|
|
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
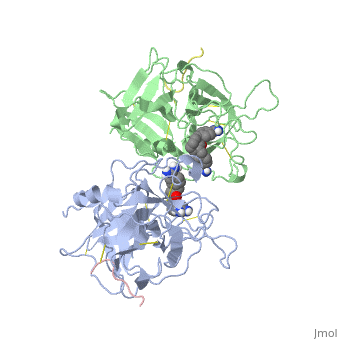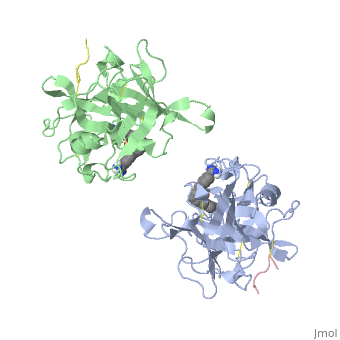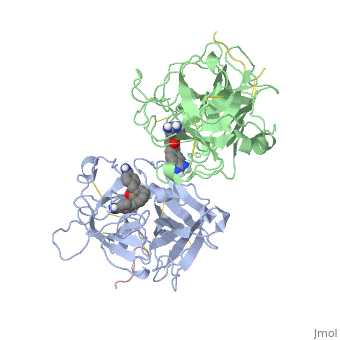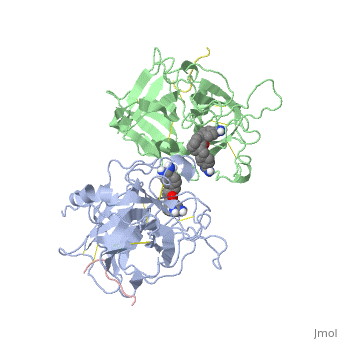
| | <StructureSection load='1a5h' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1a5h]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.90Å' scene=''> | | <StructureSection load='1a5h' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1a5h]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.90Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1a5h]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1A5H OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1A5H FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1a5h]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1A5H OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1A5H FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=BBA:2,7-BIS-(4-AMIDINOBENZYLIDENE)-CYCLOHEPTAN-1-ONE'>BBA</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.9Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T-plasminogen_activator T-plasminogen activator], with EC number [https://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.4.21.68 3.4.21.68] </span></td></tr> | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=BBA:2,7-BIS-(4-AMIDINOBENZYLIDENE)-CYCLOHEPTAN-1-ONE'>BBA</scene></td></tr> |
| | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1a5h FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1a5h OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1a5h PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1a5h RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1a5h PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1a5h ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1a5h FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1a5h OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1a5h PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1a5h RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1a5h PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1a5h ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Disease == | | == Disease == |
| - | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/TPA_HUMAN TPA_HUMAN]] Note=Increased activity of TPA results in increased fibrinolysis of fibrin blood clots that is associated with excessive bleeding. Defective release of TPA results in hypofibrinolysis that can lead to thrombosis or embolism.
| + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/TPA_HUMAN TPA_HUMAN] Note=Increased activity of TPA results in increased fibrinolysis of fibrin blood clots that is associated with excessive bleeding. Defective release of TPA results in hypofibrinolysis that can lead to thrombosis or embolism. |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/TPA_HUMAN TPA_HUMAN]] Converts the abundant, but inactive, zymogen plasminogen to plasmin by hydrolyzing a single Arg-Val bond in plasminogen. By controlling plasmin-mediated proteolysis, it plays an important role in tissue remodeling and degradation, in cell migration and many other physiopathological events. Plays a direct role in facilitating neuronal migration.
| + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/TPA_HUMAN TPA_HUMAN] Converts the abundant, but inactive, zymogen plasminogen to plasmin by hydrolyzing a single Arg-Val bond in plasminogen. By controlling plasmin-mediated proteolysis, it plays an important role in tissue remodeling and degradation, in cell migration and many other physiopathological events. Plays a direct role in facilitating neuronal migration. |
| | == Evolutionary Conservation == | | == Evolutionary Conservation == |
| | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] |
| Line 38: |
Line 38: |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Human]] | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| | [[Category: Large Structures]] | | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: T-plasminogen activator]]
| + | [[Category: Bode W]] |
| - | [[Category: Bode, W]] | + | [[Category: Renatus M]] |
| - | [[Category: Renatus, M]] | + | [[Category: Stubbs MT]] |
| - | [[Category: Stubbs, M T]] | + | |
| - | [[Category: Fibrinolytic enzyme]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Hydrolase]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Trypsin like serine protease]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Disease
TPA_HUMAN Note=Increased activity of TPA results in increased fibrinolysis of fibrin blood clots that is associated with excessive bleeding. Defective release of TPA results in hypofibrinolysis that can lead to thrombosis or embolism.
Function
TPA_HUMAN Converts the abundant, but inactive, zymogen plasminogen to plasmin by hydrolyzing a single Arg-Val bond in plasminogen. By controlling plasmin-mediated proteolysis, it plays an important role in tissue remodeling and degradation, in cell migration and many other physiopathological events. Plays a direct role in facilitating neuronal migration.
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
The recent structure determination of the catalytic domain of tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) suggested residue Arg174 could play a role in P3/P4 substrate specificity. Six synthetic chromogenic tPA substrates of the type R-Xaa-Gly-Arg-p-nitroanilide, in which R is an N-terminal protection group, were synthesized to test this property. Although changing the residue Xaa (in its L or D form) at position P3 from the hydrophobic Phe to an acidic residue, Asp or Glu, gave no improvement in catalytic efficiency, comparative analysis of the substrates indicated a preference for an acidic substituent occupying the S3 site when the S4 site contains a hydrophobic or basic moiety. The 2.9 A structure determination of the catalytic domain of human tPA in complex with the bis-benzamidine inhibitor 2, 7-bis-(4-amidinobenzylidene)-cycloheptan-1-one reveals a three-site interaction, salt bridge formation of the proximal amidino group of the inhibitor with Asp189 in the primary specificity pocket, extensive hydrophobic surface burial, and a weak electrostatic interaction between the distal amidino group of the inhibitor and two carbonyl oxygens of the protein. The latter position was previously occupied by the guanidino group of Arg174, which swings out to form the western edge of the S3 pocket. These data suggest that the side chain of Arg174 is flexible, and does not play a major role in the S4 specificity of tPA. On the other hand, this residue would modulate S3 specificity, and may be exploited to fine tune the specificity and selectivity of tPA substrates and inhibitors.
Structural mapping of the active site specificity determinants of human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Implications for the design of low molecular weight substrates and inhibitors.,Renatus M, Bode W, Huber R, Sturzebecher J, Prasa D, Fischer S, Kohnert U, Stubbs MT J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 29;272(35):21713-9. PMID:9268299[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Renatus M, Bode W, Huber R, Sturzebecher J, Prasa D, Fischer S, Kohnert U, Stubbs MT. Structural mapping of the active site specificity determinants of human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Implications for the design of low molecular weight substrates and inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 29;272(35):21713-9. PMID:9268299
|