This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Isabel Kluszynski/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
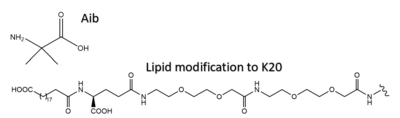
[[Image:Aib_and_C20.png|400 px|right|thumb|Structure of 2-Aminoisobutyric acid and the C20 fatty diacid moiety. Tirzepatide is modified with Aib at position 2 and 13 and the fatty diacid at K20.]] | [[Image:Aib_and_C20.png|400 px|right|thumb|Structure of 2-Aminoisobutyric acid and the C20 fatty diacid moiety. Tirzepatide is modified with Aib at position 2 and 13 and the fatty diacid at K20.]] | ||
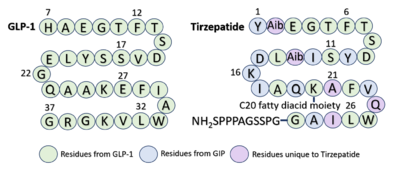
| - | Several residues have been selectively and intentionally modified during Tirzepatide drug design. <scene name='10/1037487/Interesting_tirz_modifications/3'>Aib</scene>, aminoisobutyric acid, is located at position 2 and 13 with the purpose of preventing DPP-4 cleavage. K20 of Tirzepatide has a lipid modification, specifically a C20 fatty diacid moiety, that serves to enhance binding to the protein carrier albumin and increase the half-life of the drug in the body. <ref name="Sun"/> | + | Several residues have been selectively and intentionally modified during Tirzepatide drug design. <scene name='10/1037487/Interesting_tirz_modifications/3'>Aib</scene>, aminoisobutyric acid, is located at position 2 and 13 with the purpose of preventing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dipeptidyl_peptidase-4#:~:text=Dipeptidyl%20peptidase-4%20%28DPP4%20or%20DPPIV%29%2C%20also%20known%20as,DPP4%20is%20related%20to%20FAP%2C%20DPP8%2C%20and%20DPP9. DPP-4] cleavage. K20 of Tirzepatide has a lipid modification, specifically a C20 fatty diacid moiety, that serves to enhance binding to the protein carrier albumin and increase the half-life of the drug in the body. <ref name="Sun"/> |
Similarly to GLP-1 forming several stabilizing interactions with GLP-1R, Tirzepatide also forms many key <scene name='10/1037490/Tirzepatidebonding/9'>stabilizing interactions</scene>. Beginning at the N terminus of Tirzepatide (Tirz), <scene name='10/1037490/Tirzepatidebonding/11'>Tirz E3</scene> forms a salt bridge with GLP-1R R190 and a hydrogen bond with GLP-1R Y152. Additionally, Tirz T7 hydrogen bonds with GLP-1R K197. These interactions are nearly identical to the interactions GLP-1 E9 and T13 make with the receptor. Towards the middle of the peptide, <scene name='10/1037490/Tirzepatidebonding/10'>Tirz D15</scene> forms a hydrogen bond with Y205, yet another similar interaction to GLP-1 binding. <ref name="Zhao"/> Looking at the sequence comparison of GLP-1 and Tirzepatide, GLP-1 E21 is located at the same position as Tirz D15. | Similarly to GLP-1 forming several stabilizing interactions with GLP-1R, Tirzepatide also forms many key <scene name='10/1037490/Tirzepatidebonding/9'>stabilizing interactions</scene>. Beginning at the N terminus of Tirzepatide (Tirz), <scene name='10/1037490/Tirzepatidebonding/11'>Tirz E3</scene> forms a salt bridge with GLP-1R R190 and a hydrogen bond with GLP-1R Y152. Additionally, Tirz T7 hydrogen bonds with GLP-1R K197. These interactions are nearly identical to the interactions GLP-1 E9 and T13 make with the receptor. Towards the middle of the peptide, <scene name='10/1037490/Tirzepatidebonding/10'>Tirz D15</scene> forms a hydrogen bond with Y205, yet another similar interaction to GLP-1 binding. <ref name="Zhao"/> Looking at the sequence comparison of GLP-1 and Tirzepatide, GLP-1 E21 is located at the same position as Tirz D15. | ||
Revision as of 13:45, 25 April 2024
=GLP-1R Homo Sapiens=
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Mayendraraj A, Rosenkilde MM, Gasbjerg LS. GLP-1 and GIP receptor signaling in beta cells interactions and co-stimulation. Peptides. 2022 May;151:170749. PMID:35065096 doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170749
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Seino Y, Fukushima M, Yabe D. GIP and GLP-1, the two incretin hormones: Similarities and differences. J Diabetes Investig. 2010 Apr 22;1(1-2):8-23. PMID:24843404 doi:10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00022.x
- ↑ Zhang X, Belousoff MJ, Zhao P, Kooistra AJ, Truong TT, Ang SY, Underwood CR, Egebjerg T, Šenel P, Stewart GD, Liang YL, Glukhova A, Venugopal H, Christopoulos A, Furness SGB, Miller LJ, Reedtz-Runge S, Langmead CJ, Gloriam DE, Danev R, Sexton PM, Wootten D. Differential GLP-1R Binding and Activation by Peptide and Non-peptide Agonists. Mol Cell. 2020 Nov 5;80(3):485-500.e7. PMID:33027691 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.09.020
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Zhao F, Zhou Q, Cong Z, Hang K, Zou X, Zhang C, Chen Y, Dai A, Liang A, Ming Q, Wang M, Chen LN, Xu P, Chang R, Feng W, Xia T, Zhang Y, Wu B, Yang D, Zhao L, Xu HE, Wang MW. Structural insights into multiplexed pharmacological actions of tirzepatide and peptide 20 at the GIP, GLP-1 or glucagon receptors. Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 25;13(1):1057. PMID:35217653 doi:10.1038/s41467-022-28683-0
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Sun B, Willard FS, Feng D, Alsina-Fernandez J, Chen Q, Vieth M, Ho JD, Showalter AD, Stutsman C, Ding L, Suter TM, Dunbar JD, Carpenter JW, Mohammed FA, Aihara E, Brown RA, Bueno AB, Emmerson PJ, Moyers JS, Kobilka TS, Coghlan MP, Kobilka BK, Sloop KW. Structural determinants of dual incretin receptor agonism by tirzepatide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Mar 29;119(13):e2116506119. PMID:35333651 doi:10.1073/pnas.2116506119
Student Contributors
- Isabel Kluszynski
- Makenna Marcinek