History and Discovery
In the early 1900s, amyloid protein deposits were found in the pancreatic tissue of diabetic patients. Later in 1999, the structure of the calcitonin receptors were determined, and it was determined that the amylin receptor (AMYR)[1] had a core structure of the calcitonin receptor (CTR). Additionally, it was determined that AMYR had a receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP) bound to the CTR core. In 2000, the CTR and a RAMP were co-expressed in a single cell, and later in 2016 the CTR and a RAMP were both found in rat brain cells.
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) was used to determine the structure of the calcitonin receptor and later the structure of AMYR. NMR and x-ray crystallography were also used to determine the structure but the resolution was poor relative to cryo-EM.
Structure
Cellular Domains
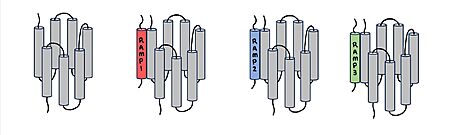
Figure 1. Three different RAMPs to compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the calcitonin receptor (shown in grey). RAMP1 is red, RAMP2 is blue, and RAMP3 is green.
AMYR has three domains: extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular. The CTR and the RAMP have both and . The calcitonin receptor is a 7-pass helix chain to which RAMP binds to become the amylin receptor.
[2] The ligand, amylin, binds within the transmembrane domain. The
G protein is located . The location of each component of the amylin receptor is essential in determining structure and function. For example, it is important for the G protein to be located inside the cell in order to initiate a signal cascade for cell signaling.
[3]
CTR and RAMP Heterodimer
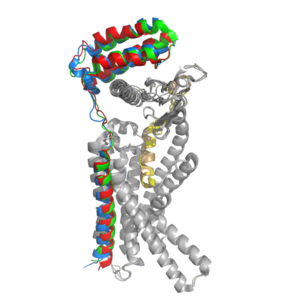
Figure 2. Superimposition of RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3. RAMP1 is red, RAMP2 is blue, and RAMP3 is green. The amylin ligand is dark yellow, and the calcitonin ligand is pale yellow.
AMYR is a heterodimer of a calcitonin receptor and a receptor activity-modifying protein. There are three different RAMPs, RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3, that compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the CTR (Figure 1). The three different RAMPs are structurally similar to each other, so all three RAMPs are able to bind to the CTR without any modification of the CTR (Figure 2).
[2]
In the absence of a RAMP, the calcitonin receptor has greater affinity for calcitonin than amylin, but because the , both calcitonin and amylin can bind to the CTR without any modification of the receptor. The two ligands have many conserved residues (highlighted in blue), therefore, the two ligands share many chemical properties which translates to structural similarity. In addition to having many conserved residues, both ligands have an amidated C-terminus (Figure 3).
[2] When the CTR is bound to a RAMP, the complex becomes the AMYR and has greater affinity for the relative to the calcitonin ligand.
[2] Therefore, the RAMP is essential to AMYR because it causes AMYR to have greater affinity for the amylin ligand rather than the calcitonin ligand.

Figure 3. Sequence alignment of rat amylin and salmon calcitonin. Conserved residues are highlighted in blue.
Ligands
The two major ligands of AMYR are calcitonin and amylin. Calcitonin is a peptide hormone secreted from the thyroid, and it is involved in the regulation of calcium and phosphate in the blood. Amylin is also a hormone and is secreted by pancreatic beta cells. Amylin binding activates many different biological processes which affects different systems within the human body. For example, amylin binding can affect the immune system, the central nervous system, and the satiation system in the brain (i.e., the area postrema).[4]
There are two required post-translational modifications of amylin in order for the ligand to have any bioactivity: (1) and (2) a between C2 and C7. The amidated C-terminus of amylin has a nitrogen present which makes three significant hydrogen bonds. There is one hydrogen bond between the end of amylin and the backbone of the CTR and two hydrogen bonds back to the backbone of amylin itself. The amidated C-terminus is essential to the bioactivity of amylin because the nitrogen participates in Hydrogen bonding and holds the amylin ligand in a specific orientation. Additionally, the hydrogen bonds orient the amylin Y37 residue in a specific orientation so the Y37 side chain can participate in non-polar interactions in the space opposite of the hydrogen bonds. The disulfide bonds between C2 and C7 inhibit the end of amylin from waving around freely while conserving the N-terminus loop structure. Additionally, it prevents amylin from aggregating which would affect amylin binding to the receptor.[3]
Calcitonin 12 Angstrom Shift
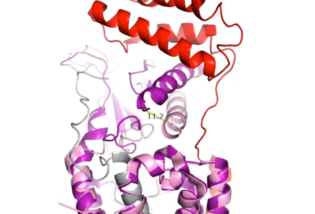
Figure 4. Active Site 12 Angstrom Shift of Receptor by RAMP Binding
When the RAMP binds to the CTR, the CTR undergoes a conformational change, or shift. The extracellular region of the calcitonin subunit, specifically in the C-alpha loop 5, of AMYR will undergo a 12 angstrom shift upwards (Figure 4).
[3] This distance shift is measured specifically from a glutamate residue, E123. This shift in the CTR facilitates the packing of the CTR extracellular domain with the antiparallel triple helix conformation of the RAMP extracellular domain.
There is little movement in the N-terminal location and midregion of the CTR when RAMP binds. This is because there is an unstructured and flexible "hinge" region between the extracellular domain and the core-binding domains, allowing these domains to remain in their original location from before RAMP binds to the CTR.
Binding Site Interactions
There are . These bonds contribute to the functional phenotype of AMYR and also causes the end of the amylin ligand to be held in a "flipped up", looped position. The hydrogen bond between amylin T6 and the CTR H302 is a conserved interaction across all peptides in the calcitonin family, and it is associated with later production of cAMP. Additionally, substituting T6 to A causes a large reduction in response to signaling.[3]
There are water molecules present in the binding site between amylin and the calcitonin receptor that support the ligand-receptor interaction. Some water molecules interact with the amylin ligand and create water-bridged Hydrogen bonds between different ligand residues, such as the . Other water molecules create . The water molecules are present in the empty space located in the ligand binding site, and they are hypothesized to stabilize the active conformation of the calcitonin receptor when amylin is bound. Substitutions of polar residues involved with the water-bridged Hydrogen bond network to nonpolar residues causes a decrease in potency and affinity of amylin to the calcitonin receptor.[3]
G Protein Activation
There are extensive nonpolar, . V322 and L323 of the CTR 2nd intracellular loop makes nonpolar interactions with I248 and V249 back to itself as well as L388 of the Gα subunit. These interactions stabilize the calcitonin receptor, which activates the G-protein to give amylin its biological role.[3] The . R180 of the 3rd intracellular loop of the calcitonin receptor makes a crucial hydrogen bond to Q390 of the Gα subunit. This interaction has been shown to maintain the biological function of amylin through cell signaling.[3] These interactions between the second and third intracellular loops of the calcitonin receptor stabilize the conformational states of the G-protein to create a more rigid domain with the nanobody.
Biological Relevance
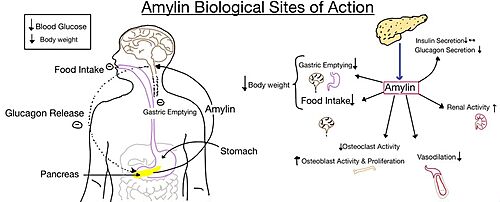
Figure 5. Different effects of amylin in the human body.
The functional pharmacology of AMYRs has relied on interference from differences between the behavior of CTRs in the presence and absence of RAMPs.[2] Thus, understanding the structural basis for binding and selectivity of peptides to CTR and AMYRs is important for future drug discovery and development.
Diabetes
Amylin, as it is a part of the calcitonin peptide family, is heavily related to the regulation of homeostatic processes to relevant drug targets. Amylin is the target for the treatment of diabetes. Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized and co-secreted with insulin. Insulin triggers glucose uptake which removes glucose from the bloodstream using it then for energy. Amylin works in negatively regulating (inhibiting) the formation of glucagon so that glucose polymers can continue to be broken down into the bloodstream for further energy storage and consumption. Therefore with the co-secretion of both amylin and insulin, it would aid in decreasing blood glucose levels thus becoming a predominant treatment plan for diabetic disorders, such as shown with the developing drug Pramlintide.[5]
Pramlintide

Figure 6. Sequence alignment of rat amylin and pramlintide.
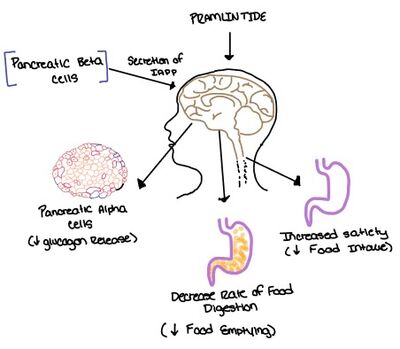
Figure 7. Pramlintide's effect on the human body. Pramlintide is a peptide agonist of human amylin and is a FDA approved treatment for diabetes.
Pramlintide, a peptide analog of human amylin, is FDA-approved for the treatment of insulin-requiring diabetes (Figure 6).[2] Pramlintide is injected into the bloodstream by the beta cells of the pancreas along with insulin after a meal, aiding in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing gastric emptying, promoting satiety via hypothalamic receptors, and inhibiting secretion of glucagon which opposes the effects of insulin and amylin (Figure 7).[6]
Alzheimer's
Alzheimer's is a neurodegenerative disease that is commonly associated with the slow progression of amyloid plaque build-up within the gray matter of the aging brain.
Amyloid plaques, also known as neuritic plaques or senile plaques, are extracellular deposits of the
amyloid beta protein that vary in both size and shape with the ability to clump together.
[4] When abnormal levels of amylin containing plaques clump together, it creates deposits within the brain region to disrupt proper cell function (Figure 8).
[7] Understanding this disruption is important due the structural overlap seen with amylin and calcitonin binding sites. It can be hypothesized that the conformational similarities between the receptor bringing regions is a key proponent in amyloid plaque build-up and neurodegenerative issues.
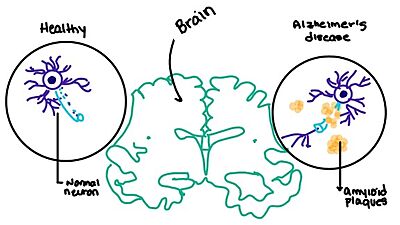
Figure 8. Amylin's effect on the brain through the buildup of amyloid plaques.








