User:Chloe Tucker/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
=== Binding/Active Site of GIPR with GIP === | === Binding/Active Site of GIPR with GIP === | ||
[[Image:GIP_hydrogen_bonds.jpg|350 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Residue Interactions with GIP]] | [[Image:GIP_hydrogen_bonds.jpg|350 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Residue Interactions with GIP]] | ||
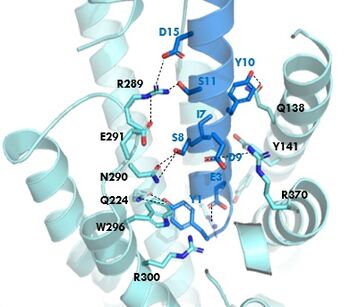
| - | The <scene name='10/1038815/Overview/3'>binding site</scene> of GIP with the GIP receptor (GIPR) is where the N-term of GIP binds with the transmembrane domain of the GIP receptor. This first interaction formed with GIPR and the N-term of GIP is a hydrogen bond between | + | The <scene name='10/1038815/Overview/3'>binding site</scene> of GIP with the GIP receptor (GIPR) is where the N-term of GIP binds with the transmembrane domain of the GIP receptor. This first interaction formed with GIPR and the N-term of GIP is a hydrogen bond between Tyrosine 1 (Y1) and Glutamine 224 (Q224) to activate the G-protein to start sending signals to the cell. |
| - | + | Many other <scene name='10/1038815/Active_site/3'>residues</scene> within the binding site are forming hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions between the ligand and the receptor. The N-term binds more strongly than the C-term and there are many different residues contributing to this, including, Tyrosine 1 (Y1) and Tryptophan (W296) are forming aromatic interactions. Serine 8 (S8) and Asparagine 290 (N290) are forming two hydrogen bonds with each other. Aspartate 9 (D9) is forming another hydrogen bond with Arginine 370 (R370). | |
=== Binding/Active Site of GIPR with Tirzepatide === | === Binding/Active Site of GIPR with Tirzepatide === | ||
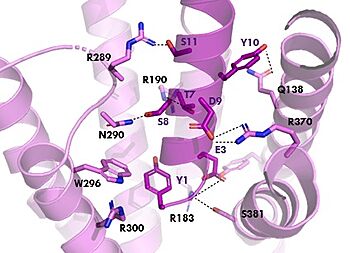
[[Image:TZ_hydrogen_bonds.jpg|350 px|right|thumb|Figure 2. Residue Interactions with Tirzepatide]] | [[Image:TZ_hydrogen_bonds.jpg|350 px|right|thumb|Figure 2. Residue Interactions with Tirzepatide]] | ||
Revision as of 13:34, 25 April 2024
GIP and GIP-R
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Sun B, Willard FS, Feng D, Alsina-Fernandez J, Chen Q, Vieth M, Ho JD, Showalter AD, Stutsman C, Ding L, Suter TM, Dunbar JD, Carpenter JW, Mohammed FA, Aihara E, Brown RA, Bueno AB, Emmerson PJ, Moyers JS, Kobilka TS, Coghlan MP, Kobilka BK, Sloop KW. Structural determinants of dual incretin receptor agonism by tirzepatide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Mar 29;119(13):e2116506119. PMID:35333651 doi:10.1073/pnas.2116506119
Student Contributors
- Chloe Tucker
- Mandy Bechman