We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Mandy Bechman/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===History=== | ===History=== | ||
The idea of incretin, and subsequently GIP, began in 1902 after the discovery of secretin by Bayliss and Starling. Inspired by their discovery, Moore et al. hypothesized that there must be some kind of gut hormone that regulates the endocrine pancreas. His experiments showed that gut extracts in patients with diabetes have reduced amounts of sugars in their urine as a result of endocrine stimulation. In 1929, a French scientist named La Barre was able to purify incretin (INtestine seCREtion INsulin) from gut extracts. The idea of incretin slowly lost attention until the 1960s when radioimmunoassay became available to measure incretin levels. GIP and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) were the two gut based hormones that were proven to act as incretins. GIP was found to be located in the K cells of the upper small intestines in humans. At first, it was titled a gastric inhibitory polypeptide because of its ability to inhibit gastric acid secretion after being isolating from porcine intestines. Later, they discovered that when GIP was administered in healthy volunteers, it stimulated insulin secretion by acting directly on pancreatic islets. As a result of these discoveries, they renamed it glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, becoming the first known incretin.<ref name="Seino"/> | The idea of incretin, and subsequently GIP, began in 1902 after the discovery of secretin by Bayliss and Starling. Inspired by their discovery, Moore et al. hypothesized that there must be some kind of gut hormone that regulates the endocrine pancreas. His experiments showed that gut extracts in patients with diabetes have reduced amounts of sugars in their urine as a result of endocrine stimulation. In 1929, a French scientist named La Barre was able to purify incretin (INtestine seCREtion INsulin) from gut extracts. The idea of incretin slowly lost attention until the 1960s when radioimmunoassay became available to measure incretin levels. GIP and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) were the two gut based hormones that were proven to act as incretins. GIP was found to be located in the K cells of the upper small intestines in humans. At first, it was titled a gastric inhibitory polypeptide because of its ability to inhibit gastric acid secretion after being isolating from porcine intestines. Later, they discovered that when GIP was administered in healthy volunteers, it stimulated insulin secretion by acting directly on pancreatic islets. As a result of these discoveries, they renamed it glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, becoming the first known incretin.<ref name="Seino"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Structure Overview== | ==Structure Overview== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
===Mechanism=== | ===Mechanism=== | ||
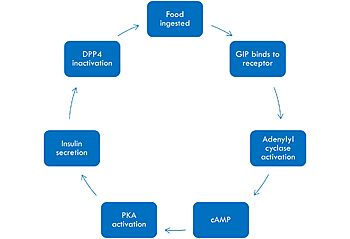
The mechanism of GIP begins with the ingestion of food. This stimulates GIP to bind to its receptor. Once bound, the activated G alpha protein moves laterally in the membrane in order to activate its target, adenylyl cyclase. Once adenylyl cyclase is activated, it catalyzes the formation of cyclic AMP (cAMP). This molecule activates Protein Kinase A (PKA), which signals the secretin of insulin. After a few minutes of active signaling, this hormone is recognized and inactivated by a peptidase called DPP-4 (dipeptidyl peptidase-4) by cleaving the first two amino acids.<ref name="Mayendraraj"/> | The mechanism of GIP begins with the ingestion of food. This stimulates GIP to bind to its receptor. Once bound, the activated G alpha protein moves laterally in the membrane in order to activate its target, adenylyl cyclase. Once adenylyl cyclase is activated, it catalyzes the formation of cyclic AMP (cAMP). This molecule activates Protein Kinase A (PKA), which signals the secretin of insulin. After a few minutes of active signaling, this hormone is recognized and inactivated by a peptidase called DPP-4 (dipeptidyl peptidase-4) by cleaving the first two amino acids.<ref name="Mayendraraj"/> | ||
| - | |||
===Diseases=== | ===Diseases=== | ||
Malfunction of the GIP protein can result in some serious life-threatening diseases. Overexpression of GIP can result in obesity by promoting fat disposition in adipocyte tissues as well as an inability to regulate food intake and control appetite. Underexpression of GIP can result in diabetes. | Malfunction of the GIP protein can result in some serious life-threatening diseases. Overexpression of GIP can result in obesity by promoting fat disposition in adipocyte tissues as well as an inability to regulate food intake and control appetite. Underexpression of GIP can result in diabetes. | ||
| + | ===Tirzepatide=== | ||
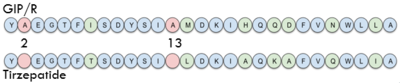
| + | One of the most promising treatments to GIP malfunction is <scene name='10/1038867/Tirzepatide/2'>Tirzepatide</scene>, also known as Mounjaro, created by Eli Lily. It is an antidiabetic as well as weight loss drug. The structure of Tirzepatide functions as an incretin receptor agonist to GIP by activating GIP's receptor and producing insulin. | ||
| + | [[Image:Sequence.png|400 px|left|thumb|Sequence comparison of the first 28 residues of GIP and Tirzepatide.]] | ||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
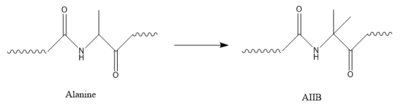
| + | [[Image:AlatoAIB.png|400 px|left|thumb|Structure of alanine converted to AIB.]] | ||
| - | ===Tirzepatide=== | ||
| - | One of the most promising treatments to GIP malfunction is <scene name='10/1038867/Tirzepatide/2'>Tirzepatide</scene>, also known as Mounjaro, created by Eli Lily. It is an antidiabetic as well as weight loss drug. The structure of Tirzepatide functions as an incretin receptor agonist to GIP by activating GIP's receptor and producing insulin. | ||
| - | [[Image:Sequence.png|400 px|left|thumb|Sequence comparison of the first 28 residues of GIP and Tirzepatide.]] | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
In GIP, the residue 2 is an <scene name='10/1038867/Alanine_2_-_gip/3'>alanine</scene> but in Tirzepatide, the residue changes to <scene name='10/1038867/Tirzepatide_-_aib/2'>AIB</scene> | In GIP, the residue 2 is an <scene name='10/1038867/Alanine_2_-_gip/3'>alanine</scene> but in Tirzepatide, the residue changes to <scene name='10/1038867/Tirzepatide_-_aib/2'>AIB</scene> | ||
| - | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | [[Image:AlatoAIB.png|400 px|left|thumb|Structure of alanine converted to AIB.]] | ||
This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
<ref name="Mayendraraj">PMID:35065096</ref>. | <ref name="Mayendraraj">PMID:35065096</ref>. | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Student Contributors== | ||
| + | Mandy M. Bechman | ||
| + | Chloe A. Tucker | ||
Revision as of 13:20, 25 April 2024
H. sapiens Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Mayendraraj A, Rosenkilde MM, Gasbjerg LS. GLP-1 and GIP receptor signaling in beta cells interactions and co-stimulation. Peptides. 2022 May;151:170749. PMID:35065096 doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170749
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Seino Y, Fukushima M, Yabe D. GIP and GLP-1, the two incretin hormones: Similarities and differences. J Diabetes Investig. 2010 Apr 22;1(1-2):8-23. PMID:24843404 doi:10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00022.x
Student Contributors
Mandy M. Bechman Chloe A. Tucker