User:Jaelin Lunato/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
===Diabetes=== | ===Diabetes=== | ||
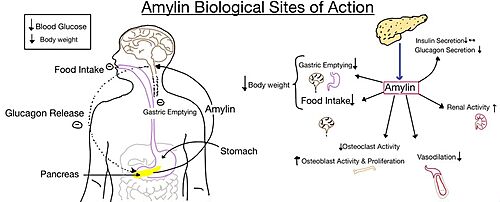
| - | Amylin, as it is a part of the calcitonin peptide family, is heavily related to the regulation of homeostatic processes to relevant drug targets. Amylin is the target for the treatment of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diabetes diabetes]. Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized and co-secreted with insulin. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin Insulin] triggers glucose uptake which removes glucose from the bloodstream using it then for energy. Amylin works in negatively regulating (inhibiting) the formation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucagon glucagon] so that glucose polymers can continue to be broken down into the bloodstream for further energy storage and consumption. Therefore with the co-secretion of both amylin and insulin, it would aid in decreasing blood glucose levels thus becoming a predominant treatment plan for diabetic disorders, such as shown with the developing drug [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pramlintide Pramlintide].<ref name="Mathiesen">PMID:33488526</ref> | + | Amylin, as it is a part of the calcitonin peptide family, is heavily related to the regulation of homeostatic processes to relevant drug targets. Amylin is the target for the treatment of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diabetes diabetes]. Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized and co-secreted with insulin. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin Insulin] triggers glucose uptake which removes glucose from the bloodstream using it then for energy. Amylin works in negatively regulating (inhibiting) the formation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucagon glucagon] so that glucose polymers can continue to be broken down into the bloodstream for further energy storage and consumption (Figure 5). Therefore with the co-secretion of both amylin and insulin, it would aid in decreasing blood glucose levels thus becoming a predominant treatment plan for diabetic disorders, such as shown with the developing drug [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pramlintide Pramlintide].<ref name="Mathiesen">PMID:33488526</ref> |
==== Pramlintide ==== | ==== Pramlintide ==== | ||
[[Image:Pram sequ.png|500px|right|thumb|'''Figure 6.''' Sequence alignment of rat amylin and pramlintide.]][[Image:Pramlintide.jpeg|400 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 7.''' Pramlintide's effect on the human body. Pramlintide is a peptide agonist of human amylin and is a FDA approved treatment for diabetes.]] | [[Image:Pram sequ.png|500px|right|thumb|'''Figure 6.''' Sequence alignment of rat amylin and pramlintide.]][[Image:Pramlintide.jpeg|400 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 7.''' Pramlintide's effect on the human body. Pramlintide is a peptide agonist of human amylin and is a FDA approved treatment for diabetes.]] | ||
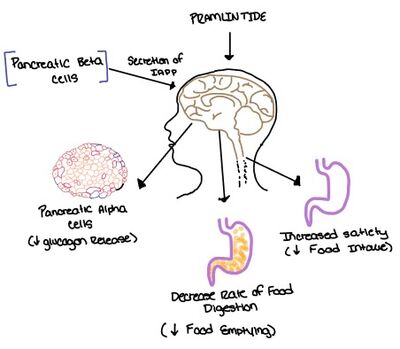
| - | Pramlintide, a peptide analog of human amylin, is FDA-approved for the treatment of insulin-requiring diabetes (Figure 6).<ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref> Pramlintide is injected into the bloodstream by the beta cells of the pancreas along with insulin after a meal, aiding in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomach gastric emptying], promoting [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satiety satiety] via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamus hypothalamic] receptors, and inhibiting secretion of glucagon which opposes the effects of insulin and amylin (Figure 7).<ref name="Thapa">Thapa, G., Kumari, A., Dasgupta, D., Bandyopadhy, S., Sarkar, N., Roy, K., Karunakaran, G., Kazmi, I., Karmakar, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2023). Chapter 5- Insight into the mechanism of action of anti-diabetic drugs. ''How Synthetic Drugs Work.'' 95-122. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1 DOI:10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1]</ref> | + | Pramlintide, a peptide analog of human amylin, is FDA-approved for the treatment of insulin-requiring diabetes. Pramlintide shares many conserved residues with amylin, so the two are chemically and structurally similar (Figure 6).<ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref> Pramlintide is injected into the bloodstream by the beta cells of the pancreas along with insulin after a meal, aiding in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomach gastric emptying], promoting [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satiety satiety] via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamus hypothalamic] receptors, and inhibiting secretion of glucagon which opposes the effects of insulin and amylin (Figure 7).<ref name="Thapa">Thapa, G., Kumari, A., Dasgupta, D., Bandyopadhy, S., Sarkar, N., Roy, K., Karunakaran, G., Kazmi, I., Karmakar, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2023). Chapter 5- Insight into the mechanism of action of anti-diabetic drugs. ''How Synthetic Drugs Work.'' 95-122. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1 DOI:10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1]</ref> |
===Alzheimer's=== | ===Alzheimer's=== | ||
Revision as of 01:44, 26 April 2024
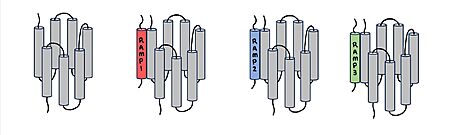
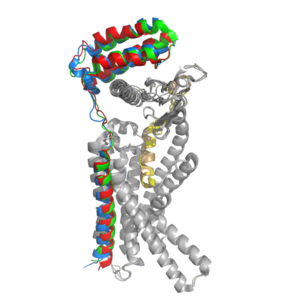
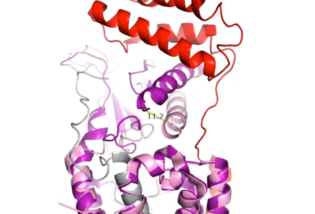
Amylin Receptor (AMYR)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):564-600. PMID:26071095 doi:10.1124/pr.115.010629
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Press, M., Jung, T., Konig, J., Grune, T., & Hohn, A. (2019) Protein aggregates and proteostasis in aging: Amylin and β-cell function. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 3, 46-54. DOI:10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010
- ↑ Mathiesen DS, Lund A, Vilsbøll T, Knop FK, Bagger JI. Amylin and Calcitonin: Potential Therapeutic Strategies to Reduce Body Weight and Liver Fat. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 8;11:617400. PMID:33488526 doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.617400
- ↑ Thapa, G., Kumari, A., Dasgupta, D., Bandyopadhy, S., Sarkar, N., Roy, K., Karunakaran, G., Kazmi, I., Karmakar, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2023). Chapter 5- Insight into the mechanism of action of anti-diabetic drugs. How Synthetic Drugs Work. 95-122. DOI:10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1
- ↑ Grizzanti J, Corrigan R, Casadesus G. Neuroprotective Effects of Amylin Analogues on Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Cognition. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(1):11-23. PMID:30282360 doi:10.3233/JAD-180433