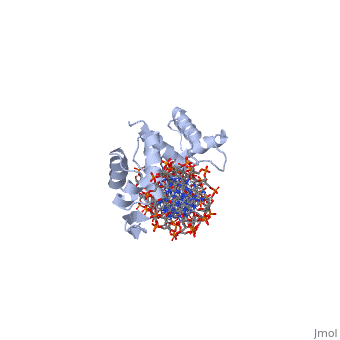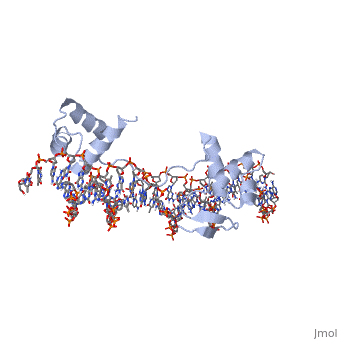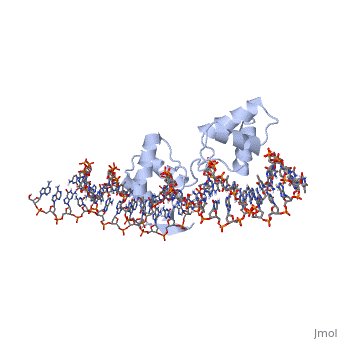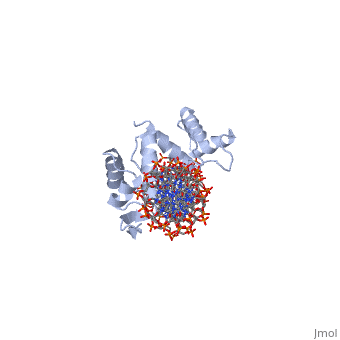
| Structural highlights
Disease
PAX6_HUMAN Defects in PAX6 are the cause of aniridia (AN) [MIM:106210. A congenital, bilateral, panocular disorder characterized by complete absence of the iris or extreme iris hypoplasia. Aniridia is not just an isolated defect in iris development but it is associated with macular and optic nerve hypoplasia, cataract, corneal changes, nystagmus. Visual acuity is generally low but is unrelated to the degree of iris hypoplasia. Glaucoma is a secondary problem causing additional visual loss over time.[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] Defects in PAX6 are a cause of Peters anomaly (PAN) [MIM:604229. Peters anomaly consists of a central corneal leukoma, absence of the posterior corneal stroma and Descemet membrane, and a variable degree of iris and lenticular attachments to the central aspect of the posterior cornea.[21] [22] [23] Defects in PAX6 are a cause of foveal hypoplasia (FOVHYP) [MIM:136520. Foveal hypoplasia can be isolated or associated with presenile cataract. Inheritance is autosomal dominant.[24] [25] Defects in PAX6 are a cause of keratitis hereditary (KERH) [MIM:148190. An ocular disorder characterized by corneal opacification, recurrent stromal keratitis and vascularization. Defects in PAX6 are a cause of coloboma of iris choroid and retina (COI) [MIM:120200; also known as uveoretinal coloboma. Ocular colobomas are a set of malformations resulting from abnormal morphogenesis of the optic cup and stalk, and the fusion of the fetal fissure (optic fissure). Severe colobomatous malformations may cause as much as 10% of the childhood blindness. The clinical presentation of ocular coloboma is variable. Some individuals may present with minimal defects in the anterior iris leaf without other ocular defects. More complex malformations create a combination of iris, uveoretinal and/or optic nerve defects without or with microphthalmia or even anophthalmia.[26] Defects in PAX6 are a cause of coloboma of optic nerve (COLON) [MIM:120430. Defects in PAX6 are a cause of bilateral optic nerve hypoplasia (BONH) [MIM:165550; also known as bilateral optic nerve aplasia. A congenital anomaly in which the optic disc appears abnormally small. It may be an isolated finding or part of a spectrum of anatomic and functional abnormalities that includes partial or complete agenesis of the septum pellucidum, other midline brain defects, cerebral anomalies, pituitary dysfunction, and structural abnormalities of the pituitary.[27] Defects in PAX6 are a cause of aniridia cerebellar ataxia and mental deficiency (ACAMD) [MIM:206700; also known as Gillespie syndrome. A rare condition consisting of partial rudimentary iris, cerebellar impairment of the ability to perform coordinated voluntary movements, and mental retardation.[28]
Function
PAX6_HUMAN Transcription factor with important functions in the development of the eye, nose, central nervous system and pancreas. Required for the differentiation of pancreatic islet alpha cells (By similarity). Competes with PAX4 in binding to a common element in the glucagon, insulin and somatostatin promoters. Regulates specification of the ventral neuron subtypes by establishing the correct progenitor domains (By similarity). Isoform 5a appears to function as a molecular switch that specifies target genes.
