Journal:MicroPubl Biol:000867
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Most plants require light for the biosynthesis of the green pigment chlorophyll, which is central to the process of photosynthesis. One of the later steps of the chlorophyll biosynthetic pathway is facilitated by protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase (POR), a light-dependent enzyme<ref name="Lee">PMID:24151298</ref>. To complete chlorophyll biosynthesis, the POR enzyme must be post-translationally imported into the chloroplast. The chaperone-like protein of POR1 (CPP1) in Arabidopsis has been shown to regulate POR transport and function during this process although its specific role in the process is still unclear<ref name="Lee">PMID:24151298</ref>. Due to the structural similarity between the J-like domain in CPP1 and the J domain in the DnaJ/HSP70 protein family, it has been suggested that CPP1 has a function similar to the “holdase” chaperone function of the J domain that helps organize interactions with Hsp70 chaperone partners<ref name="Kelley">PMID:9644977</ref>. A functionally conserved His-Pro-Asp (HPD) motif within J-domains facilitates this interaction and, although very similar in structure to the J domain, the HPD motif is absent in J-like domain proteins such as CPP1, indicating these domains may perform a similar molecular function but may have diverged interaction partners. | Most plants require light for the biosynthesis of the green pigment chlorophyll, which is central to the process of photosynthesis. One of the later steps of the chlorophyll biosynthetic pathway is facilitated by protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase (POR), a light-dependent enzyme<ref name="Lee">PMID:24151298</ref>. To complete chlorophyll biosynthesis, the POR enzyme must be post-translationally imported into the chloroplast. The chaperone-like protein of POR1 (CPP1) in Arabidopsis has been shown to regulate POR transport and function during this process although its specific role in the process is still unclear<ref name="Lee">PMID:24151298</ref>. Due to the structural similarity between the J-like domain in CPP1 and the J domain in the DnaJ/HSP70 protein family, it has been suggested that CPP1 has a function similar to the “holdase” chaperone function of the J domain that helps organize interactions with Hsp70 chaperone partners<ref name="Kelley">PMID:9644977</ref>. A functionally conserved His-Pro-Asp (HPD) motif within J-domains facilitates this interaction and, although very similar in structure to the J domain, the HPD motif is absent in J-like domain proteins such as CPP1, indicating these domains may perform a similar molecular function but may have diverged interaction partners. | ||
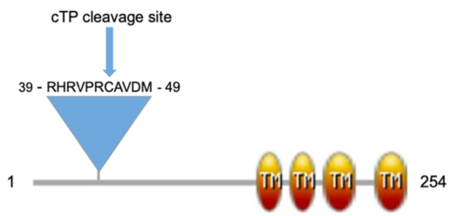
| - | Sequence analysis of GhCPP1-A0A1U8HKT6 indicated it has a N-terminal chloroplast transit peptide with a cleavage site at amino acid 45 along with four predicted TM regions in the C-terminal half of the protein. A domain architecture was created to visualize these sequence features. Interestingly, ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' and ''Nicotiana benthamiana'' CPP1 proteins are indicated to contain three, not four, TM regions <ref name="Lee">PMID:24151298</ref>. However, a homolog of Arabidopsis CPP1, At2g20920, has been identified to also contain four TM regions<ref name="Kawai">PMID:24097264</ref> suggesting a potential structural or functional difference between these family members. | + | Sequence analysis of GhCPP1-A0A1U8HKT6 indicated it has a N-terminal chloroplast transit peptide with a cleavage site at amino acid 45 along with four predicted TM regions in the C-terminal half of the protein. A domain architecture was created to visualize these sequence features (see static image below): |
| + | [[Image:Dom arch.png|left|thumb|450px|The coagulation cascade.]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Interestingly, ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' and ''Nicotiana benthamiana'' CPP1 proteins are indicated to contain three, not four, TM regions <ref name="Lee">PMID:24151298</ref>. However, a homolog of Arabidopsis CPP1, At2g20920, has been identified to also contain four TM regions<ref name="Kawai">PMID:24097264</ref> suggesting a potential structural or functional difference between these family members. | ||
The <scene name='97/977777/Alphafold_model/1'>AlphaFold model structure of GhCPP1-A0A1U8HKT6</scene> (colored in rainbow format with the N-terminus in blue and C-terminus in red) depicts <scene name='97/977777/Alphafold_model/2'>two high-confidence modeled domain regions</scene> between amino acids 56-119 and 150-254 and a low-confidence modeled region between them from amino acids 119-150 (shown transparent). The predicted TM regions are seen as a 4-helix bundle that exhibits expected <scene name='97/977777/Hydrophobic_surface/2'>high hydrophobicity</scene> ({{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}}, {{Template:ColorKey_Polar}}). <scene name='97/977777/Overlay2dn9/1'>The aqueous N-terminal domain is a predicted J-like domain (in orange-red) that when overlaid with the J-domain of the human DnaJ family member Tid1</scene> (PDB ID: [[2dn9]]; in deep sky blue) displays a similar anti-parallel hairpin between the horizontally-displayed alpha helices II and III, although the GhCPP1-A0A1U8HKT6 J-like domain lacks the fourth helix of human Tid1 and has a shorter loop. | The <scene name='97/977777/Alphafold_model/1'>AlphaFold model structure of GhCPP1-A0A1U8HKT6</scene> (colored in rainbow format with the N-terminus in blue and C-terminus in red) depicts <scene name='97/977777/Alphafold_model/2'>two high-confidence modeled domain regions</scene> between amino acids 56-119 and 150-254 and a low-confidence modeled region between them from amino acids 119-150 (shown transparent). The predicted TM regions are seen as a 4-helix bundle that exhibits expected <scene name='97/977777/Hydrophobic_surface/2'>high hydrophobicity</scene> ({{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}}, {{Template:ColorKey_Polar}}). <scene name='97/977777/Overlay2dn9/1'>The aqueous N-terminal domain is a predicted J-like domain (in orange-red) that when overlaid with the J-domain of the human DnaJ family member Tid1</scene> (PDB ID: [[2dn9]]; in deep sky blue) displays a similar anti-parallel hairpin between the horizontally-displayed alpha helices II and III, although the GhCPP1-A0A1U8HKT6 J-like domain lacks the fourth helix of human Tid1 and has a shorter loop. | ||
Revision as of 15:17, 24 July 2023
| |||||||||||
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.