|
|
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
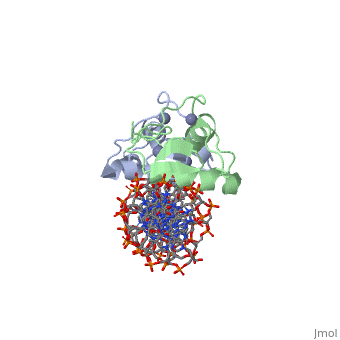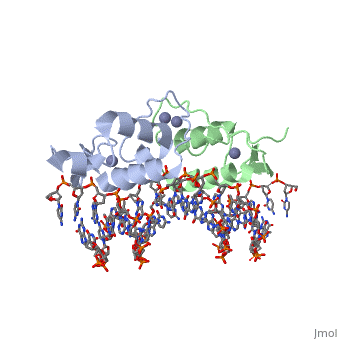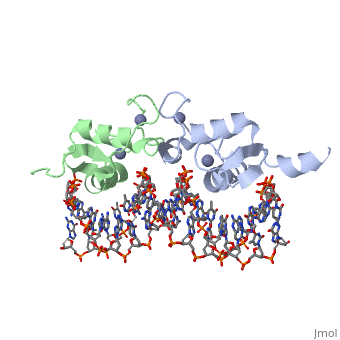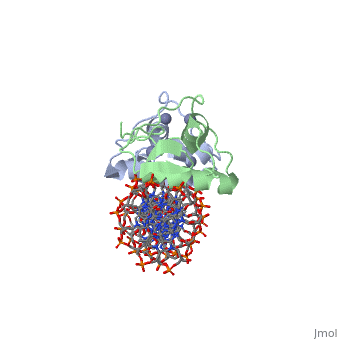
| | <StructureSection load='3g6r' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3g6r]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> | | <StructureSection load='3g6r' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3g6r]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3g6r]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Buffalo_rat Buffalo rat]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3G6R OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3G6R FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3g6r]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rattus_norvegicus Rattus norvegicus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3G6R OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3G6R FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.3Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><div style='overflow: auto; max-height: 3em;'>[[3fyl|3fyl]], [[3g6q|3g6q]], [[3g6p|3g6p]], [[3g6t|3g6t]], [[3g6u|3g6u]], [[3g8x|3g8x]], [[3g97|3g97]]</div></td></tr> | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">Grl, Nr3c1 ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=10116 Buffalo rat])</td></tr>
| + | |
| | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3g6r FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3g6r OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3g6r PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3g6r RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3g6r PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3g6r ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3g6r FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3g6r OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3g6r PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3g6r RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3g6r PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3g6r ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/GCR_RAT GCR_RAT]] Receptor for glucocorticoids (GC). Has a dual mode of action: as a transcription factor that binds to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE), both for nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and as a modulator of other transcription factors. Affects inflammatory responses, cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Could act as a coactivator for STAT5-dependent transcription upon growth hormone (GH) stimulation and could reveal an essential role of hepatic GR in the control of body growth. Involved in chromatin remodeling. Plays a significant role in transactivation (By similarity).<ref>PMID:12917342</ref>
| + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/GCR_RAT GCR_RAT] Receptor for glucocorticoids (GC). Has a dual mode of action: as a transcription factor that binds to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE), both for nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and as a modulator of other transcription factors. Affects inflammatory responses, cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Could act as a coactivator for STAT5-dependent transcription upon growth hormone (GH) stimulation and could reveal an essential role of hepatic GR in the control of body growth. Involved in chromatin remodeling. Plays a significant role in transactivation (By similarity).<ref>PMID:12917342</ref> |
| | == Evolutionary Conservation == | | == Evolutionary Conservation == |
| | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] |
| Line 38: |
Line 37: |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Buffalo rat]] | |
| | [[Category: Large Structures]] | | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Meijsing, S H]] | + | [[Category: Rattus norvegicus]] |
| - | [[Category: Pufall, M A]] | + | [[Category: Meijsing SH]] |
| - | [[Category: Yamamoto, K R]] | + | [[Category: Pufall MA]] |
| - | [[Category: Allostery]] | + | [[Category: Yamamoto KR]] |
| - | [[Category: Alternative initiation]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Chromatin regulator]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Cytoplasm]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Dna-binding]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Glucocorticoid]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Hormone]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Lever arm]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Lipid-binding]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Metal-binding]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Nucleus]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Phosphoprotein]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Polymorphism]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Receptor]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Steroid-binding]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Transcription]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Transcription regulation]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Transcription-dna complex]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Ubl conjugation]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Zinc]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Zinc-finger]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Function
GCR_RAT Receptor for glucocorticoids (GC). Has a dual mode of action: as a transcription factor that binds to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE), both for nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and as a modulator of other transcription factors. Affects inflammatory responses, cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Could act as a coactivator for STAT5-dependent transcription upon growth hormone (GH) stimulation and could reveal an essential role of hepatic GR in the control of body growth. Involved in chromatin remodeling. Plays a significant role in transactivation (By similarity).[1]
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
Genes are not simply turned on or off, but instead their expression is fine-tuned to meet the needs of a cell. How genes are modulated so precisely is not well understood. The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) regulates target genes by associating with specific DNA binding sites, the sequences of which differ between genes. Traditionally, these binding sites have been viewed only as docking sites. Using structural, biochemical, and cell-based assays, we show that GR binding sequences, differing by as little as a single base pair, differentially affect GR conformation and regulatory activity. We therefore propose that DNA is a sequence-specific allosteric ligand of GR that tailors the activity of the receptor toward specific target genes.
DNA binding site sequence directs glucocorticoid receptor structure and activity.,Meijsing SH, Pufall MA, So AY, Bates DL, Chen L, Yamamoto KR Science. 2009 Apr 17;324(5925):407-10. PMID:19372434[2]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Hsiao PW, Fryer CJ, Trotter KW, Wang W, Archer TK. BAF60a mediates critical interactions between nuclear receptors and the BRG1 chromatin-remodeling complex for transactivation. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Sep;23(17):6210-20. PMID:12917342
- ↑ Meijsing SH, Pufall MA, So AY, Bates DL, Chen L, Yamamoto KR. DNA binding site sequence directs glucocorticoid receptor structure and activity. Science. 2009 Apr 17;324(5925):407-10. PMID:19372434 doi:324/5925/407
|