Finasteride
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==='''Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)'''=== | ==='''Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)'''=== | ||
| - | [[Aromatase]] and 5α-reductase is responsible for converting androgen hormones into estrogen and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This chemical process of androgen hormones leads to a decrease in testosterone, but raises levels of DHT and estrogen <ref name="eight">Tacklind, J., Fink, H.A., MacDonald, R., Rutks, I., Wilt, T.J. (2010). Finasteride for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2010, Issue 10. Art. No.: CD006015. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006015.pub3. </ref>. Estrogen is a key role in cells proliferating in the prostate and DHT is an anabolic hormone much more potent (dissociated from the androgen receptor slowly) than testosterone that when combined, causes a synergy to induce BPH <ref name="nine">Dragan, I., Misso, M. (2012). Lycopene for the prevention and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer: A systematic review. Maturitas, 72 (4), 269 </ref>. The enzyme 5α-reductase is responsible for the synthesis of DHT in the prostate from circulating testosterone. 5α-reductase is located in the stromal cells, which is the main site for the synthesis of DHT, but it can also diffuse into epithelial cells close-by <ref name= "ten"> Bartsch, G., Rittmaster, R.S., Klocker, H. (2000). Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition in human benign prostatic hyperplasia. European Urology. 37 (4): 367–80. doi:10.1159/000020181 </ref>. In both stromal and epithelial cells, DHT binds to nuclear androgen receptors and signals for transcription for cell growth. Finasteride is used to inhibit the 5α-reductase enzyme, which blocks the conversion of testosterone and inhibits the production of DHT, reducing prostate volume and BPH symptoms (urinating complication). Using finasteride could increase the risk for erectile dysfunction, decrease libido, and ejaulation disorder due to 5α-reductase being inhibited <ref name=""> Robaire, B., Henderson, N.A. (2006). Actions of 5alpha-reductase inhibitors on the epididymis. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 250 (1-2): 190–5. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.12.044 </ref>. | + | [[Aromatase]] and 5α-reductase is responsible for converting [[androgen hormones]] into estrogen and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This chemical process of androgen hormones leads to a decrease in testosterone, but raises levels of DHT and estrogen <ref name="eight">Tacklind, J., Fink, H.A., MacDonald, R., Rutks, I., Wilt, T.J. (2010). Finasteride for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2010, Issue 10. Art. No.: CD006015. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006015.pub3. </ref>. Estrogen is a key role in cells proliferating in the prostate and DHT is an anabolic hormone much more potent (dissociated from the androgen receptor slowly) than testosterone that when combined, causes a synergy to induce BPH <ref name="nine">Dragan, I., Misso, M. (2012). Lycopene for the prevention and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer: A systematic review. Maturitas, 72 (4), 269 </ref>. The enzyme 5α-reductase is responsible for the synthesis of DHT in the prostate from circulating testosterone. 5α-reductase is located in the stromal cells, which is the main site for the synthesis of DHT, but it can also diffuse into epithelial cells close-by <ref name= "ten"> Bartsch, G., Rittmaster, R.S., Klocker, H. (2000). Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition in human benign prostatic hyperplasia. European Urology. 37 (4): 367–80. doi:10.1159/000020181 </ref>. In both stromal and epithelial cells, DHT binds to nuclear androgen receptors and signals for transcription for cell growth. Finasteride is used to inhibit the 5α-reductase enzyme, which blocks the conversion of testosterone and inhibits the production of DHT, reducing prostate volume and BPH symptoms (urinating complication). Using finasteride could increase the risk for erectile dysfunction, decrease libido, and ejaulation disorder due to 5α-reductase being inhibited <ref name=""> Robaire, B., Henderson, N.A. (2006). Actions of 5alpha-reductase inhibitors on the epididymis. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 250 (1-2): 190–5. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.12.044 </ref>. |
==='''Prostate Cancer'''=== | ==='''Prostate Cancer'''=== | ||
Current revision
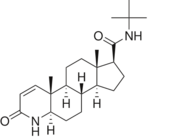
N-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-oxo-(5α,17β)-4-azaandrost-1-ene-17-carboxamide (Finasteride)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 121, 246. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Yamana K, Labrie F, Luu-The V (January 2010). Human type 3 5α-reductase is expressed in peripheral tissues at higher levels than types 1 and 2 and its activity is potently inhibited by finasteride and dutasteride. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation. 2 (3). doi:10.1515/hmbci.2010.035
- ↑ Varothai, S; Bergfeld, WF (Jul 2014). "Androgenetic alopecia: an evidence-based treatment update.". American journal of clinical dermatology. 15 (3): 217–30. doi:10.1007/s40257-014-0077-5. PMID 24848508
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Lednicer D (2011). Steroid Chemistry at a Glance. Hoboken: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-66084-3
- ↑ Burkhard Fugmann; Susanne Lang-Fugmann; Wolfgang Steglich (28 May 2014). RÖMPP Encyclopedia Natural Products, 1st Edition, 2000. Thieme. pp. 1918–. ISBN 978-3-13-179551-9
- ↑ Schieck, Cynthia L.(1998, August) "Finasteride (Propecia ®)". http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/finasteride/Finasteride%20(Propecia)%20-%20Feature%20Molecule.htm
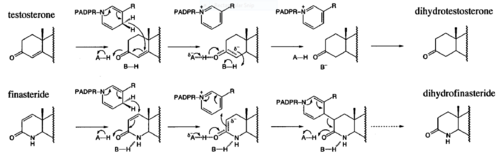
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Bull, Herbert G.*Garcia-Calvo,Margarita Andersson,Stefan†, Baginsky, Walter F.,Chan,H. Karen,Ellsworth,‡ Dina E., Miller,§ Randall R., Stearns,Ralph A.,Bakshi,Raman K.,Rasmusson, Gary H.,Tolman,Richard L., Myers,Robert W.,Kozarich,John W.,Harris,Georgianna S. (1995, August 6) Mechanism-Based Inhibition of Human Steroid 5R-Reductase by Finasteride: Enzyme-Catalyzed Formation of NADP-Dihydrofinasteride, a Potent Bisubstrate Analog Inhibitor. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja953069t
- ↑ Tacklind, J., Fink, H.A., MacDonald, R., Rutks, I., Wilt, T.J. (2010). Finasteride for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2010, Issue 10. Art. No.: CD006015. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006015.pub3.
- ↑ Dragan, I., Misso, M. (2012). Lycopene for the prevention and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer: A systematic review. Maturitas, 72 (4), 269
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Robaire, B., Henderson, N.A. (2006). Actions of 5alpha-reductase inhibitors on the epididymis. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 250 (1-2): 190–5. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.12.044
- ↑ Paus, R., Cotsarelis, G. (1999).The biology of hair follicles. N. Engl. J. Med., 34, 491–497.
- ↑ Olsen, E. A., Hordinsky, M., & Whiting, D., et al. (2006, December).
- ↑ Leyden, James et al.(June 1999)."Finasteride in the treatment of men with frontal male pattern hair loss." Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. Volume 40 , Issue 6 , 930 - 937
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Cody J Cubbage, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky