User:Nane Milene Sposito Almeida Pereira/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
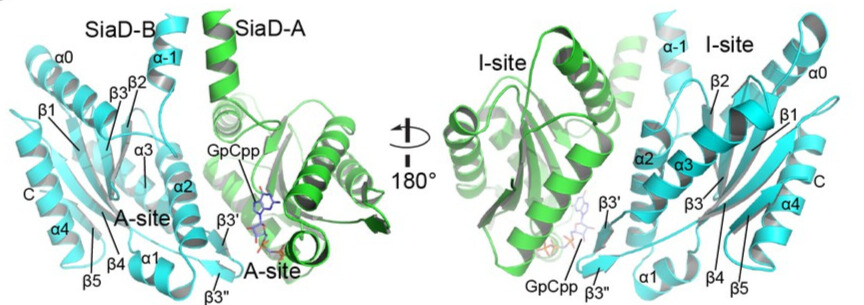
| - | Cyclic dimeric (3'–5') guanosine monophosphate | + | Cyclic dimeric (3'–5') guanosine monophosphate ([[C-di-GMP]]) is a bacterial second messenger present in several biological aspects of several environmental and pathogenic bacteria. This second messenger is capable of regulating the cell cycle, biofilm formation, dispersal, motility, and virulence. The synthesis and degradation of c-diGMP are controlled by the activities of two classes of proteins: '''diguanylate cyclases''' (DGCs), with an active GGDEF domain, and specific phosphodiesterases (PDEs), with an EAL or HD-GYP domain. SiaD has DGC activity modulated by its binding partner through direct interaction with SiaC, forming the '''SiaC-SiaD complex''' <ref>DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67289</ref>. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 20:09, 21 June 2023
SiaC-SiaD Complex
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Chen G, Zhou J, Zuo Y, Huo W, Peng J, Li M, Zhang Y, Wang T, Zhang L, Zhang L, Liang H. Structural basis for diguanylate cyclase activation by its binding partner in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Elife. 2021 Sep 9;10:e67289. PMID:34498587 doi:10.7554/eLife.67289