This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Brynn Baker/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Amylin == | == Amylin == | ||
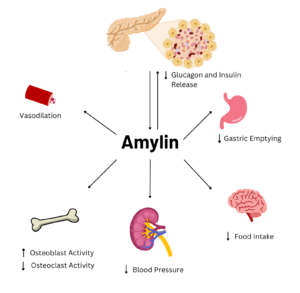
[[Image:AmylinFlowchart.png|300 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Effects of Amylin in Humans]] | [[Image:AmylinFlowchart.png|300 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Effects of Amylin in Humans]] | ||
| - | Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized with insulin in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_cell beta cells] of pancreatic islets. It can cross the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood%E2%80%93brain_barrier blood-brain barrier] and regulates glucose homeostasis via inhibiting gastric emptying, inhibiting the release of glucagon, and inducing meal-ending satiety<ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. In doing so, it prevents spikes in blood glucose and overeating, making it a suitable target for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes Type 2 Diabetes] treatments and therapies. | + | Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized with insulin in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_cell beta cells] of pancreatic islets. It can cross the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood%E2%80%93brain_barrier blood-brain barrier] and regulates glucose homeostasis via inhibiting gastric emptying, inhibiting the release of glucagon, and inducing meal-ending satiety<ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. In doing so, it prevents spikes in blood glucose and overeating, making it a suitable target for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes Type 2 Diabetes] treatments and therapies. Since Type 2 Diabetes is a major risk factor for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer%27s_disease Alzheimer's Disease], as Type 2 Diabetes cases continue to increase, there will likely be a spike in Alzheimer’s Disease as well<ref name="Grizzanti">PMID:30282360</ref>. Therefore, it is vital that amylin, its receptor, and analogs, such as pramlintide, are understood to aid in rational drug design. |
| - | + | ||
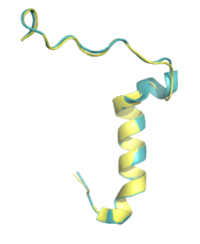
Amylin is extremely conserved among species to maintain proper structure and function. Some of the <scene name='10/1037520/Conserved_residues/1'>main conserved residues</scene> are Lysine 1, Cysteine 2, Alanine 5, Threonine 6, and Cysteine 7. These conserved residues exhibit extensive hydrogen bonding networks between other residues or surrounding water molecules. There is also a disulfide bond between C2 and C7 that is conserved across almost every species. This disulfide causes the N-terminus of amylin to wrap around. | Amylin is extremely conserved among species to maintain proper structure and function. Some of the <scene name='10/1037520/Conserved_residues/1'>main conserved residues</scene> are Lysine 1, Cysteine 2, Alanine 5, Threonine 6, and Cysteine 7. These conserved residues exhibit extensive hydrogen bonding networks between other residues or surrounding water molecules. There is also a disulfide bond between C2 and C7 that is conserved across almost every species. This disulfide causes the N-terminus of amylin to wrap around. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Amylin_alignment_sequence.png|400 px|left|thumb|Figure 2. Amylin sequence alignment for human amylin, rat amylin, and pramlintide. Green represents fully conserved residues, pink represents positive to positive, red is nonpolar to nonpolar, and black is polar to nonpolar.]] | ||
=== Structure === | === Structure === | ||
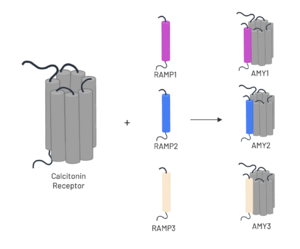
== Amylin Receptor == | == Amylin Receptor == | ||
Revision as of 00:22, 25 April 2024
Homo sapiens Amylin3 Receptor, AMYR3
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):564-600. PMID:26071095 doi:10.1124/pr.115.010629
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Grizzanti J, Corrigan R, Casadesus G. Neuroprotective Effects of Amylin Analogues on Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Cognition. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(1):11-23. PMID:30282360 doi:10.3233/JAD-180433
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bower RL, Hay DL. Amylin structure-function relationships and receptor pharmacology: implications for amylin mimetic drug development. Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;173(12):1883-98. PMID:27061187 doi:10.1111/bph.13496
Student Contributors
- Brynn Baker
- Emily Berkman
- Sepp Hall