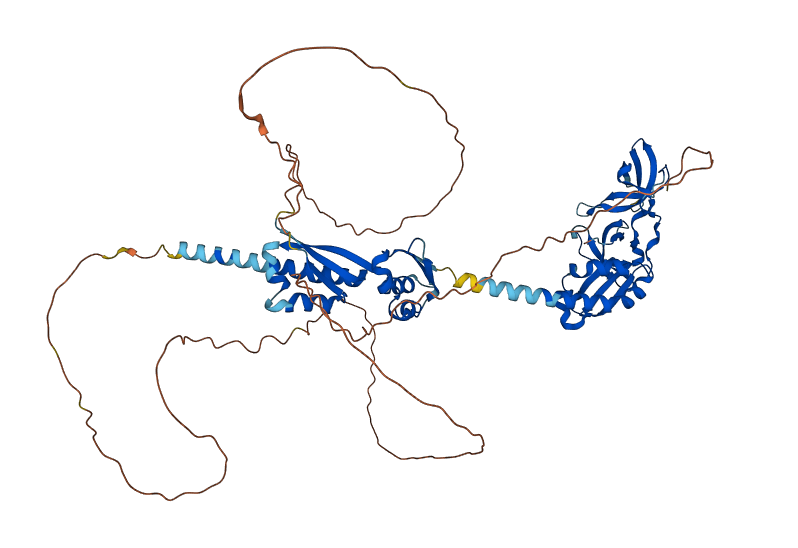
Structure of FMRP
Predicted FMRP
Fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein (FMRP) is encoded by the fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1 (FMR1) gene, located in the X chromosome, and is associated with the fragile X syndrome (FXS), Fragile X Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) and Premature Ovarian Failure (POF1). FMRP functions as a synaptic regulator by binding to mRNAs and inhibiting its translation, therefore regulating the synthesis of proteins in the synapse. It is also an RNA binding protein, which is responsible for the transportation of mRNAs to the cytoplasm. The FMRP can also bind to its own FMR1 transcripts, possibly as a self-regulatory mechanism.
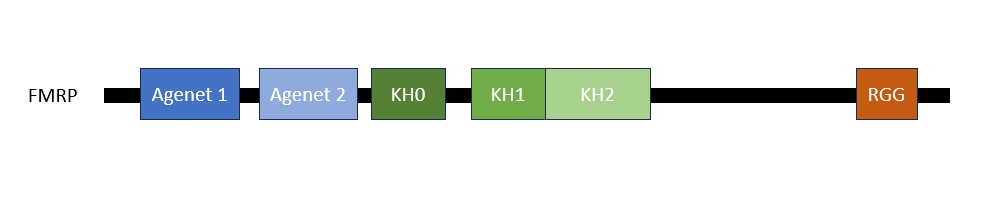
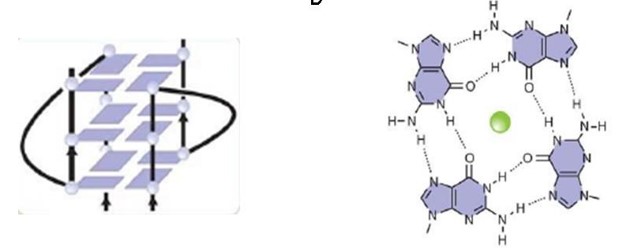
The FMRP is highly expressed in neurons and genitalia, and it's located mostly in the cytoplasm and lower levels in the nucleus. It contains domains related to its RNA binding function, either in the N-terminal or C-terminal domain; the Agenet and the KH0-motif are located in the N-terminal domain, and they, respectively, exerce functions in binding to methylated lysin and RNA binding; the KH1 and KH2 motifs are located in the central region of the protein; and the RGG box, in the C-terminal domain, acts as a binding to RNA, especifically to G-quadruplexes, a secondary RNA structure. The KH1, KH2 and RGG box domains allow the FMRP to bind and translate a number of mRNAs related to the synaptic plasticity. [1]
The protein has 20 non-redundant isoforms and the most common is isoform 7, and the longest isoform contains 632 aminoacids. [2].
The predicted image was generated from Ensembl, by the AlphaFold program.
Overall structure
| |||||||||||