We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
2v6b
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
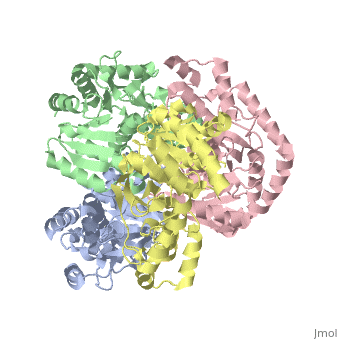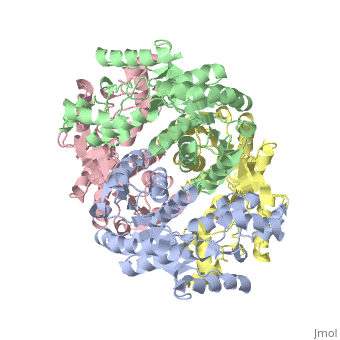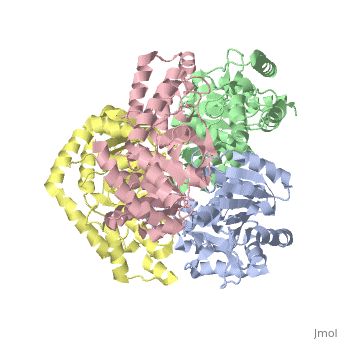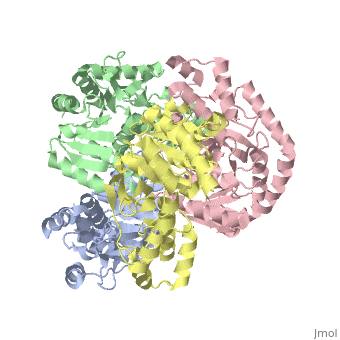
<StructureSection load='2v6b' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2v6b]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.50Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2v6b' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2v6b]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.50Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2v6b]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2v6b]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deinococcus_radiodurans Deinococcus radiodurans]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2V6B OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2V6B FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id=' | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.5Å</td></tr> |
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2v6b FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2v6b OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2v6b PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2v6b RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2v6b PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2v6b ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2v6b FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2v6b OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2v6b PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2v6b RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2v6b PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2v6b ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/LDH_DEIRA LDH_DEIRA] | ||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 35: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Deinococcus radiodurans]] |
| - | + | ||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Coquelle | + | [[Category: Coquelle N]] |
| - | [[Category: Fioravanti | + | [[Category: Fioravanti E]] |
| - | [[Category: Vellieux | + | [[Category: Vellieux F]] |
| - | [[Category: Weik | + | [[Category: Weik M]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
Crystal structure of lactate dehydrogenase from Deinococcus Radiodurans (apo form)
| |||||||||||