User:Karisma Moll/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
The picture of the mechanism is inserted but not visible, maybe too high of a quality? | The picture of the mechanism is inserted but not visible, maybe too high of a quality? | ||
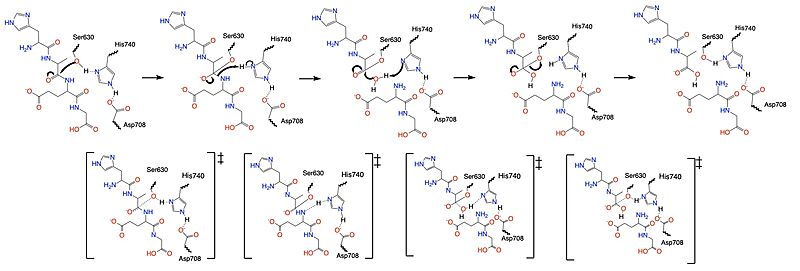
Once a substrate is bound in the active site, DPPIV utilizes a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_catalysis#Covalent_catalysis covalent catalysis] mechanism to cleave the substrate at the penultimate position. Asp708 of the <scene name='10/1037489/Catalytic_triad/5'>catalytic triad</scene> (Ser630, His 740, Asp708) pulls electron density from His740 allowing the histidine to pull electron density from Ser630, making serine a stronger nucleophile. The water molecule attacks the carbonyl carbon, breaking the newly formed covalent bond, and releasing the first two residues of the starting substrate. The active site resets. | Once a substrate is bound in the active site, DPPIV utilizes a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_catalysis#Covalent_catalysis covalent catalysis] mechanism to cleave the substrate at the penultimate position. Asp708 of the <scene name='10/1037489/Catalytic_triad/5'>catalytic triad</scene> (Ser630, His 740, Asp708) pulls electron density from His740 allowing the histidine to pull electron density from Ser630, making serine a stronger nucleophile. The water molecule attacks the carbonyl carbon, breaking the newly formed covalent bond, and releasing the first two residues of the starting substrate. The active site resets. | ||
| - | [[Image:DPPIV_Mech_SS.jpg| | + | [[Image:DPPIV_Mech_SS.jpg|800 px|center|thumb|Figure 5. Mechanism of the catalytic triad of DPPIV.]] |
=== Inhibitors === | === Inhibitors === | ||
Gliptins, a class of oral antidiabetic medications, are DPPIV [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_inhibitor inhibitors]. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the following: sitagliptin, alogliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has approved all of those aforementioned in addition to vildagliptin. Each gliptin is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Small_molecule small molecule] (≤ 1000 Da). | Gliptins, a class of oral antidiabetic medications, are DPPIV [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_inhibitor inhibitors]. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the following: sitagliptin, alogliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has approved all of those aforementioned in addition to vildagliptin. Each gliptin is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Small_molecule small molecule] (≤ 1000 Da). | ||
Revision as of 14:40, 9 April 2024
DPPIV in Humans
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Ahrén B. DPP-4 Inhibition and the Path to Clinical Proof. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jun 19;10:376. PMID:31275243 doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00376
- ↑ Khalse M, Bhargava A. A Review on Cardiovascular Outcome Studies of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Sep-Oct;22(5):689-695. PMID:30294582 doi:10.4103/ijem.IJEM_104_18
- ↑ Hocher B, Reichetzeder C, Alter ML. Renal and cardiac effects of DPP4 inhibitors--from preclinical development to clinical research. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2012;36(1):65-84. PMID:22947920 doi:10.1159/000339028
- ↑ Zhong J, Rajagopalan S. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Regulation of SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis: Implications for Cardiovascular Disease. Front Immunol. 2015 Sep 25;6:477. PMID:26441982 doi:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00477
- ↑ Sharma A, Ren X, Zhang H, Pandey GN. Effect of depression and suicidal behavior on neuropeptide Y (NPY) and its receptors in the adult human brain: A postmortem study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2022 Jan 10;112:110428. PMID:34411658 doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110428
- ↑ Ntafam CN, Beutler BD, Harris RD. Incarcerated gravid uterus: A rare but potentially devastating obstetric complication. Radiol Case Rep. 2022 Mar 10;17(5):1583-1586. PMID:35309386 doi:10.1016/j.radcr.2022.02.034
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Hiramatsu H, Kyono K, Higashiyama Y, Fukushima C, Shima H, Sugiyama S, Inaka K, Yamamoto A, Shimizu R. The structure and function of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV, possessing a unique eight-bladed beta-propeller fold. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Mar 21;302(4):849-54. PMID:12646248
- ↑ Abbott CA, McCaughan GW, Levy MT, Church WB, Gorrell MD. Binding to human dipeptidyl peptidase IV by adenosine deaminase and antibodies that inhibit ligand binding involves overlapping, discontinuous sites on a predicted beta propeller domain. Eur J Biochem. 1999 Dec;266(3):798-810. PMID:10583373 doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00902.x
Student Contributors
- Karisma Moll
- Merritt Jugo
- Sam Magnabosco