Sandbox324
From Proteopedia
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
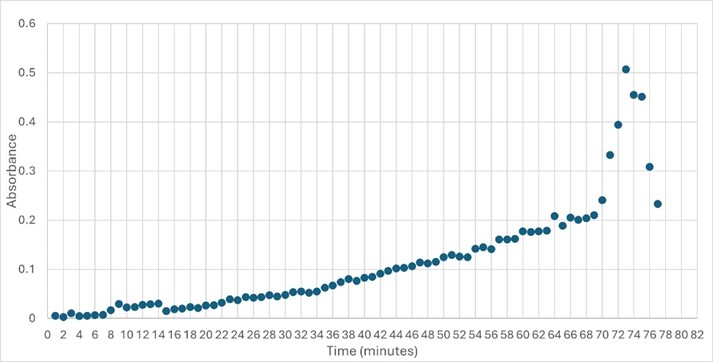
SwissDock and Chimera allowed for protein-ligand docking studies. Many of the highlighted interactions were ester-containing ligands and others were susceptible to hydrolysis. The hydrolase activity of the protein needed to be tested with a substrate known to work with hydrolases. This substrate is p-nitrophenyl acetate PNP when hydrolyzed produces a yellow colored product. The yellow product will lead to the solution absorbing more at 405nm. <ref>Zhang, S.; Sun, W.; Xu, L.; Zheng, X.; Chu, X.; Tian, J.; Wu, N.; Fan, Y. Identification of the Para-Nitrophenol Catabolic Pathway, and Characterization of Three Enzymes Involved in the Hydroquinone Pathway, in Pseudomonas Sp. 1-7. BMC Microbiology 2012, 12 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-27. | SwissDock and Chimera allowed for protein-ligand docking studies. Many of the highlighted interactions were ester-containing ligands and others were susceptible to hydrolysis. The hydrolase activity of the protein needed to be tested with a substrate known to work with hydrolases. This substrate is p-nitrophenyl acetate PNP when hydrolyzed produces a yellow colored product. The yellow product will lead to the solution absorbing more at 405nm. <ref>Zhang, S.; Sun, W.; Xu, L.; Zheng, X.; Chu, X.; Tian, J.; Wu, N.; Fan, Y. Identification of the Para-Nitrophenol Catabolic Pathway, and Characterization of Three Enzymes Involved in the Hydroquinone Pathway, in Pseudomonas Sp. 1-7. BMC Microbiology 2012, 12 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-27. | ||
| - | </ref>. This allows for the activity of the enzyme to be tracked by measuring the increase in absorbance over time. The isolated protein was introduced to p-nitrophenyl acetate in a buffer with a determined optimal pH of 6. Enzyme activity was measured via a change in absorbance at 405nm over 80 minutes. The data collected was consistent with that of hydrolases in other studies.<ref>[https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081346]</ref> | + | </ref>. This allows for the activity of the enzyme to be tracked by measuring the increase in absorbance over time. The isolated protein was introduced to p-nitrophenyl acetate in a buffer with a determined optimal pH of 6. Enzyme activity was measured via a change in absorbance at 405nm over 80 minutes. The data collected was consistent with that of hydrolases in other studies.<ref>[[https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081346]]</ref> |
[[Image:Enzymeactivity.jpeg]] | [[Image:Enzymeactivity.jpeg]] | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 00:00, 26 April 2024
Protein 4DIU: Structure, Function, and Significance in Biological Systems
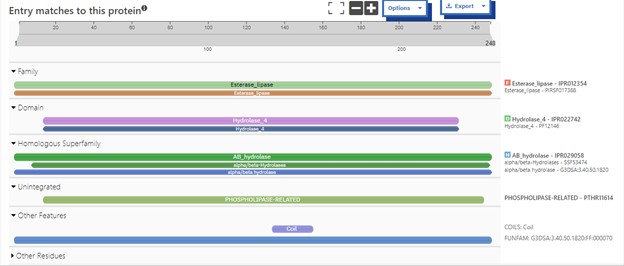
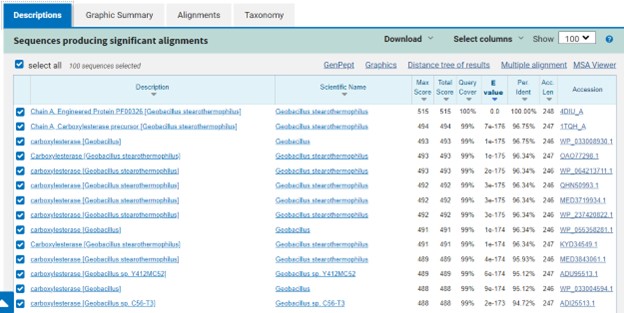
The protein 4DIU has been identified and characterized as a potential esterase enzyme based on in-depth analyses including bioinformatics, molecular docking studies, and laboratory experiments. Online tools such as BLAST, Dali, and InterPro often matched 4DIU with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. This suggests that its function involves hydrolysis of esters. In part to data from Swiss Dock, 4DIU is predicted to have binding sites with an affinity to substrates such as acetate, butyrate, phosphate, proline, decanoate, and dodecanoate. The protein 4DIU was grown, harvested, and isolated in a laboratory. SDS-PAGE analysis was used to confirm the identity of the protein via molecular weight. Once identified the enzyme's activity on the substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate was measured. This substrate was chosen because many hydrolases have an affinity for it and can hydrolyze the substrate. It was determined that the 4DIU protein functions best at a pH of 6.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Zhang, S.; Sun, W.; Xu, L.; Zheng, X.; Chu, X.; Tian, J.; Wu, N.; Fan, Y. Identification of the Para-Nitrophenol Catabolic Pathway, and Characterization of Three Enzymes Involved in the Hydroquinone Pathway, in Pseudomonas Sp. 1-7. BMC Microbiology 2012, 12 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-27.
- ↑ [[1]]