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
See Also
References
- ↑ Xu HE, Rould MA, Xu W, Epstein JA, Maas RL, Pabo CO. Crystal structure of the human Pax6 paired domain-DNA complex reveals specific roles for the linker region and carboxy-terminal subdomain in DNA binding. Genes Dev. 1999 May 15;13(10):1263-75. PMID:10346815
- ↑ Hanson IM, Seawright A, Hardman K, Hodgson S, Zaletayev D, Fekete G, van Heyningen V. PAX6 mutations in aniridia. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):915-20. PMID:8364574
- ↑ Azuma N, Nishina S, Yanagisawa H, Okuyama T, Yamada M. PAX6 missense mutation in isolated foveal hypoplasia. Nat Genet. 1996 Jun;13(2):141-2. PMID:8640214 doi:10.1038/ng0696-141
- ↑ Tang HK, Chao LY, Saunders GF. Functional analysis of paired box missense mutations in the PAX6 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1997 Mar;6(3):381-6. PMID:9147640
- ↑ Axton RA, Hanson IM, Love J, Seawright A, Prosser J, van Heyningen V. Combined SSCP/heteroduplex analysis in the screening for PAX6 mutations. Mol Cell Probes. 1997 Aug;11(4):287-92. PMID:9281415 doi:S0890-8508(97)90117-1
- ↑ Wolf MT, Lorenz B, Winterpacht A, Drechsler M, Schumacher V, Royer-Pokora B, Blankenagel A, Zabel B, Wildhardt G. Ten novel mutations found in Aniridia. Hum Mutat. 1998;12(5):304-13. PMID:9792406 doi:<304::AID-HUMU3>3.0.CO;2-D 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1998)12:5<304::AID-HUMU3>3.0.CO;2-D
- ↑ Azuma N, Hotta Y, Tanaka H, Yamada M. Missense mutations in the PAX6 gene in aniridia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998 Dec;39(13):2524-8. PMID:9856761
- ↑ Gronskov K, Rosenberg T, Sand A, Brondum-Nielsen K. Mutational analysis of PAX6: 16 novel mutations including 5 missense mutations with a mild aniridia phenotype. Eur J Hum Genet. 1999 Apr;7(3):274-86. PMID:10234503 doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200308
- ↑ Hanson I, Churchill A, Love J, Axton R, Moore T, Clarke M, Meire F, van Heyningen V. Missense mutations in the most ancient residues of the PAX6 paired domain underlie a spectrum of human congenital eye malformations. Hum Mol Genet. 1999 Feb;8(2):165-72. PMID:9931324
- ↑ Epstein JA, Glaser T, Cai J, Jepeal L, Walton DS, Maas RL. Two independent and interactive DNA-binding subdomains of the Pax6 paired domain are regulated by alternative splicing. Genes Dev. 1994 Sep 1;8(17):2022-34. PMID:7958875
- ↑ Sonoda S, Isashiki Y, Tabata Y, Kimura K, Kakiuchi T, Ohba N. A novel PAX6 gene mutation (P118R) in a family with congenital nystagmus associated with a variant form of aniridia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000 Jul;238(7):552-8. PMID:10955655
- ↑ Chao LY, Huff V, Strong LC, Saunders GF. Mutation in the PAX6 gene in twenty patients with aniridia. Hum Mutat. 2000;15(4):332-9. PMID:10737978 doi:<332::AID-HUMU5>3.0.CO;2-1 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(200004)15:4<332::AID-HUMU5>3.0.CO;2-1
- ↑ Malandrini A, Mari F, Palmeri S, Gambelli S, Berti G, Bruttini M, Bardelli AM, Williamson K, van Heyningen V, Renieri A. PAX6 mutation in a family with aniridia, congenital ptosis, and mental retardation. Clin Genet. 2001 Aug;60(2):151-4. PMID:11553050
- ↑ Singh S, Chao LY, Mishra R, Davies J, Saunders GF. Missense mutation at the C-terminus of PAX6 negatively modulates homeodomain function. Hum Mol Genet. 2001 Apr 15;10(9):911-8. PMID:11309364
- ↑ Morrison D, FitzPatrick D, Hanson I, Williamson K, van Heyningen V, Fleck B, Jones I, Chalmers J, Campbell H. National study of microphthalmia, anophthalmia, and coloboma (MAC) in Scotland: investigation of genetic aetiology. J Med Genet. 2002 Jan;39(1):16-22. PMID:11826019
