We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox324
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Protein 4DIU: Structure, Function, and Significance in Biological Systems== | ==Protein 4DIU: Structure, Function, and Significance in Biological Systems== | ||
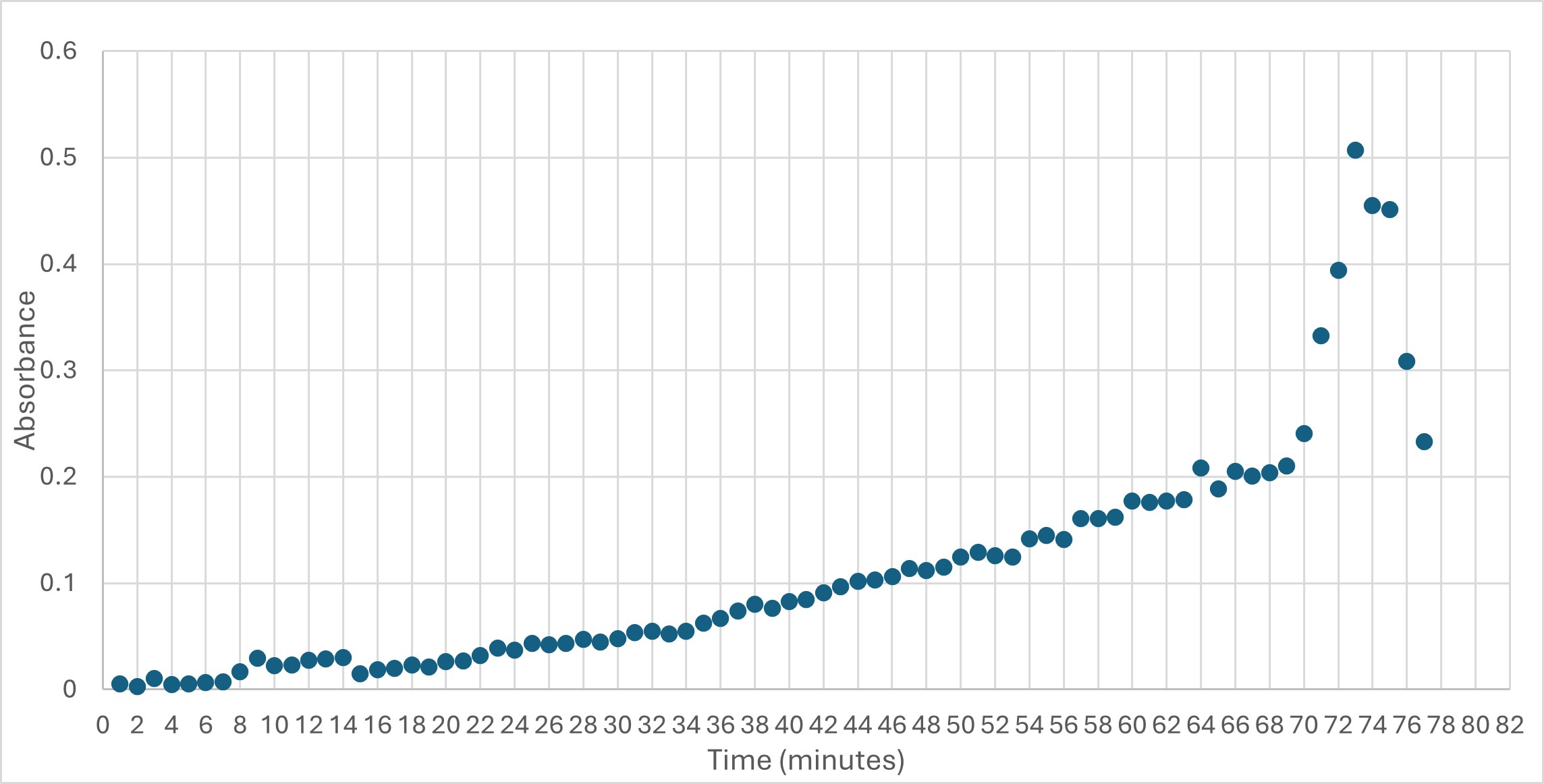
| - | The protein 4DIU has been identified and characterized as a potential esterase enzyme based on in-depth analyses including bioinformatics, molecular docking studies, and laboratory experiments. Online tools such as BLAST, Dali, and InterPro often matched 4DIU with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. This suggests that its function involves hydrolysis of esters. | + | The protein 4DIU has been identified and characterized as a potential esterase enzyme based on in-depth analyses including bioinformatics, molecular docking studies, and laboratory experiments. Online tools such as BLAST, Dali, and InterPro often matched 4DIU with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. This suggests that its function involves hydrolysis of esters. The protein 4DIU was grown, harvested, and isolated in a laboratory. SDS-PAGE analysis was used to confirm the identity of the protein via molecular weight. Once identified the enzyme's activity on the substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate was measured. |
<StructureSection load='4diu' size='340' side='right' caption='Structural Model of Protein 4DIU' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4diu' size='340' side='right' caption='Structural Model of Protein 4DIU' scene=''> | ||
Revision as of 19:42, 24 April 2024
Protein 4DIU: Structure, Function, and Significance in Biological Systems
The protein 4DIU has been identified and characterized as a potential esterase enzyme based on in-depth analyses including bioinformatics, molecular docking studies, and laboratory experiments. Online tools such as BLAST, Dali, and InterPro often matched 4DIU with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. This suggests that its function involves hydrolysis of esters. The protein 4DIU was grown, harvested, and isolated in a laboratory. SDS-PAGE analysis was used to confirm the identity of the protein via molecular weight. Once identified the enzyme's activity on the substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate was measured.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644