We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Ben Whiteside
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
===Chemical Modifications to Amylin=== | ===Chemical Modifications to Amylin=== | ||
====N-Terminus Disulfide==== | ====N-Terminus Disulfide==== | ||
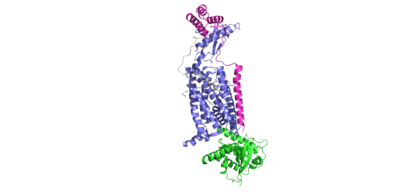
| - | The amylin peptide contains a <scene name='10/1038819/N_term_disulfide/3'>covalent disulfide linkage</scene> between residues C2 and C7. This disulfide provides stability and rigidity to the helical structure of the peptide, allowing for favorable binding to the extracellular domain (ECD). | + | The amylin peptide contains a <scene name='10/1038819/N_term_disulfide/3'>covalent disulfide linkage</scene> between residues C2 and C7. This disulfide provides stability and rigidity to the helical structure of the peptide, allowing for favorable binding to the extracellular domain (ECD). Notable interactions formed by this disulfide include hydrogen bonds between E294 of the transmembrane domain with K1 of amylin, and both R362 and W361 of the transmembrane domain forming a hydrogen bond with N3 of amylin. |
====Amidated C-Terminus==== | ====Amidated C-Terminus==== | ||
The <scene name='10/1038819/Amidated_c_term/9'>C-Terminus</scene> of amylin contains an amide group, rather than a carboxylic acid group. This chemical modification allows for more extensive hydrogen bonding to nearby residues, due to the added hydrogen bond donor on the NH2 group. In turn, this allows for favorable hydrogen bonds between S129 of the transmembrane domain and the main chain of Y37 on amylin. This interaction causes a "kink" in the random coil of amylin, displacing Y37 into a hydrophobic pocket, allowing for favorable hydrophobic interactions with W79 of the transmembrane domain. This amidation is thought to be a post-translational modification. | The <scene name='10/1038819/Amidated_c_term/9'>C-Terminus</scene> of amylin contains an amide group, rather than a carboxylic acid group. This chemical modification allows for more extensive hydrogen bonding to nearby residues, due to the added hydrogen bond donor on the NH2 group. In turn, this allows for favorable hydrogen bonds between S129 of the transmembrane domain and the main chain of Y37 on amylin. This interaction causes a "kink" in the random coil of amylin, displacing Y37 into a hydrophobic pocket, allowing for favorable hydrophobic interactions with W79 of the transmembrane domain. This amidation is thought to be a post-translational modification. | ||
Revision as of 17:40, 23 April 2024
AMYR
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
Student Contributors
Andrew Helmerich,Mathias Vander Eide, Ben Whiteside