- ↑ Azuma N, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H, Tadokoro K, Asaka A, Kawase E, Yamada M. Mutations of the PAX6 gene detected in patients with a variety of optic-nerve malformations. Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Jun;72(6):1565-70. Epub 2003 Apr 29. PMID:12721955 doi:S0002-9297(07)60456-X
- ↑ Vincent MC, Pujo AL, Olivier D, Calvas P. Screening for PAX6 gene mutations is consistent with haploinsufficiency as the main mechanism leading to various ocular defects. Eur J Hum Genet. 2003 Feb;11(2):163-9. PMID:12634864 doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200940
- ↑ Chao LY, Mishra R, Strong LC, Saunders GF. Missense mutations in the DNA-binding region and termination codon in PAX6. Hum Mutat. 2003 Feb;21(2):138-45. PMID:12552561 doi:10.1002/humu.10163
- ↑ D'Elia AV, Puppin C, Pellizzari L, Pianta A, Bregant E, Lonigro R, Tell G, Fogolari F, van Heyningen V, Damante G. Molecular analysis of a human PAX6 homeobox mutant. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006 Jun;14(6):744-51. PMID:16493447 doi:5201579
- ↑ Zhang X, Wang P, Li S, Xiao X, Guo X, Zhang Q. Mutation spectrum of PAX6 in Chinese patients with aniridia. Mol Vis. 2011;17:2139-47. Epub 2011 Aug 11. PMID:21850189
- ↑ Azuma N, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H, Tadokoro K, Asaka A, Kawase E, Yamada M. Mutations of the PAX6 gene detected in patients with a variety of optic-nerve malformations. Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Jun;72(6):1565-70. Epub 2003 Apr 29. PMID:12721955 doi:S0002-9297(07)60456-X
- ↑ Hanson IM, Fletcher JM, Jordan T, Brown A, Taylor D, Adams RJ, Punnett HH, van Heyningen V. Mutations at the PAX6 locus are found in heterogeneous anterior segment malformations including Peters' anomaly. Nat Genet. 1994 Feb;6(2):168-73. PMID:8162071 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng0294-168
- ↑ Azuma N, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H, Hayakawa M, Kanai A, Yamada M. Missense mutation in the alternative splice region of the PAX6 gene in eye anomalies. Am J Hum Genet. 1999 Sep;65(3):656-63. PMID:10441571 doi:S0002-9297(07)62316-7
- ↑ Azuma N, Nishina S, Yanagisawa H, Okuyama T, Yamada M. PAX6 missense mutation in isolated foveal hypoplasia. Nat Genet. 1996 Jun;13(2):141-2. PMID:8640214 doi:10.1038/ng0696-141
- ↑ Hanson I, Churchill A, Love J, Axton R, Moore T, Clarke M, Meire F, van Heyningen V. Missense mutations in the most ancient residues of the PAX6 paired domain underlie a spectrum of human congenital eye malformations. Hum Mol Genet. 1999 Feb;8(2):165-72. PMID:9931324
- ↑ Azuma N, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H, Tadokoro K, Asaka A, Kawase E, Yamada M. Mutations of the PAX6 gene detected in patients with a variety of optic-nerve malformations. Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Jun;72(6):1565-70. Epub 2003 Apr 29. PMID:12721955 doi:S0002-9297(07)60456-X
- ↑ Azuma N, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H, Tadokoro K, Asaka A, Kawase E, Yamada M. Mutations of the PAX6 gene detected in patients with a variety of optic-nerve malformations. Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Jun;72(6):1565-70. Epub 2003 Apr 29. PMID:12721955 doi:S0002-9297(07)60456-X
- ↑ Graziano C, D'Elia AV, Mazzanti L, Moscano F, Guidelli Guidi S, Scarano E, Turchetti D, Franzoni E, Romeo G, Damante G, Seri M. A de novo nonsense mutation of PAX6 gene in a patient with aniridia, ataxia, and mental retardation. Am J Med Genet A. 2007 Aug 1;143A(15):1802-5. PMID:17595013 doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.31808
|