User:Jaelin Lunato/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
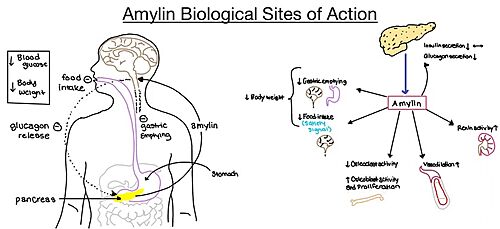
| - | Amylin, as it is a part of the calcitonin peptide family, is heavily related to the regulation of homeostatic processes to relevant drug targets. Amylin is the target for the treatment of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diabetes diabetes]. Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized and co-secreted with insulin. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin Insulin] triggers glucose uptake which removes glucose from the bloodstream using it then for energy. Amylin works in negatively regulating (inhibiting) the formation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucagon glucagon], | + | Amylin, as it is a part of the calcitonin peptide family, is heavily related to the regulation of homeostatic processes to relevant drug targets. Amylin is the target for the treatment of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diabetes diabetes]. Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized and co-secreted with insulin. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin Insulin] triggers glucose uptake which removes glucose from the bloodstream using it then for energy. Amylin works in negatively regulating (inhibiting) the formation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucagon glucagon] so that glucose polymers can continue to be broken down into the bloodstream for further energy storage and consumption. Therefore with the co-secretion of both amylin and insulin, it would aid in decreasing blood glucose levels thus becoming a predominant treatment plan for diabetic disorders, such as shown with the developing drug [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pramlintide Pramlintide]. |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Pramlintide ==== | ||
| + | Pramlintide, a peptide analog of human amylin, is FDA-approved for the treatment of insulin-requiring diabetes. Pramlintide is injected into the bloodstream by the beta cells of the pancreas along with insulin after a meal, aiding in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomach gastric emptying], promoting [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satiety satiety] via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamus hypothalamic] receptors, and inhibiting secretion of glucagon which opposes the effects of insulin and amylin. | ||
Revision as of 17:40, 21 April 2024
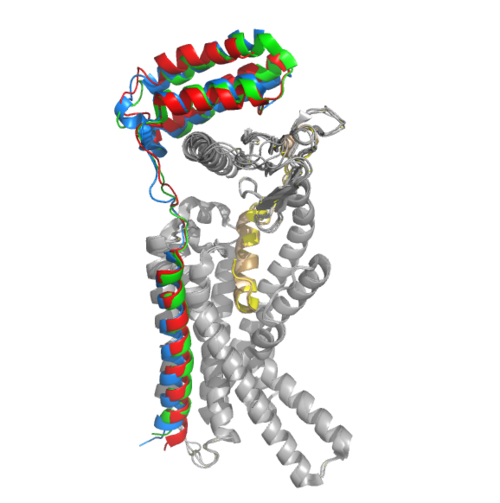
The molecular structure and function of the amylin receptor AMYR
| |||||||||||