We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Lily Lindemann/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
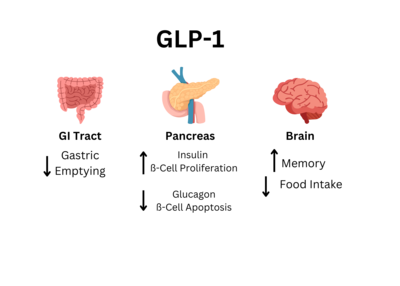
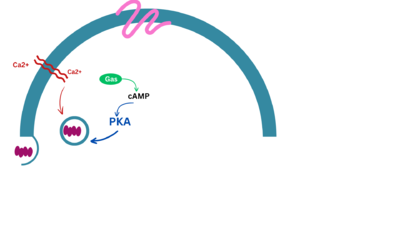
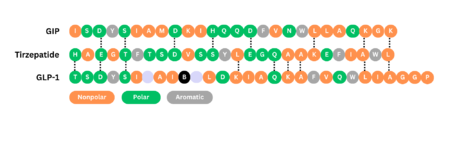
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor or GLP1-R uses the glucagon-like peptide to signal the body to secrete insulin and inhibit glucagon secretion. When glucose levels in the blood rise (usually after consuming food), GLP-1R activates, creating a signaling cascade to signal cAMP. After the signaling cascade, the final result is the secretion of insulin to the rest of the body. Discovered in 1990s while trying to understand the mechanism of GLP-1 action. [https://www.biochempeg.com/article/299.html#:~:text=In%20the%201970s%2C%20the%20first,(Figure%201)%20were%20unraveled] The structure was determined using cryogenic electron microscopy. | Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor or GLP1-R uses the glucagon-like peptide to signal the body to secrete insulin and inhibit glucagon secretion. When glucose levels in the blood rise (usually after consuming food), GLP-1R activates, creating a signaling cascade to signal cAMP. After the signaling cascade, the final result is the secretion of insulin to the rest of the body. Discovered in 1990s while trying to understand the mechanism of GLP-1 action. [https://www.biochempeg.com/article/299.html#:~:text=In%20the%201970s%2C%20the%20first,(Figure%201)%20were%20unraveled] The structure was determined using cryogenic electron microscopy. | ||
[[Image:GLP Body Effect Graphic.png|400 px|right|]] | [[Image:GLP Body Effect Graphic.png|400 px|right|]] | ||
| - | |||
Revision as of 14:26, 11 April 2024
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor (GLP1-R)
Introduction
| |||||||||||