Introduction
In 1900, amylin deposits were first discovered in pancreatic islet cells in diabetic patients. Later in 1943, it was determined that these amylin deposits were amyloid in nature. By the 1980s, the 37 amino acid sequence of amylin was identified. By 1995, the first analogue of amylin, pramlintide, was synthesized. In the late 1990s, it was discovered, through cryogenic electron microscopy, that the amylin receptor was made of the calcitonin receptor (CT) core, which heterodimerizes with a receptor-activating modifying protein (RAMP) to form different amylin receptors. The human amylin receptor is also a G-protein coupled receptor.
Amylin
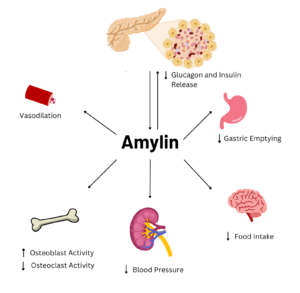
Figure 1. Effects of Amylin in Humans
Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized with insulin in the beta cells of pancreatic islets. It can cross the blood-brain barrier and regulates glucose homeostasis via inhibiting gastric emptying, inhibiting the release of glucagon, and inducing meal-ending satiety[1]. In doing so, it prevents spikes in blood glucose and overeating, making it a suitable target for Type 2 Diabetes treatments and therapies. Seeing as Type 2 Diabetes is a major risk factor for Alzheimer's Disease, as Type 2 Diabetes cases continue to increase, there will likely be a spike in Alzheimer’s Disease as well[2]. Therefore, it is vital that amylin, its receptor, and analogs, such as pramlintide, are understood to aid in rational drug design.

Figure 2. Amylin sequence alignment for human amylin, rat amylin, and pramlintide. Green represents fully conserved residues, pink represents positive to positive, red is nonpolar to nonpolar, and black is polar to nonpolar.
Amylin is extremely conserved among species to maintain proper structure and function. Some of the are Lysine 1, Cysteine 2, Alanine 5, Threonine 6, and Cysteine 7. These conserved residues exhibit extensive hydrogen bonding networks between other residues or surrounding water molecules. There is also a disulfide bond between C2 and C7 that is conserved across almost every species. This disulfide causes the N-terminus of amylin to wrap around.
Structure
Amylin Receptor
The amylin receptor (AMYR) is the result of the heterodimerization of the and a RAMP, such as . The patterns of peptide interaction between CT and AMYR are very similar overall, but amylin has a higher affinity for AMYR1 and AMYR3 than AMYR2[3].
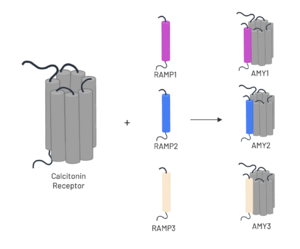
Figure 3. Heterodimerization of CT and RAMPs
Calcitonin Receptor and G-alpha Interactions
The calcitonin receptor forms several highly conserved interactions with the Gɑ subunit. The , as do the , respectively[3].
RAMPs
To form the full AMYR complex, the calcitonin receptor must bind to one of three RAMPs: , , . The three RAMPs have 31% sequence identity and bind very similarly to the CT, except RAMP2 has slightly looser packing[3]. All three RAMPs serve the purpose of drastically increasing the CT’s binding affinity for amylin. RAMP3 is the version most heavily implicated in pramlintide targeting and Alzheimer’s Disease.
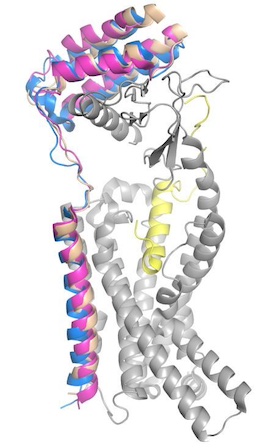
Figure 4. Superimposed RAMP1 (pink), RAMP2 (blue), and RAMP3 (tan) in the human amylin receptor (CT is gray).
