User:Jaelin Lunato/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
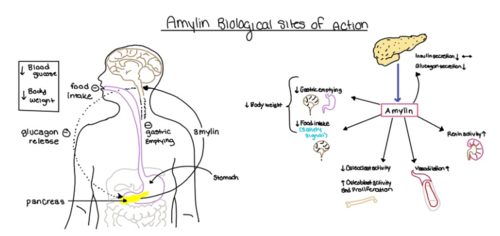
[[Image:Amylin_biological_role.png|500 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 4.''' Different effects of amylin in the human body.]] | [[Image:Amylin_biological_role.png|500 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 4.''' Different effects of amylin in the human body.]] | ||
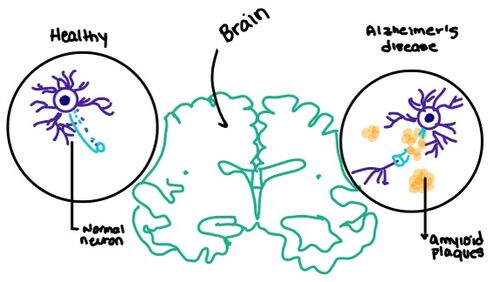
| - | [[Image:Amylin brain.jpeg|500 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 5.''' Amylin's effect on the brain through the buildup of amyloid plaques.]] | ||
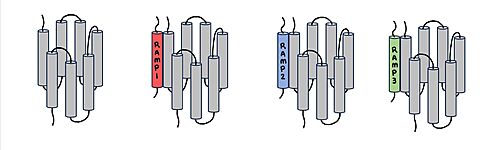
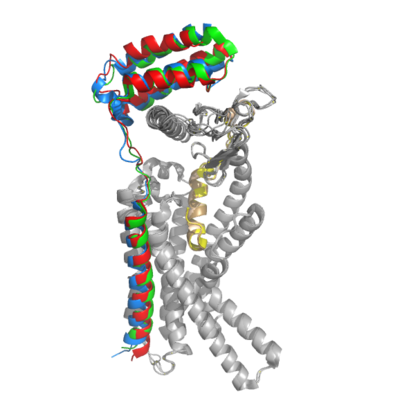
The functional pharmacology of AMYRs has relied on interference from differences between the behavior of CTRs in the presence and absence of RAMPs. Thus, understanding the structural basis for binding and selectivity of peptides to CTR and AMYRs is important for future drug discovery and development. | The functional pharmacology of AMYRs has relied on interference from differences between the behavior of CTRs in the presence and absence of RAMPs. Thus, understanding the structural basis for binding and selectivity of peptides to CTR and AMYRs is important for future drug discovery and development. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 42: | ||
==== Pramlintide ==== | ==== Pramlintide ==== | ||
| - | [[Image:Pram sequ.png|500px|left|thumb|'''Figure | + | [[Image:Pram sequ.png|500px|left|thumb|'''Figure 5.''' Sequence alignment of rat amylin and pramlintide.]] |
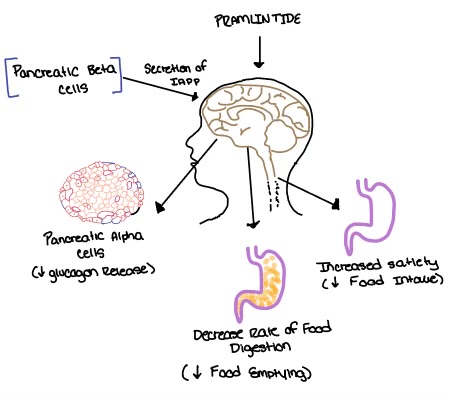
| - | Pramlintide, a peptide analog of human amylin, is FDA-approved for the treatment of insulin-requiring diabetes (Figure | + | Pramlintide, a peptide analog of human amylin, is FDA-approved for the treatment of insulin-requiring diabetes (Figure 5). Pramlintide is injected into the bloodstream by the beta cells of the pancreas along with insulin after a meal, aiding in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomach gastric emptying], promoting [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satiety satiety] via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamus hypothalamic] receptors, and inhibiting secretion of glucagon which opposes the effects of insulin and amylin (Figure 6). |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Pramlintide.jpeg|500 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 6.''' Pramlintide's effect on the human body. Pramlintide is a peptide agonist of human amylin and is a FDA approved treatment for diabetes.]] | ||
| - | [[Image:Pramlintide.jpeg|500 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 7.''' Pramlintide's effect on the human body. Pramlintide is a peptide agonist of human amylin and is a FDA approved treatment for diabetes.]] | ||
===Alzheimer's=== | ===Alzheimer's=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Amylin brain.jpeg|500 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 7.''' Amylin's effect on the brain through the buildup of amyloid plaques.]] | ||
| + | |||
Revision as of 21:56, 22 April 2024
Amylin Receptor (AMYR)
| |||||||||||