We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
3rif
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<StructureSection load='3rif' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3rif]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.34Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3rif' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3rif]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.34Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
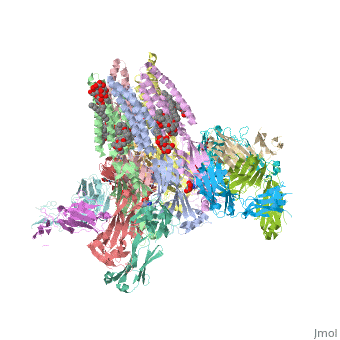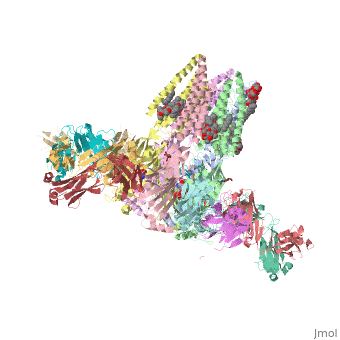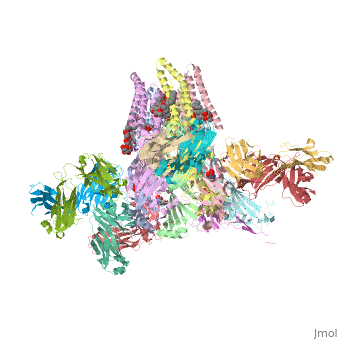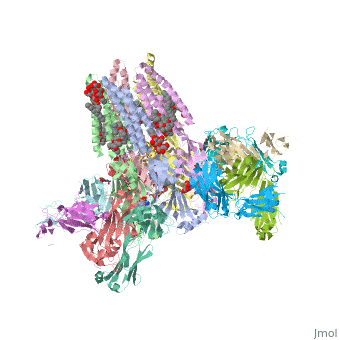
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3rif]] is a 15 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3rif]] is a 15 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caenorhabditis_elegans Caenorhabditis elegans] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mus_musculus Mus musculus]. The November 2015 RCSB PDB [https://pdb.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/index.html Molecule of the Month] feature on ''Glutamate-gated Chloride Receptors'' by David Goodsell is [https://dx.doi.org/10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2015_11 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2015_11]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3RIF OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3RIF FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CL:CHLORIDE+ION'>CL</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=GLU:GLUTAMIC+ACID'>GLU</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=IVM:(2AE,4E,5S,6S,6R,7S,8E,11R,13R,15S,17AR,20R,20AR,20BS)-6-[(2S)-BUTAN-2-YL]-20,20B-DIHYDROXY-5,6,8,19-TETRAMETHYL-17-OXO-3,4,5,6,6,10,11,14,15,17,17A,20,20A,20B-TETRADECAHYDRO-2H,7H-SPIRO[11,15-METHANOFURO[4,3,2-PQ][2,6]BENZODIOXACYCLOOCTADECINE-13,2-PYRAN]-7-YL+2,6-DIDEOXY-4-O-(2,6-DIDEOXY-3-O-METHYL-ALPHA-L-ARABINO-HEXOPYRANOSYL)-3-O-METHYL-ALPHA-L-ARABINO-HEXOPYRANOSIDE'>IVM</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=LMT:DODECYL-BETA-D-MALTOSIDE'>LMT</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=NAG:N-ACETYL-D-GLUCOSAMINE'>NAG</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=OCT:N-OCTANE'>OCT</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=UND:UNDECANE'>UND</scene> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 3.345Å</td></tr> |
| - | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CL:CHLORIDE+ION'>CL</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=GLU:GLUTAMIC+ACID'>GLU</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=IVM:(2AE,4E,5S,6S,6R,7S,8E,11R,13R,15S,17AR,20R,20AR,20BS)-6-[(2S)-BUTAN-2-YL]-20,20B-DIHYDROXY-5,6,8,19-TETRAMETHYL-17-OXO-3,4,5,6,6,10,11,14,15,17,17A,20,20A,20B-TETRADECAHYDRO-2H,7H-SPIRO[11,15-METHANOFURO[4,3,2-PQ][2,6]BENZODIOXACYCLOOCTADECINE-13,2-PYRAN]-7-YL+2,6-DIDEOXY-4-O-(2,6-DIDEOXY-3-O-METHYL-ALPHA-L-ARABINO-HEXOPYRANOSYL)-3-O-METHYL-ALPHA-L-ARABINO-HEXOPYRANOSIDE'>IVM</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=LMT:DODECYL-BETA-D-MALTOSIDE'>LMT</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=NAG:N-ACETYL-D-GLUCOSAMINE'>NAG</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=OCT:N-OCTANE'>OCT</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=UND:UNDECANE'>UND</scene></td></tr> | |
| - | + | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3rif FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3rif OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3rif PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3rif RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3rif PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3rif ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3rif FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3rif OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3rif PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3rif RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3rif PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3rif ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| - | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| - | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| - | Fast inhibitory neurotransmission is essential for nervous system function and is mediated by binding of inhibitory neurotransmitters to receptors of the Cys-loop family embedded in the membranes of neurons. Neurotransmitter binding triggers a conformational change in the receptor, opening an intrinsic chloride channel and thereby dampening neuronal excitability. Here we present the first three-dimensional structure, to our knowledge, of an inhibitory anion-selective Cys-loop receptor, the homopentameric Caenorhabditis elegans glutamate-gated chloride channel alpha (GluCl), at 3.3 A resolution. The X-ray structure of the GluCl-Fab complex was determined with the allosteric agonist ivermectin and in additional structures with the endogenous neurotransmitter l-glutamate and the open-channel blocker picrotoxin. Ivermectin, used to treat river blindness, binds in the transmembrane domain of the receptor and stabilizes an open-pore conformation. Glutamate binds in the classical agonist site at subunit interfaces, and picrotoxin directly occludes the pore near its cytosolic base. GluCl provides a framework for understanding mechanisms of fast inhibitory neurotransmission and allosteric modulation of Cys-loop receptors. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Principles of activation and permeation in an anion-selective Cys-loop receptor.,Hibbs RE, Gouaux E Nature. 2011 May 15. PMID:21572436<ref>PMID:21572436</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
| - | </div> | ||
| - | <div class="pdbe-citations 3rif" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Ion channels 3D structures|Ion channels 3D structures]] | *[[Ion channels 3D structures|Ion channels 3D structures]] | ||
*[[Monoclonal Antibodies 3D structures|Monoclonal Antibodies 3D structures]] | *[[Monoclonal Antibodies 3D structures|Monoclonal Antibodies 3D structures]] | ||
| - | == References == | ||
| - | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Caenorhabditis elegans]] |
[[Category: Glutamate-gated Chloride Receptors]] | [[Category: Glutamate-gated Chloride Receptors]] | ||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Mus musculus]] |
[[Category: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month]] | [[Category: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Gouaux | + | [[Category: Gouaux E]] |
| - | [[Category: Hibbs | + | [[Category: Hibbs RE]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 12:25, 14 March 2024
C. elegans glutamate-gated chloride channel (GluCl) in complex with Fab, ivermectin and glutamate.
| |||||||||||