We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Mandy Bechman/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='7ra3' size='400' side='right' caption='GIP Structure' scene='10/1038867/Structure_overview/7'> | <StructureSection load='7ra3' size='400' side='right' caption='GIP Structure' scene='10/1038867/Structure_overview/7'> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
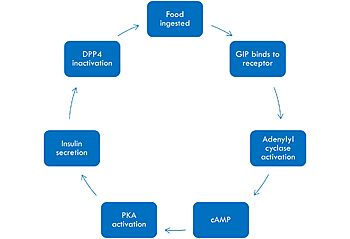
| - | + | <scene name='10/1038867/Structure_overview/7'>Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide</scene>([https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35065096/ GIP]) <ref name="Mayendraraj"/> is a gastric inhibitory polypeptide, composed of 42 amino acids. It is categorized as a incretin, which is a gut-based hormone that is secreted upon the ingestion of food. It is found in K cells in the upper small intestines of humans. | |
===History=== | ===History=== | ||
The idea of incretin, and subsequently GIP, began in 1902 after the discovery of secretin by Bayliss and Starling. Inspired by their discovery, Moore et al. hypothesized that there must be some kind of gut hormone that regulates the endocrine pancreas. His experiments showed that gut extracts in patients with diabetes have reduced amounts of sugars in their urine as a result of endocrine stimulation. In 1929, a French scientist named La Barre was able to purify incretin (INtestine seCREtion INsulin) from gut extracts. The idea of incretin slowly lost attention until the 1960s when radioimmunoassay became available to measure incretin levels. GIP and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) were the two gut based hormones that were proven to act as incretins. GIP was found to be located in the K cells of the upper small intestines in humans. At first, it was titled a gastric inhibitory polypeptide because of its ability to inhibit gastric acid secretion after being isolating from porcine intestines. Later, they discovered that when GIP was administered in healthy volunteers, it stimulated insulin secretion by acting directly on pancreatic islets. As a result of these discoveries, they renamed it glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, becoming the first known incretin.<ref name="Seino"/> | The idea of incretin, and subsequently GIP, began in 1902 after the discovery of secretin by Bayliss and Starling. Inspired by their discovery, Moore et al. hypothesized that there must be some kind of gut hormone that regulates the endocrine pancreas. His experiments showed that gut extracts in patients with diabetes have reduced amounts of sugars in their urine as a result of endocrine stimulation. In 1929, a French scientist named La Barre was able to purify incretin (INtestine seCREtion INsulin) from gut extracts. The idea of incretin slowly lost attention until the 1960s when radioimmunoassay became available to measure incretin levels. GIP and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) were the two gut based hormones that were proven to act as incretins. GIP was found to be located in the K cells of the upper small intestines in humans. At first, it was titled a gastric inhibitory polypeptide because of its ability to inhibit gastric acid secretion after being isolating from porcine intestines. Later, they discovered that when GIP was administered in healthy volunteers, it stimulated insulin secretion by acting directly on pancreatic islets. As a result of these discoveries, they renamed it glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, becoming the first known incretin.<ref name="Seino"/> | ||
Revision as of 13:23, 18 April 2024
H. sapiens Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mayendraraj A, Rosenkilde MM, Gasbjerg LS. GLP-1 and GIP receptor signaling in beta cells interactions and co-stimulation. Peptides. 2022 May;151:170749. PMID:35065096 doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170749
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Seino Y, Fukushima M, Yabe D. GIP and GLP-1, the two incretin hormones: Similarities and differences. J Diabetes Investig. 2010 Apr 22;1(1-2):8-23. PMID:24843404 doi:10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00022.x
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644