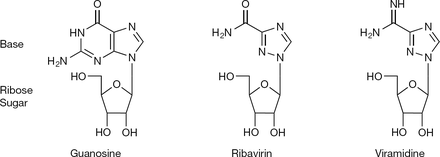
Ribavirin1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Nucleoside transporters facilitate the transport of nucleosides across cell membranes to be used in protein synthesis. Concentrated NTs (CNTs) use the energy of ion gradients for active transportation , while equilibrative NTs (ENTs) transport nucleosides passively down their concentration gradient. Ribavirin is a substrate of ENT1, ENT2, and CNT2. CNT2 binds to the ribose of the ribavirin via hydrogen bonding involving glutamic acid at position 332, asparagine at position 368, and serine at position 371<ref>doi:10.7554/eLife.03604</ref>. | Nucleoside transporters facilitate the transport of nucleosides across cell membranes to be used in protein synthesis. Concentrated NTs (CNTs) use the energy of ion gradients for active transportation , while equilibrative NTs (ENTs) transport nucleosides passively down their concentration gradient. Ribavirin is a substrate of ENT1, ENT2, and CNT2. CNT2 binds to the ribose of the ribavirin via hydrogen bonding involving glutamic acid at position 332, asparagine at position 368, and serine at position 371<ref>doi:10.7554/eLife.03604</ref>. | ||
| - | <scene name='55/559112/Ribavirin_interacting_4pb1/1'> | + | <scene name='55/559112/Ribavirin_interacting_4pb1/1'>Ribavirin with 4PB1</scene> ([[4pb1]]) |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
===Hepatitis C=== | ===Hepatitis C=== | ||
Current revision
1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide [1]
| |||||||||||
References
- Gish, R. G. Treating HCV with ribavirin analogue and ribavirin-like molecules. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2005, November 17;1-6. doi:10.1093/jac/dki405
- Thomas, E., Ghany, M., Liang, J., The application and mechanism of action of ribavirin in therapy of hepatitis C. Antiviral Chemistry & Chemotherapy 23:1-12 (2012)doi: 10.3851/IMP2125
- Chung, R.T., Gale, M.J., Polyak, S.J., Lemon, S.M., Liang, T.J., & Hoofnagle, J.H. Mechanisms of action of interferon and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C: Summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2008;47 (1), 306-320. doi: 10.1002/hep.22070
- Paeshuyse, J, Dallmeier, K, Neyts, J. Ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a review of the proposed mechanisms of action. Current Opinion in Virology. 2011;1(6) 590-598. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.030
- National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Pneumonia. 2016, September 26; Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pnu
- Foster, G. Pegylated interferons for the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C. Drugs. 2010;70(2):147-165. doi:10.2165/11531990-000000000-00000
- Hofmann WP, Herrmann E, Sarrazin C, Zeuzem S. Ribavirin mode of action in chronic hepatitis C: from clinical use back to molecular mechanisms. Liver Int. 2008, 28:1332-1343. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01896.x
- Alam, I., Lee, J., Cho, K. J., Han, K.R., Yang, J.M., Chung, M.S., & Kim, K. H. Crystal structures of murine norovirus-1 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in complex with 2-thiouridine or ribavirin. Virology. 2012, 426: 143-151. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2012.01.016
- Johnson, ZL, Lee, JH, Lee, M, Kwon, DY, Hong, J, Lee, SY. Structural basis of nucleoside and nucleoside drug selectivity by concentrative nucleoside transporters. eLife. 2014, 3:e03604. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03604.
- Fujimoto T, Tomimatsu M, Iga D, Endo H, Otsuka K. Changes in the Th1/Th2 ratio during a 24-week course of an interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin combination therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23:E432- E437. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05320.x
- Feld, JJ, Nanda, S, Huang, Y, Chen, W, Cam, M, Pusek, SN, Schwigler, LM, Theodore, D, Zacks, SL, Liang, TJ, Fried, MW. Hepatic gene expression during treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin: Identifying molecule pathways for treatment response. Hepatol. 2007, 46(5): 1548-1563. doi: 10.1002/hep.21853
- Thomas E, Feld JJ, Li QS, Hu ZY, Fried MW, Liang TJ. Ribavirin potentiates interferon action by augmenting interferon stimulated gene induction in hepatitis C virus cell culture models. Hepatology 2011, 53:32-41. doi: 10.1002/hep.23985
- Shu QN, Nair V. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) as a target in drug discovery. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28:219-232. doi: 10.1002/chin.200823265
- Streeter, DG, Witkowski, JT, Khare, GP, Sidwell, RW, Bauer, RJ, Robins, RK, Simon, LN. Mechanisms of action of 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (virazole) a new broad spectrum antiviral agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1973, 70:1174-1178. PMID: 4197928
- Kentsis, A, Topisirovic, I, Culjkovic, B, Shao, L, Borden, KLB. Ribavirin suppresses eIF4E-mediated oncogenic transformation by physical mimicry of the guanosine mRNA cap. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101:18105-18110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406927102
- Graci, JD, Cameron, CE. Mechanisms of action of ribavirin against distinct viruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16: 37-48. doi: 10.1002/rmv.483