User:Daniel Key Takemoto/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
==RGG motif== | ==RGG motif== | ||
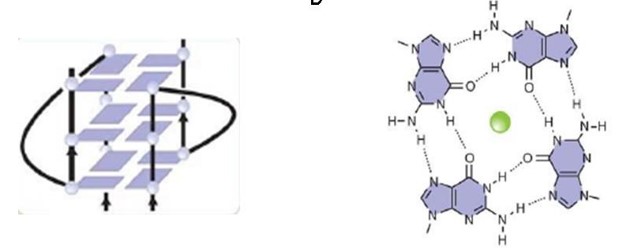
| - | An important motif of the FMRP is the RGG box, which the protein uses to bind to guanine G-quadruplexes, a structure that consists of nucleic acid folding in which four guanines arrange in a planar conformation stabilized by Hoogsteen-trype hydrogen bonds, named tetrad. FMRP RGG motifs seem to prefer binding to specific structures, not linear motifs. | + | An important motif of the FMRP is the <scene name='96/969643/Rgg_box/1'>RGG box</scene>, which the protein uses to bind to guanine G-quadruplexes, a structure that consists of nucleic acid folding in which four guanines arrange in a planar conformation stabilized by Hoogsteen-trype hydrogen bonds, named tetrad. FMRP RGG motifs seem to prefer binding to specific structures, not linear motifs. |
| - | Different domains and motifs mediate the RNA binding mechanism, and the exon 15-encoded RGG (arginine - glycine - glycine) motif is one of them. The FMRP RGG motif is located in the C-terminal region of the protein and is well conserved in vertebrates. To easily represent the RGG motif binding to RNA, this motif will be highlighted in the scene RGG MOTIF Crystal structure of the complex between the human FMRP RGG motif and G-quadruplex RNA The RGG motif binds to G-quadruplexes when it adopts a sharp turn and specifically binds to guanines from two consecutive G-C base pairs in the duplex-quadruplex junction. Several tetrads can stack in a single G-quadruplex structure and be stabilized further by potassium cations, in the case of FMRP targets, whereas they are destabilized by lithium cations. | + | Different domains and motifs mediate the RNA binding mechanism, and the exon 15-encoded <scene name='96/969643/Rgg_motif/2'>RGG</scene> (arginine - glycine - glycine) motif is one of them. The FMRP RGG motif is located in the C-terminal region of the protein and is well conserved in vertebrates. To easily represent the RGG motif binding to RNA, this motif will be highlighted in the scene RGG MOTIF Crystal structure of the complex between the human FMRP RGG motif and G-quadruplex RNA The RGG motif binds to <scene name='96/969643/Sc1_gquadruplexes/1'>G-quadruplexes</scene> when it adopts a sharp turn and specifically binds to guanines from two consecutive G-C base pairs in the duplex-quadruplex junction. Several tetrads can stack in a single G-quadruplex structure and be stabilized further by potassium cations, in the case of FMRP targets, whereas they are destabilized by lithium cations. |
The regulation of particular mRNAs and the binding of FMRP with ribosomes and proteins depend on this interaction between the RGG motif and G-quadruplex RNA. | The regulation of particular mRNAs and the binding of FMRP with ribosomes and proteins depend on this interaction between the RGG motif and G-quadruplex RNA. | ||
Revision as of 16:50, 22 June 2023
Structure of FMRP
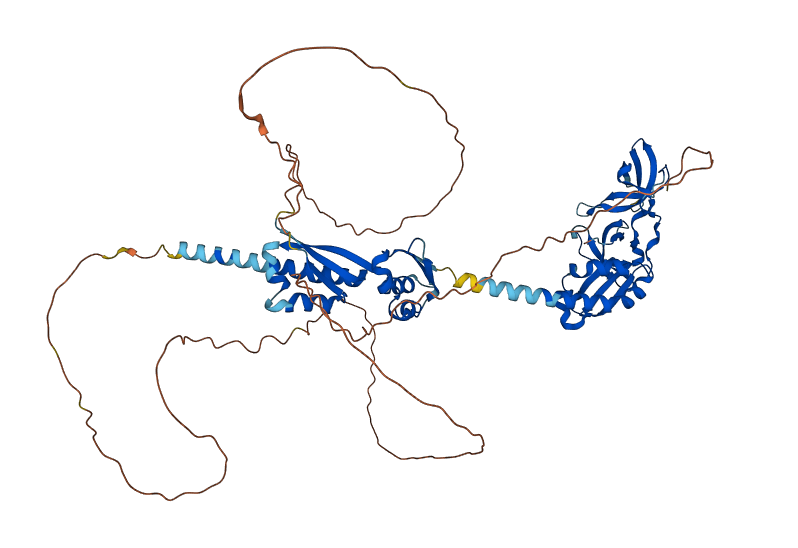
Predicted FMRP
Fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein (FMRP) is encoded by the fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1 (FMR1) gene, located in the X chromosome, and is associated with the fragile X syndrome (FXS), Fragile X Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) and Premature Ovarian Failure (POF1). FMRP functions as a synaptic regulator by binding to mRNAs and inhibiting its translation, therefore regulating the synthesis of proteins in the synapse. It is also an RNA binding protein, which is responsible for the transportation of mRNAs to the cytoplasm. The FMRP can also bind to its own FMR1 transcripts, possibly as a self-regulatory mechanism.
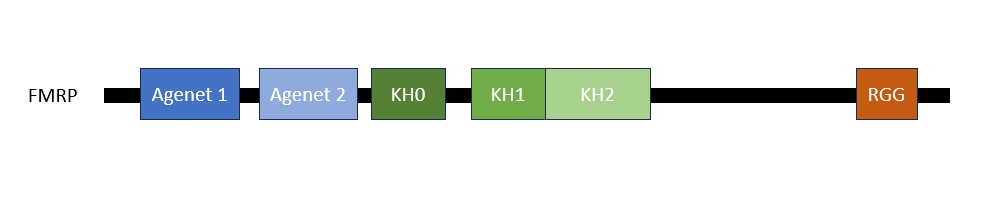
The FMRP is highly expressed in neurons and genitalia, and it's located mostly in the cytoplasm and lower levels in the nucleus. It contains domains related to its RNA binding function, either in the N-terminal or C-terminal domain; the Agenet and the KH0-motif are located in the N-terminal domain, and they, respectively, exerce functions in binding to methylated lysin and RNA binding; the KH1 and KH2 motifs are located in the central region of the protein; and the RGG box, in the C-terminal domain, acts as a binding to RNA, especifically to G-quadruplexes, a secondary RNA structure. The KH1, KH2 and RGG box domains allow the FMRP to bind and translate a number of mRNAs related to the synaptic plasticity. [1]
The protein has 20 non-redundant isoforms and the most common is isoform 7, and the longest isoform contains 632 aminoacids. [2].
The predicted image was generated from Ensembl, by the AlphaFold program.
Overall structure
| |||||||||||