This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Jaelin Lunato/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
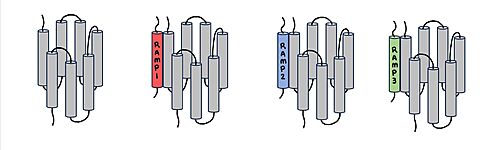
[[Image:RAMP_diagram.jpg|500px|right|thumb|'''Figure 1.''' Three different RAMPs to compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the calcitonin receptor (shown in grey). RAMP1 is in red, RAMP2 is in blue, and RAMP3 is in green.]] AMYR has three domains: extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular. The CTR and the RAMP have both <scene name='10/1037495/Extracellular_domain/7'>extracellular domains</scene> and <scene name='10/1037495/Transmembrane/6'>transmembrane domains</scene>. The calcitonin receptor is a 7-pass helix chain to which RAMP binds to become the amylin receptor. The ligand, amylin, binds within the transmembrane domain. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein G protein] is located <scene name='10/1037495/Intracellular_domain/2'>inside the cell</scene>. The location of each component of the amylin receptor is essential in determining structure and function. For example, it is important for the G protein to be located inside the cell in order to initiate a signal cascade for cell signaling. | [[Image:RAMP_diagram.jpg|500px|right|thumb|'''Figure 1.''' Three different RAMPs to compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the calcitonin receptor (shown in grey). RAMP1 is in red, RAMP2 is in blue, and RAMP3 is in green.]] AMYR has three domains: extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular. The CTR and the RAMP have both <scene name='10/1037495/Extracellular_domain/7'>extracellular domains</scene> and <scene name='10/1037495/Transmembrane/6'>transmembrane domains</scene>. The calcitonin receptor is a 7-pass helix chain to which RAMP binds to become the amylin receptor. The ligand, amylin, binds within the transmembrane domain. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein G protein] is located <scene name='10/1037495/Intracellular_domain/2'>inside the cell</scene>. The location of each component of the amylin receptor is essential in determining structure and function. For example, it is important for the G protein to be located inside the cell in order to initiate a signal cascade for cell signaling. | ||
| - | === Receptor | + | === Receptor Overview === |
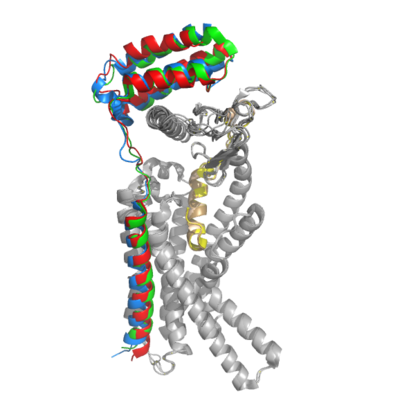
[[Image:Overlay of RAMPs.png|400 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 2.''' Superimposition of RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3. RAMP1 is red, RAMP2 is blue, and RAMP3 is green. The amylin ligand is dark yellow, and the calcitonin ligand is pale yellow.]] AMYR is a heterodimer of a calcitonin receptor and a receptor activity-modifying protein. There are three different RAMPs, RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3, that compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the CTR (Figure 1). The three different RAMPs are structurally similar to each other, so all three RAMPs are able to bind to the CTR without any modification of the CTR (Figure 2). | [[Image:Overlay of RAMPs.png|400 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 2.''' Superimposition of RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3. RAMP1 is red, RAMP2 is blue, and RAMP3 is green. The amylin ligand is dark yellow, and the calcitonin ligand is pale yellow.]] AMYR is a heterodimer of a calcitonin receptor and a receptor activity-modifying protein. There are three different RAMPs, RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3, that compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the CTR (Figure 1). The three different RAMPs are structurally similar to each other, so all three RAMPs are able to bind to the CTR without any modification of the CTR (Figure 2). | ||
In the absence of a RAMP, the calcitonin receptor has greater affinity for calcitonin than amylin, but because the <scene name='10/1037495/Overlay_of_ligands/1'>two ligands are structurally similar</scene>, both calcitonin and amylin can bind to the CTR without any modification of the receptor. The two ligands have many conserved residues (highlighted in blue), and this shows that the two ligands share many chemical properties which explains why they are structurally similar. In addition to having many conserved residues, both ligands also have an amidated C-terminus (Figure 3). When the CTR is bound to a RAMP, the complex becomes the AMYR and has greater affinity for the <scene name='10/1037495/Ligand_in_membrane/2'>amylin ligand</scene> relative to the calcitonin ligand. Therefore, the RAMP is essential to AMYR because it causes AMYR to have greater affinity for the amylin ligand rather than the calcitonin ligand. [[Image:Sequence alignment ligands.png|500px|left|thumb|'''Figure 3.''' Sequence alignment of rat amylin and salmon calcitonin. Conserved residues are highlighted in blue.]] | In the absence of a RAMP, the calcitonin receptor has greater affinity for calcitonin than amylin, but because the <scene name='10/1037495/Overlay_of_ligands/1'>two ligands are structurally similar</scene>, both calcitonin and amylin can bind to the CTR without any modification of the receptor. The two ligands have many conserved residues (highlighted in blue), and this shows that the two ligands share many chemical properties which explains why they are structurally similar. In addition to having many conserved residues, both ligands also have an amidated C-terminus (Figure 3). When the CTR is bound to a RAMP, the complex becomes the AMYR and has greater affinity for the <scene name='10/1037495/Ligand_in_membrane/2'>amylin ligand</scene> relative to the calcitonin ligand. Therefore, the RAMP is essential to AMYR because it causes AMYR to have greater affinity for the amylin ligand rather than the calcitonin ligand. [[Image:Sequence alignment ligands.png|500px|left|thumb|'''Figure 3.''' Sequence alignment of rat amylin and salmon calcitonin. Conserved residues are highlighted in blue.]] | ||
| + | === Ligands === | ||
The two major ligands of the calcitonin receptor are [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcitonin calcitonin] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amylin amylin]. Calcitonin is a peptide hormone secreted from the thyroid, and it is involved in the regulation of calcium and phosphate in the blood. Amylin is also a hormone and is secreted by pancreatic beta cells. Amylin binding activates many different biological processes affecting different systems with the human body. For example, amylin binding can affect the immune system, the central nervous system, and the satiation system in the brain (i.e., the area postrema). There are two required post-translational modifications of amylin in order for the ligand to have any bioactivity: (1) <scene name='10/1037495/C-term_amide/2'>amidation of the C-terminus</scene> and (2) a <scene name='10/1037495/Amylin_disulfide_bond2/4'>disulfide bond</scene> between C2 and C7. | The two major ligands of the calcitonin receptor are [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcitonin calcitonin] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amylin amylin]. Calcitonin is a peptide hormone secreted from the thyroid, and it is involved in the regulation of calcium and phosphate in the blood. Amylin is also a hormone and is secreted by pancreatic beta cells. Amylin binding activates many different biological processes affecting different systems with the human body. For example, amylin binding can affect the immune system, the central nervous system, and the satiation system in the brain (i.e., the area postrema). There are two required post-translational modifications of amylin in order for the ligand to have any bioactivity: (1) <scene name='10/1037495/C-term_amide/2'>amidation of the C-terminus</scene> and (2) a <scene name='10/1037495/Amylin_disulfide_bond2/4'>disulfide bond</scene> between C2 and C7. | ||
Revision as of 18:49, 24 April 2024
Amylin Receptor (AMYR)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
Student Contributors
- Kylie Blake
- Natalie Link
- Jaelin Lunato