Amylin Binding
Y37 of amylin, the C-terminal residue, forms hydrogen bonds with or . It also forms van der Waals interactions with or W84 and P85 in both and . Uniquely, in RAMP3, W84 can adopt two conformations in RAMP3; one of which lies closer to Y37 and the other aligns almost perfectly with W84’s placement in RAMP1[3].
Amylin Receptor Functional Overview
Hydrophobic Interactions
on the C-terminus of the amylin peptide has extensive van der Waals interactions with the CT and RAMP3. The pi stacking and hydrophobic interactions increase the affinity and interactions between the amylin peptide, CT, and RAMP3, aiding in their association.
Amidated C-Terminus
Y37 of amylin is amidated. The on the calcitonin receptor. All biological activity was lost when this amide group was experimentally removed[3].
T6
, a highly conserved residue of amylin in the disulfide loop, interacts with H302 on the calcitonin receptor[3].
R11
is situated toward the N-terminal end of amylin’s main alpha helix and is packed against the residues at the N-terminus. This residue forms multiple interactions with various residues to keep the N-terminal end of the helix and the disulfide loop in place. R11 pulls on the backbones of C2 and C4 in the disulfide loop and interacts with the backbones of N3 and A8. It also attracts the hydroxyl group of Y372 of the calcitonin receptor. Furthermore, R11 stabilizes various nearby waters to form bridges between amylin and the receptor[3].
R18
lies at the C-terminal end of the main alpha helix and can adopt two different configurations. The “upper” configuration provides stronger interactions with various residues on the calcitonin receptor and is potentially what causes the helix to terminate around R18. Specifically, R18 interacts with the sidechain of D97 and the backbones of F99, P100, and F102. The latter three residues may also form van der Waals interactions and pi stacking with each other[3].
T9 Water Network
Threonine 9 is an essential residue for stabilization of amylin in the receptor, as its side chain is polar which allows it to hydrogen bond with other nearby polar groups, leading to extensive networks of interactions. T9 interacts with the of the calcitonin receptor and many surrounding water molecules, but it also interacts with the . All of these interactions create a very strong interaction between amylin and the receptor. The water network also helps stabilize the active receptor conformation.
Disease
Pramlintide Analogue
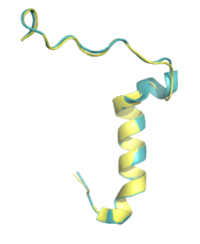
Figure 5. Pramlintide (teal) and Rat Amylin (yellow) have very similar structures and binding interactions with AMYR3. PDB: 7TZF and 8F2B
The first human amylin analogue, , was developed in 1995, and marked a significant advancement in the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes[4]. As of 2024, it is the only FDA-approved drug for the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes using the AMYR as a target. Recent studies in rodent Alzheimer’s Disease models suggest that pramlintide reduces amyloid-beta plaques, making it a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s Disease[2].
There is limited knowledge about how human amylin binds to the human AMYR, so many studies utilize rat amylin as the peptide for the human AMYR. Rat amylin and pramlintide showcase very similar structures and maintain a high sequence similarity. For instance, the N-term lysine residue is conserved between and , as well as human amylin[3], suggesting that the lysine is integral for binding to AMYR. One of these residue changes is . Another mutation is . S19 is highly conserved in most observed variants of amylin, as the [3] [4]. Other mutations include in rat amylin to in pramlintide and in rat amylin to in pramlintide. While these residues differ, the overall properties of the various residues remain consistent, so many of the same interactions with AMYR are likely still able to form.
Rat amylin and pramlintide have 3 proline residues, which are absent in human amylin. Human amylin and pramlintide only differ at these 3 residues, with all three being changed to proline in pramlintide. The mutations break the helical nature present in human amylin, which likely prevents the aggregation of amyloid beta plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease.





