Sandbox324
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Protein 4DIU: Structure, Function, and Significance in Biological Systems== | ==Protein 4DIU: Structure, Function, and Significance in Biological Systems== | ||
| - | |||
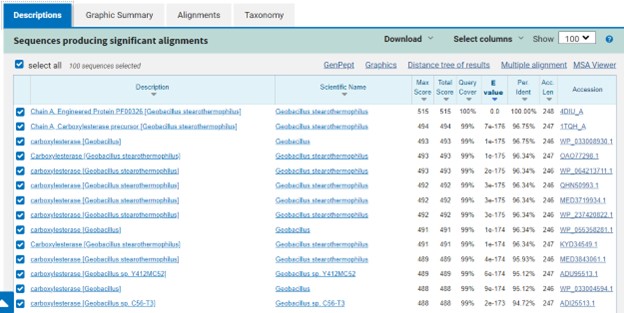
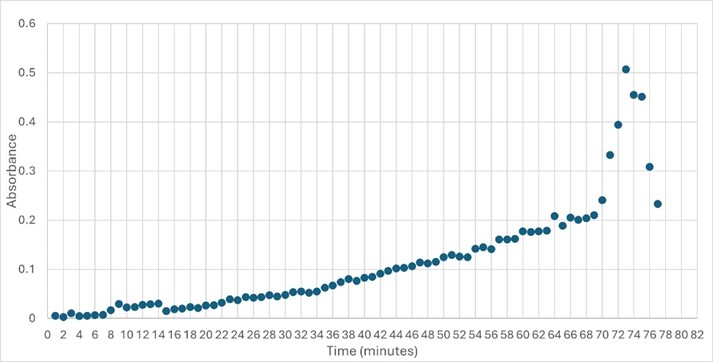
The protein 4DIU has been identified and characterized as a potential esterase enzyme based on in-depth analyses including bioinformatics, molecular docking studies, and laboratory experiments. Online tools such as BLAST, Dali, and InterPro often matched 4DIU with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. This suggests that its function involves hydrolysis of esters. In part to data from Swiss Dock, 4DIU is predicted to have binding sites with an affinity to substrates such as acetate, butyrate, phosphate, proline, decanoate, and dodecanoate. The protein 4DIU was grown, harvested, and isolated in a laboratory. SDS-PAGE analysis was used to confirm the identity of the protein via molecular weight. Once identified the enzyme's activity on the substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate was measured. This substrate was chosen because many hydrolases have an affinity for it and can hydrolyze the substrate. It was determined that the 4DIU protein functions best at a pH of 6. | The protein 4DIU has been identified and characterized as a potential esterase enzyme based on in-depth analyses including bioinformatics, molecular docking studies, and laboratory experiments. Online tools such as BLAST, Dali, and InterPro often matched 4DIU with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. This suggests that its function involves hydrolysis of esters. In part to data from Swiss Dock, 4DIU is predicted to have binding sites with an affinity to substrates such as acetate, butyrate, phosphate, proline, decanoate, and dodecanoate. The protein 4DIU was grown, harvested, and isolated in a laboratory. SDS-PAGE analysis was used to confirm the identity of the protein via molecular weight. Once identified the enzyme's activity on the substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate was measured. This substrate was chosen because many hydrolases have an affinity for it and can hydrolyze the substrate. It was determined that the 4DIU protein functions best at a pH of 6. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 11: | ||
== Proposed Function == | == Proposed Function == | ||
| - | |||
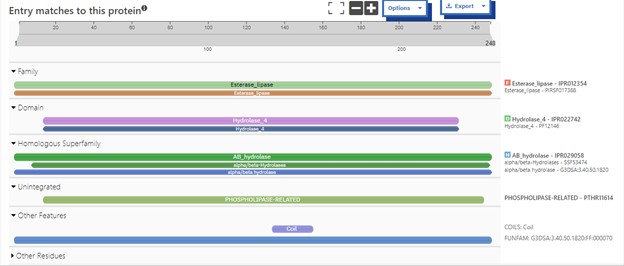
This protein has alpha/beta-hydrolase activity and is of the esterase family. The SPRITE, BLAST, InterPro, and Dali Search along with other bioinformatics analyses consistently matched with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. SPRITE provided proteins that had similar residues in the active site of the enzyme. Multiple of the matching proteins were esterases and had an RMSD value of <0.5. The RMSD value gives insight into how similar the overlapping sections for the unknown and known proteins are. A value of less than 2 is desired when choosing proteins for reference as a value closer to zero means less deviation between sites.[[Image:Sprite.jpg]] | This protein has alpha/beta-hydrolase activity and is of the esterase family. The SPRITE, BLAST, InterPro, and Dali Search along with other bioinformatics analyses consistently matched with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. SPRITE provided proteins that had similar residues in the active site of the enzyme. Multiple of the matching proteins were esterases and had an RMSD value of <0.5. The RMSD value gives insight into how similar the overlapping sections for the unknown and known proteins are. A value of less than 2 is desired when choosing proteins for reference as a value closer to zero means less deviation between sites.[[Image:Sprite.jpg]] | ||
Additional evidence is provided by InteroPro which provided more information about the classification of the protein. As well, the BLAST search gave results of matching proteins and the specific functions of the proteins. All results again matched what was suggested by Sprite and Blast, further solidifying that 4DIU is an esterase with alpha/beta-hydrolase activity. | Additional evidence is provided by InteroPro which provided more information about the classification of the protein. As well, the BLAST search gave results of matching proteins and the specific functions of the proteins. All results again matched what was suggested by Sprite and Blast, further solidifying that 4DIU is an esterase with alpha/beta-hydrolase activity. | ||
Revision as of 22:56, 25 April 2024
Protein 4DIU: Structure, Function, and Significance in Biological Systems
The protein 4DIU has been identified and characterized as a potential esterase enzyme based on in-depth analyses including bioinformatics, molecular docking studies, and laboratory experiments. Online tools such as BLAST, Dali, and InterPro often matched 4DIU with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. This suggests that its function involves hydrolysis of esters. In part to data from Swiss Dock, 4DIU is predicted to have binding sites with an affinity to substrates such as acetate, butyrate, phosphate, proline, decanoate, and dodecanoate. The protein 4DIU was grown, harvested, and isolated in a laboratory. SDS-PAGE analysis was used to confirm the identity of the protein via molecular weight. Once identified the enzyme's activity on the substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate was measured. This substrate was chosen because many hydrolases have an affinity for it and can hydrolyze the substrate. It was determined that the 4DIU protein functions best at a pH of 6.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1186%2F1471-2180-12-27