We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
1lpa
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
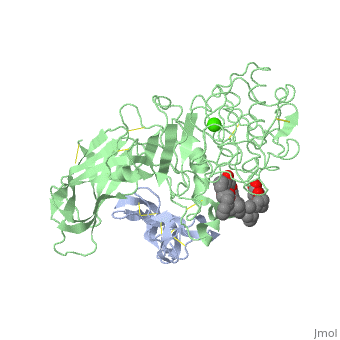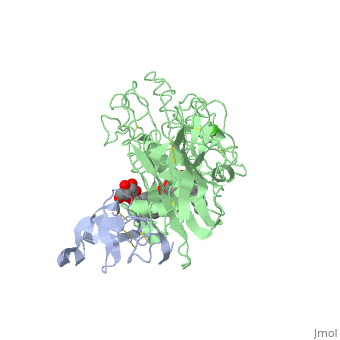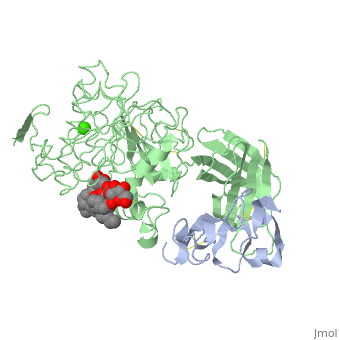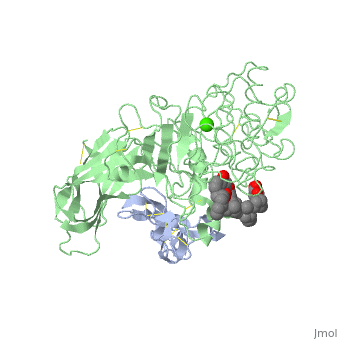
<StructureSection load='1lpa' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1lpa]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.04Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1lpa' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1lpa]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.04Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1lpa]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1lpa]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sus_scrofa Sus scrofa]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1LPA OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1LPA FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=BNG:B-NONYLGLUCOSIDE'>BNG</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=CA:CALCIUM+ION'>CA</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=PLC:DIUNDECYL+PHOSPHATIDYL+CHOLINE'>PLC</scene | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 3.04Å</td></tr> |
| - | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=BNG:B-NONYLGLUCOSIDE'>BNG</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=CA:CALCIUM+ION'>CA</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=PLC:DIUNDECYL+PHOSPHATIDYL+CHOLINE'>PLC</scene></td></tr> | |
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1lpa FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1lpa OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1lpa PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1lpa RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1lpa PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1lpa ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1lpa FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1lpa OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1lpa PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1lpa RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1lpa PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1lpa ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/COL_PIG COL_PIG] Colipase is a cofactor of pancreatic lipase. It allows the lipase to anchor itself to the lipid-water interface. Without colipase the enzyme is washed off by bile salts, which have an inhibitory effect on the lipase. Enterostatin has a biological activity as a satiety signal. | |
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1lpa ConSurf]. | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1lpa ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
| - | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| - | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| - | The three-dimensional structure of the lipase-procolipase complex, co-crystallized with mixed micelles of phosphatidylcholine and bile salt, has been determined at 3 A resolution by X-ray crystallography. The lid, a surface helix covering the catalytic triad of lipase, adopts a totally different conformation which allows phospholipid to bind to the enzyme's active site. The open lid is an essential component of the active site and interacts with procolipase. Together they form the lipid-water interface binding site. This reorganization of the lid structure provokes a second drastic conformational change in an active site loop, which in its turn creates the oxyanion hole (induced fit). | ||
| - | |||
| - | Interfacial activation of the lipase-procolipase complex by mixed micelles revealed by X-ray crystallography.,van Tilbeurgh H, Egloff MP, Martinez C, Rugani N, Verger R, Cambillau C Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):814-20. PMID:8479519<ref>PMID:8479519</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
| - | </div> | ||
| - | <div class="pdbe-citations 1lpa" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Lipase 3D Structures|Lipase 3D Structures]] | *[[Lipase 3D Structures|Lipase 3D Structures]] | ||
| - | == References == | ||
| - | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
[[Category: Large Structures]] | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Sus scrofa]] |
| - | + | [[Category: Cambillau C]] | |
| - | [[Category: Cambillau | + | [[Category: Egloff M-P]] |
| - | [[Category: Egloff | + | [[Category: Van Tilbeurgh H]] |
| - | [[Category: Tilbeurgh | + | |
Revision as of 08:25, 10 April 2024
INTERFACIAL ACTIVATION OF THE LIPASE-PROCOLIPASE COMPLEX BY MIXED MICELLES REVEALED BY X-RAY CRYSTALLOGRAPHY
| |||||||||||