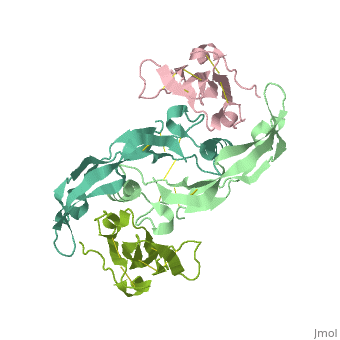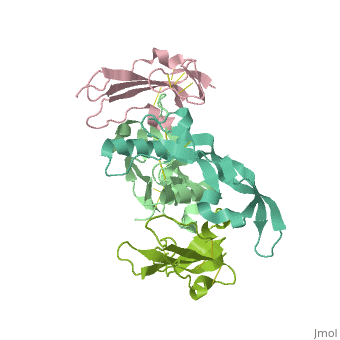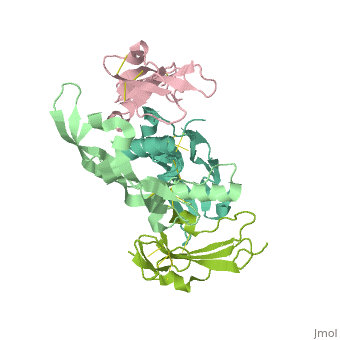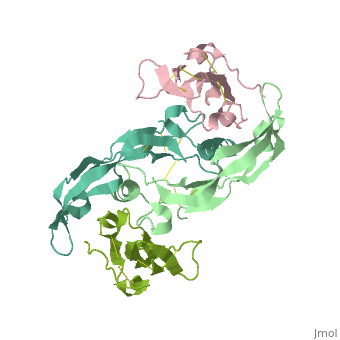This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
3evs
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<StructureSection load='3evs' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3evs]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.10Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3evs' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3evs]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.10Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3evs]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3evs]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mus_musculus Mus musculus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3EVS OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3EVS FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id=' | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.1Å</td></tr> |
| - | + | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3evs FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3evs OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3evs PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3evs RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3evs PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3evs ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3evs FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3evs OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3evs PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3evs RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3evs PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3evs ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/GDF5_HUMAN GDF5_HUMAN] Defects in GDF5 are the cause of acromesomelic chondrodysplasia Grebe type (AMDG) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/200700 200700]. Acromesomelic chondrodysplasias are rare hereditary skeletal disorders characterized by short stature, very short limbs, and hand/foot malformations. The severity of limb abnormalities increases from proximal to distal with profoundly affected hands and feet showing brachydactyly and/or rudimentary fingers (knob-like fingers). AMDG is an autosomal recessive form characterized by normal axial skeletons and missing or fused skeletal elements within the hands and feet.<ref>PMID:9288098</ref> Defects in GDF5 are the cause of acromesomelic chondrodysplasia Hunter-Thompson type (AMDH) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/201250 201250]. AMDH is an autosomal recessive form of dwarfism. Patients have limb abnormalities, with the middle and distal segments being most affected and the lower limbs more affected than the upper. AMDH is characterized by normal axial skeletons and missing or fused skeletal elements within the hands and feet. Defects in GDF5 are the cause of brachydactyly type C (BDC) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/113100 113100]. BDC is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by an abnormal shortness of the fingers and toes. Note=Some BDC patients with GDF5 mutations also manifest clinical features of ASPED angel-shaped phalango-epiphyseal dysplasia (ASPED), an autosomal dominant skeletal abnormality characterized by a typical angel-shaped phalanx, brachydactyly, specific radiological findings, abnormal dentition, hip dysplasia, and delayed bone age. This suggests that BDC and ASPED are part of the same clinical spectrum (PubMed:22828468).<ref>PMID:22828468</ref> <ref>PMID:14735582</ref> Defects in GDF5 are the cause of Du Pan syndrome (DPS) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/228900 228900]; also known as fibular hypoplasia and complex brachydactyly. Du Pan syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive condition characterized by absence of the fibulae and severe acromesomelic limb shortening with small, non-functional toes. Although milder, the phenotype resembles the autosomal recessive Hunter-Thompson and Grebe types of acromesomelic chondrodysplasia.<ref>PMID:12121354</ref> <ref>PMID:16222676</ref> <ref>PMID:18629880</ref> Defects in GDF5 are a cause of symphalangism proximal syndrome (SYM1) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/185800 185800]. SYM1 is characterized by the hereditary absence of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints (Cushing symphalangism). Severity of PIP joint involvement diminishes towards the radial side. Distal interphalangeal joints are less frequently involved and metacarpophalangeal joints are rarely affected whereas carpal bone malformation and fusion are common. In the lower extremities, tarsal bone coalition is common. Conducive hearing loss is seen and is due to fusion of the stapes to the petrous part of the temporal bone.<ref>PMID:16127465</ref> <ref>PMID:16892395</ref> <ref>PMID:18283415</ref> Defects in GDF5 are the cause of multiple synostoses syndrome type 2 (SYNS2) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/610017 610017]. Multiple synostoses syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by progressive joint fusions of the fingers, wrists, ankles and cervical spine, characteristic facies and progressive conductive deafness.[:]<ref>PMID:16532400</ref> Defects in GDF5 are a cause of brachydactyly type A2 (BDA2) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/112600 112600]. Brachydactylies (BDs) are a group of inherited malformations characterized by shortening of the digits due to abnormal development of the phalanges and/or the metacarpals. They have been classified on an anatomic and genetic basis into five groups, A to E, including three subgroups (A1 to A3) that usually manifest as autosomal dominant traits.<ref>PMID:16127465</ref> <ref>PMID:18203755</ref> Genetic variations in GDF5 are associated with susceptibility to osteoarthritis type 5 (OS5) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/612400 612400]. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease of the joints characterized by degradation of the hyaline articular cartilage and remodeling of the subchondral bone with sclerosis. Clinical symptoms include pain and joint stiffness often leading to significant disability and joint replacement. Defects in GDF5 may be a cause of brachydactyly type A1 (BDA1) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/112500 112500]. Brachydactylies (BDs) are a group of inherited malformations characterized by shortening of the digits due to abnormal development of the phalanges and/or the metacarpals. They have been classified on an anatomic and genetic basis into five groups, A to E, including three subgroups (A1 to A3) that usually manifest as autosomal dominant traits.<ref>PMID:20683927</ref> | |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/GDF5_HUMAN GDF5_HUMAN] Could be involved in bone and cartilage formation. Chondrogenic signaling is mediated by the high-affinity receptor BMPR1B.<ref>PMID:15530414</ref> <ref>PMID:19229295</ref> | |
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 39: | Line 38: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
[[Category: Large Structures]] | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Mus musculus]] |
| - | [[Category: Kotzsch | + | [[Category: Kotzsch A]] |
| - | [[Category: Mueller | + | [[Category: Mueller TD]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
Crystal structure of the GDF-5:BMP receptor IB complex.
| |||||||||||